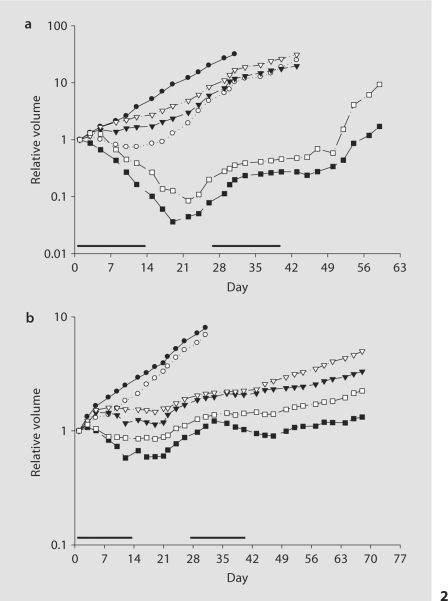
Fig. 2.
The effect of Apo2L/TRAIL alone and in combination with CPT-11 on 2 patients’ colon tumors grown in SCID mice: tumor 11124 (a) and 11501 (b). a On day 14, at the end of the first cycle, the tumors treated with Apo2L/TRAIL alone (○) were significantly smaller than those of the control (•; p < 0.05). A dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth was observed with CPT-11 alone. The treatment with either 20 mg/kg (▾) or 10 mg/kg (▿) CPT-11 also inhibited tumor growth, and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05). The combination treatment with Apo2L/TRAIL and either 20 (▪) or 10 mg/kg (□) CPT-11 resulted not only in growth inhibition but also in tumor regression (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively). b On day 14, the tumors treated with Apo2L/TRAIL alone (○) were slightly smaller than those of the control (•), but the difference was not statistically significant. A dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth was observed with CPT-11 alone at either 20 (▾) or 10 mg/kg (▿; p < 0.01 for both). Combination treatment with Apo2L/TRAIL and either 20 (▪) or 10 mg/kg (□) CPT-11 initially resulted in significant inhibition (p < 0.01 for both compared to control) and in slight tumor regression. Four of 5 tumors remained palpable in each group on day 43, however there was a significant difference in size between the tumors treated with CPT-11 alone and those that received combination treatment. Bars indicate cycles of treatment. n = 5.