Abstract
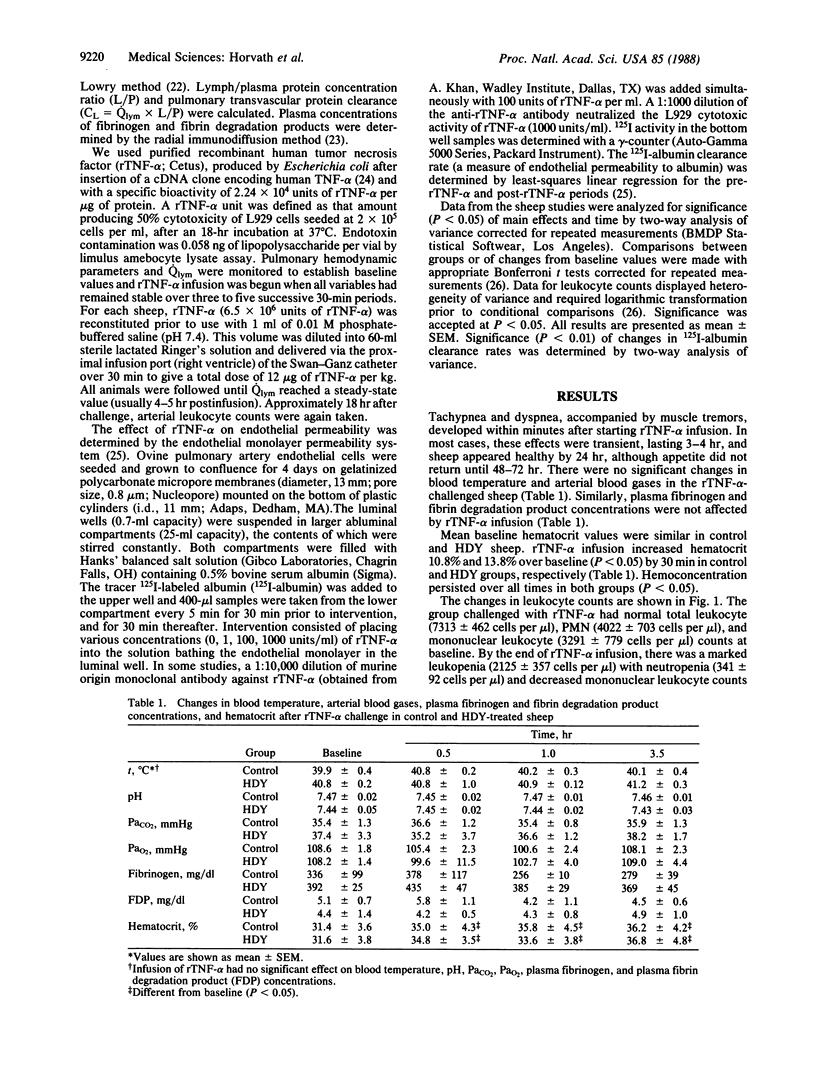
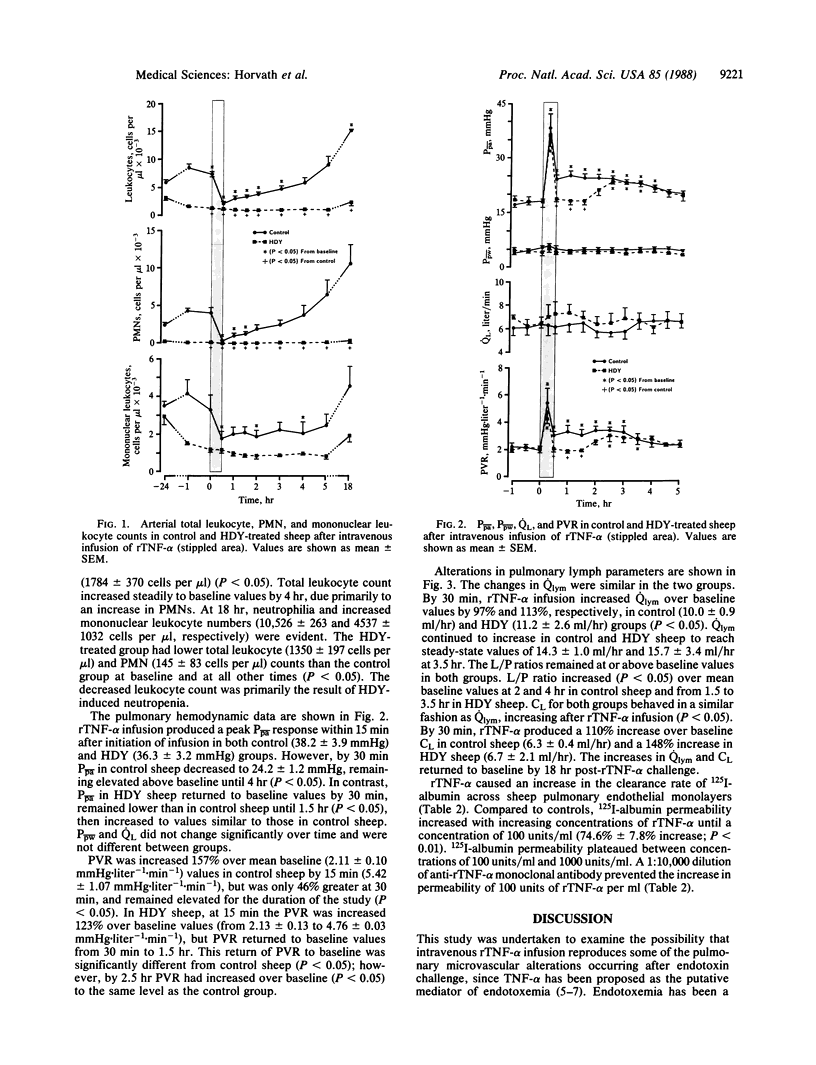
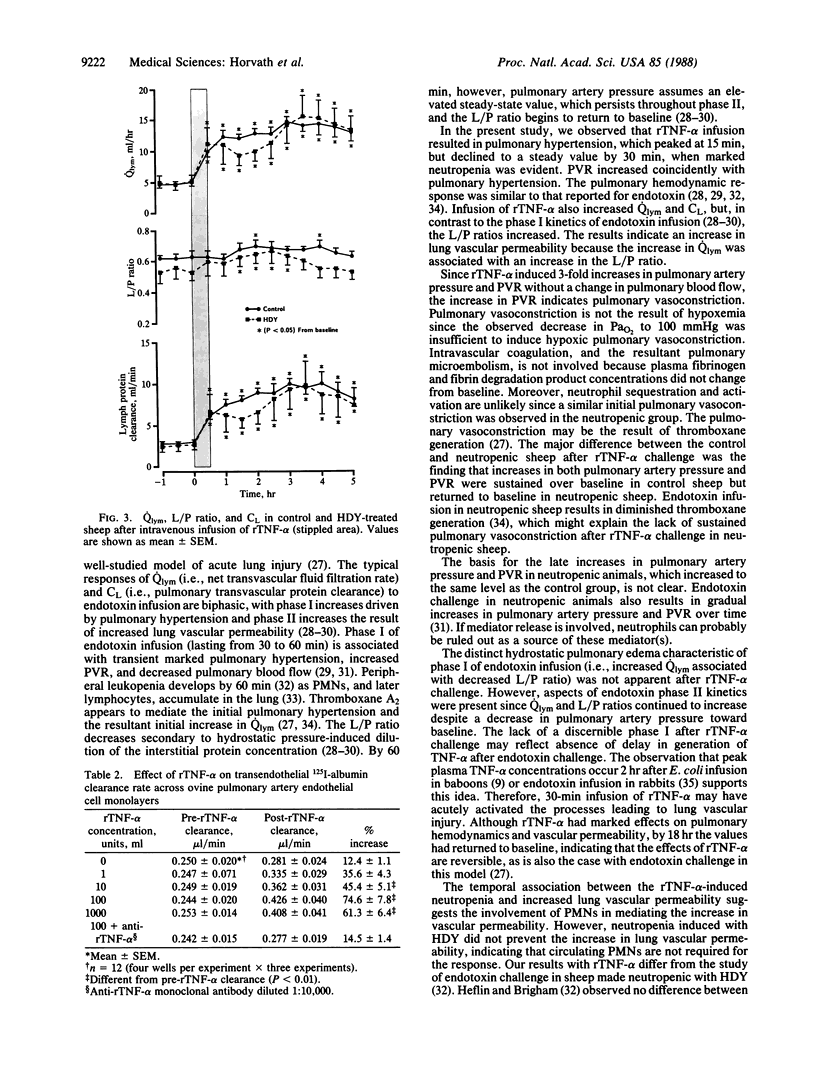
We studied the effects of intravenous infusion of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor type alpha (rTNF-alpha; 12 micrograms/kg) on lung fluid balance in sheep prepared with chronic lung lymph fistulas. The role of neutrophils was examined in sheep made neutropenic with hydroxyurea (200 mg/kg for 4 or 5 days) before receiving rTNF-alpha. Infusion of rTNF-alpha resulted in respiratory distress and 3-fold increases in pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance within 15 min, indicating intense pulmonary vasoconstriction. Pulmonary lymph flow (i.e., net transvascular fluid filtration rate) and transvascular protein clearance rate (a measure of vascular permeability to protein) increased 2-fold within 30 min. The increased permeability was associated with leukopenia and neutropenia. The pulmonary hypertension and vasoconstriction subsided but fluid filtration and vascular permeability continued to increase. Sheep made neutropenic had similar increases in pulmonary transvascular fluid filtration and vascular permeability. rTNF-alpha also produced concentration-dependent increases in permeability of 125I-labeled albumin across ovine endothelial cell monolayers in the absence of neutrophils or other inflammatory mediators. The results indicate that rTNF-alpha increases pulmonary vascular permeability to protein by an effect on the endothelium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Fiers W., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollon A. P., Berent S. L., Torczynski R. M., Hill N. O., Lemeshev Y., Hill J. M., Jia F. L., Joher A., Pichyangkul S., Khan A. Human cytokines, tumor necrosis factor, and interferons: gene cloning, animal studies, and clinical trials. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Apr;36(4):353–367. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Bowers R., Haynes J. Increased sheep lung vascular permeability caused by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Circ Res. 1979 Aug;45(2):292–297. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Bussolino F., Salvidio G., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin stimulates peritoneal macrophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and vascular endothelial cells to synthesize and release platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1390–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D., Saegusa Y., Ziff M. Stimulation of endothelial cell binding of lymphocytes by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1855–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Del Vecchio P. J., Minnear F. L., Burhop K. E., Selig W. M., Garcia J. G., Malik A. B. Measurement of albumin permeability across endothelial monolayers in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demling R. H., Smith M., Gunther R., Flynn J. T., Gee M. H. Pulmonary injury and prostaglandin production during endotoxemia in conscious sheep. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):H348–H353. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.240.3.H348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figari I. S., Mori N. A., Palladino M. A., Jr Regulation of neutrophil migration and superoxide production by recombinant tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta: comparison to recombinant interferon-gamma and interleukin-1 alpha. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):979–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabel J. C., Hansen T. N., Drake R. E. Effect of endotoxin on lung fluid balance in unanesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Feb;56(2):489–494. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.2.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. L. Repeated measurement: sensitive tests for experiments with few animals. J Anim Sci. 1986 Sep;63(3):943–954. doi: 10.2527/jas1986.633943x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heflin A. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. Prevention by granulocyte depletion of increased vascular permeability of sheep lung following endotoxemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1253–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI110371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttemeier P. C., Watkins W. D., Peterson M. B., Zapol W. M. Acute pulmonary hypertension and lung thromboxane release after endotoxin infusion in normal and leukopenic sheep. Circ Res. 1982 May;50(5):688–694. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M. A radial immunodiffusion method for the measurement of rat fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products. Vox Sang. 1979;36(2):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1979.tb04400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivuranta-Vaara P., Banda D., Goldstein I. M. Bacterial-lipopolysaccharide-induced release of lactoferrin from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: role of monocyte-derived tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2956–2961. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2956-2961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth R. S., Edgington T. S. Tumor necrosis factor production by human monocytes is a regulated event: induction of TNF-alpha-mediated cellular cytotoxicity by endotoxin. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2585–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Brigham K. L. Acute effects of Escherichia coli endotoxin on the pulmonary microcirculation of anesthetized sheep structure:function relationships. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):458–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Moore R. N., Mergenhagen S. E. Macrophages as a source of tumoricidal activity (tumor-necrotizing factor). Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):523–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.523-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI113241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seow W. K., Thong Y. H., Ferrante A. Macrophage-neutrophil interactions: contrasting effects of the monokines interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor (cachectin) on human neutrophil adherence. Immunology. 1987 Nov;62(3):357–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Bland R. D., Brigham K. L., Demling R., Erdmann A. J., 3rd, Woolverton W. C. Preparation of chronic lung lymph fistulas in sheep. J Surg Res. 1975 Nov;19(5):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(75)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Albert J. D., Fong Y., Hesse D., Beutler B., Manogue K. R., Calvano S., Wei H. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces lethal shock and stress hormone responses in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987 May;164(5):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R., Harlan J., Nadir B., Harker L., Hildebrandt J. Thromboxane A2 mediates lung vasoconstriction but not permeability after endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):911–918. doi: 10.1172/JCI111062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R., Maunder R., Chi E., Harlan J. Neutrophil depletion does not prevent lung edema after endotoxin infusion in goats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jan;62(1):116–121. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


