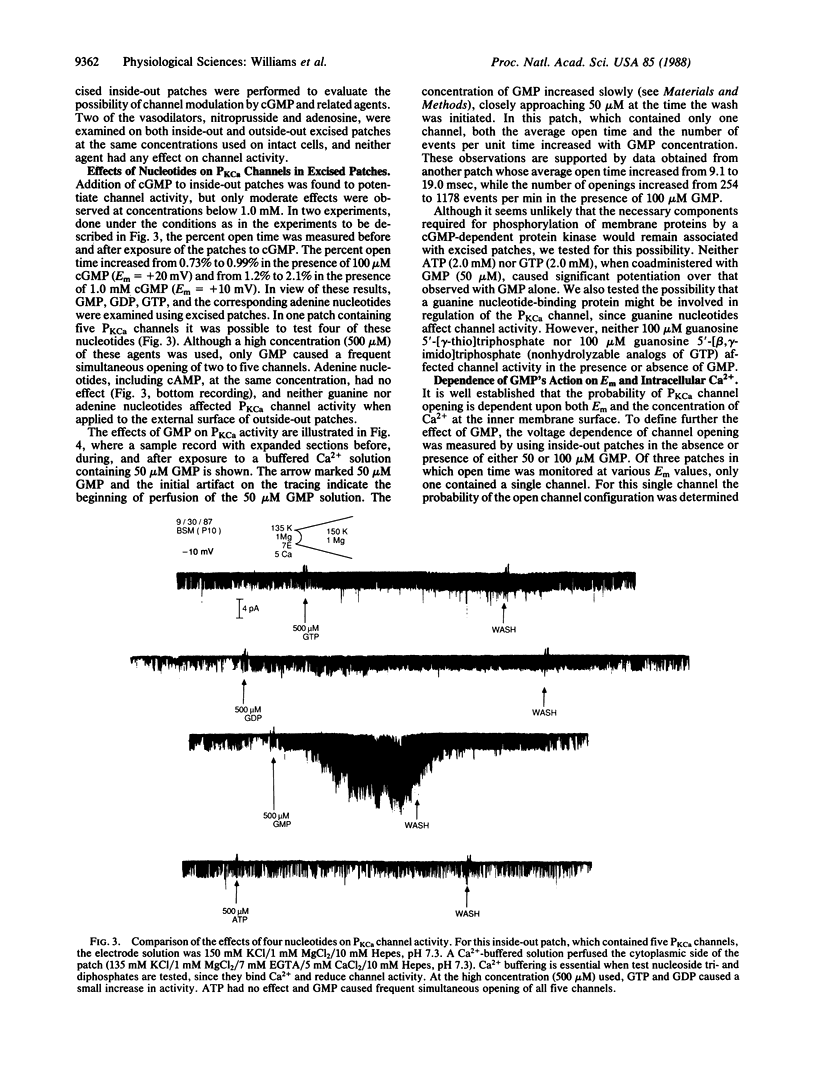
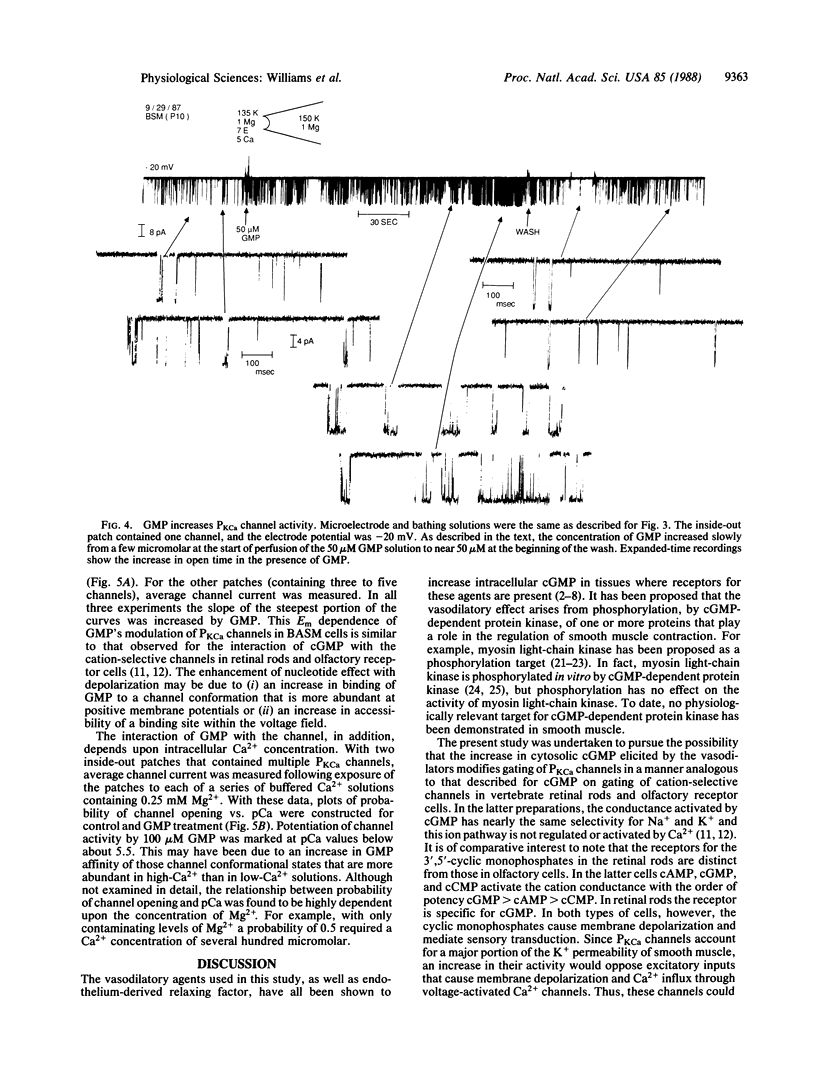
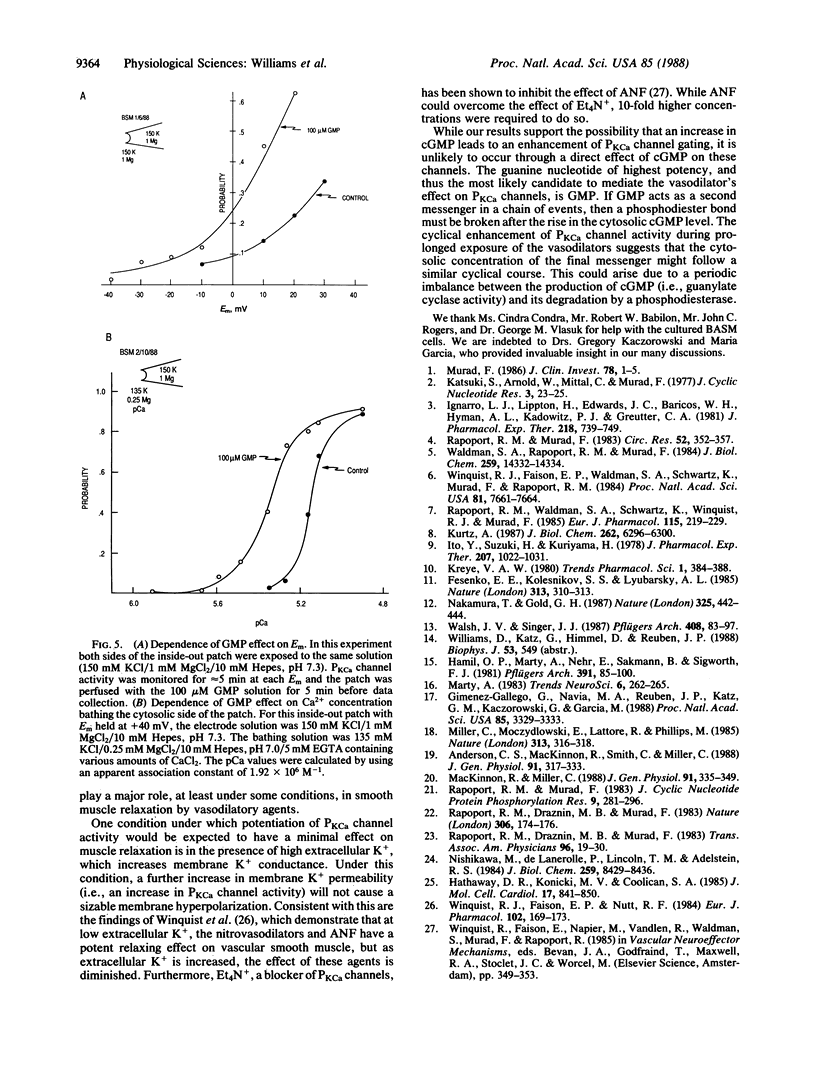
Abstract
Ca2+-activated K+ channels (PKCa channels) account for the predominant K+ permeability of many types of smooth muscle cells. When activated, they oppose depolarization due to Na+ and Ca2+ channel activity. Several vasodilatory agents that increase intracellular cGMP levels (e.g., nitroprusside, adenosine, and atrial natriuretic factor) enhance the activity of these high-conductance PKCa channels in on-cell patches of bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. In addition, dibutyryl-cGMP (1.0 mM) causes a similar increase in channel activity. To pursue the mechanism of channel modulation by these agents, a series of guanine and adenine nucleotides were evaluated by using inside-out excised patches. Whereas cAMP, AMP, ADP, and ATP were ineffective, all of the corresponding guanine nucleotides potentiated PKCa channel activity when tested at a high concentration (500 microM). However, only GMP consistently enhanced channel activity in the 1-100 microM range by increasing the percent open time and frequency of opening of these channels over a wide range of potentials and Ca2+ levels without affecting single-channel conductance. Thus, GMP is a potent modulator of PKCa channels and it, rather than cGMP, may mediate the action of the vasodilators examined in this study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. S., MacKinnon R., Smith C., Miller C. Charybdotoxin block of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Effects of channel gating, voltage, and ionic strength. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):317–333. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Navia M. A., Reuben J. P., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Konicki M. V., Coolican S. A. Phosphorylation of myosin light chain kinase from vascular smooth muscle by cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Sep;17(9):841–850. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kuriyama H. Effects of sodium nitroprusside on smooth muscle cells of rabbit pulmonary artery and portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Dec;207(3):1022–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Arnold W., Mittal C., Murad F. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin and nitric oxide in various tissue preparations and comparison to the effects of sodium azide and hydroxylamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Feb;3(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A. Adenosine stimulates guanylate cyclase activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6296–6300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mechanism of charybdotoxin block of the high-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):335–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Gold G. H. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):442–444. doi: 10.1038/325442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., de Lanerolle P., Lincoln T. M., Adelstein R. S. Phosphorylation of mammalian myosin light chain kinases by the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8429–8436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):174–176. doi: 10.1038/306174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent vasodilator-and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation may be mediated through cyclic GMP formation and cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1983;96:19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle: role of cyclic GMP. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):281–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Winquist R. J., Murad F. Effects of atrial natriuretic factor, sodium nitroprusside, and acetylcholine on cyclic GMP levels and relaxation in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 24;115(2-3):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90694-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Identification and characterization of major ionic currents in isolated smooth muscle cells using the voltage-clamp technique. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00581336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Nutt R. F. Vasodilator profile of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 15;102(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Murad F., Rapoport R. M. Atrial natriuretic factor elicits an endothelium-independent relaxation and activates particulate guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7661–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


