Abstract
Degenerin/epithelial Na+ channels (DEG/ENaC) represent a diverse family of voltage-insensitive cation channels whose functions include Na+ transport across epithelia, mechanosensation, nociception, salt sensing, modification of neurotransmission, and detecting the neurotransmitter FMRFamide. We previously showed that the Drosophila melanogaster Deg/ENaC gene lounge lizard (llz) is co-transcribed in an operon-like locus with another gene of unknown function, CheB42a. Because operons often encode proteins in the same biochemical or physiological pathway, we hypothesized that CHEB42A and LLZ might function together. Consistent with this hypothesis, we found both genes expressed in cells previously implicated in sensory functions during male courtship. Furthermore, when coexpressed, LLZ coprecipitated with CHEB42A, suggesting that the two proteins form a complex. Although LLZ expressed either alone or with CHEB42A did not generate ion channel currents, CHEB42A increased current amplitude of another DEG/ENaC protein whose ligand (protons) is known, acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a). We also found that CHEB42A was cleaved to generate a secreted protein, suggesting that CHEB42A may play an important role in the extracellular space. These data suggest that CHEB42A is a modulatory subunit for sensory-related Deg/ENaC signaling. These results are consistent with operon-like transcription of CheB42a and llz and explain the similar contributions of these genes to courtship behavior.
Introduction
Organization of genes in operons provides a mechanism for coordinating the quantitative, temporal, and spatial transcription of genes that contribute to the same biochemical or physiological process [1], [2]. Although operons are abundant in archea and bacteria, they are thought to be rare in eukaryotes outside the nematode lineage [1], [3]. We recently reported the existence of operon-like loci in Drosophila [4]. The first operon-like locus we identified included a degenerin/epithelial Na+ channel (DEG/ENaC) gene (lounge lizard; llz) co-transcribed with CheB42a, a gene with unknown function [5], which resides less than 100 bp upstream [6]. Previous work suggested that llz (also called ppk25 [7]) contributes to male courtship behavior because mutations in the gene result in delayed male courtship [7]. The contributions of CheB42a to male courtship have been less clear. CheB42a mutations were reported not to alter male courtship [7], but a later publication suggested that CheB42a increased male courtship behavior [8]. Furthermore, it was suggested that CheB42a expressing cells might enwrap gustatory neurons that express the gustatory receptor Gr68a, a gene that has also been identified as essential for courtship behavior [8], [9]. Organization of CheB42a and llz in an operon-like structure and the contribution of both genes to courtship behavior (although in somewhat opposing ways) suggested that the protein products of llz and CheB42a might functionally interact.
llz is a member of the DEG/ENaC family of genes that encode non-voltage gated cation channels [10], [11], [12]. Like other DEG/ENaC proteins, LLZ is predicted to contain two transmembrane domains, intracellular N- and C-termini, and a large extracellular domain with fourteen conserved cysteines and several small conserved amino acid motifs. DEG/ENaC channel subunits combine to form homo-and/or hetero-multimeric channels comprised of three subunits [13]. Some DEG/ENaC channels are regulated by interactions with ligands; for example, extracellular protons gate acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) [14], and the peptide FMRFamide gates the Helix aspersa FaNaCh [15]. DEG/ENaC genes also contribute to salt absorption [16], mechanosensation [17], nociception [18], and learning and memory [14]. Although all DEG/ENaC proteins are thought to form ion channels, in many cases their ion channel function has not been demonstrated, presumably because we do not know the appropriate ligand or regulatory mechanism.
CheB42a is a member of a family of at least 12 Drosophila genes of unknown molecular function. Members of this family are predicted to have a single transmembrane domain, a short intracellular N-terminus, and a larger extracellular domain. The CHEB42A extracellular domain shows limited sequence similarity to aryl sulfotransferases of the SULT1A subfamily (Fig. 1). Recent work speculated that CheB genes are homologous to the mammalian Tay-Sachs Gm2-activator protein [5], a lysosomal co-factor involved in the degradation of the ganglioside GM2 [19].
Figure 1. CheB42a encodes a protein with sequence similarity to aryl sulfotransferase 1A.
Top line shows predicted aminoa acid sequence of Drosophila melanogaster CheB42a, and second and third lines show predicted amino acid sequences of Ornithorhynchus anatinus (platypus) and Homo sapiens (human) aryl sulfotransferase. Green, conserved residues; yellow, conserved residues in two of the aligned proteins; blue, similar residues. Accession numbers for the aligned proteins are: CheB42a, NM_206043.2; O_anatinus, NP_001121091; H_sapiens, NP_003157.1.
The predicted protein structure of CHEB42A also indicated it might interact with LLZ. First, the CHEB42A structure resembles that of the accessory subunits of other ion channels: an example is the human protein MiRP1, which associates with the HERG K+ channel [20]. In addition, the C. elegans protein MEC-6 has a similar general predicted structure to the CHEB42A protein and associates with the DEG/ENaC channel subunits MEC-4 and MEC-10 [21]. Accessory subunits can alter the gating and regulation of ion channels [22] and/or serve as a chaperone to regulate the level of channel presence on the cell surface [23]. Thus, we considered that CHEB42A might associate with LLZ and modulate its function. Second, the predicted CHEB42A structure is similar to that of some odorant binding proteins in which a transmembrane segment can act as a signal peptide, anchoring an extracellular odorant binding domain that is released from the membrane following protease cleavage [24]. Thus, we considered that CHEB42A might be proteolytically released from the membrane and interact with LLZ as a secreted protein.
Based on this background, we hypothesized that CHEB42A and LLZ are functionally related and that CHEB42A might act by directly modulating LLZ channel functions in a cell-autonomous fashion. Such a relationship might explain their contribution to similar behavioral processes.
Results
CheB42a and llz Are Expressed in Male Chemosensory Structures
Our earlier in situ hybridization in embryos revealed exactly the same pattern for CheB42a and llz expression; the heads of late stage larvae showed these genes expressed in two classes of sensory neurons: gustatory-like external sensory neurons and putative mechanosensitive multidendritic neurons [4]. These results suggested that the same cells express both CheB42a and llz [4]. Studies of adults suggested that the locus is expressed in cells associated with external chemosensory bristles on male legs, suggesting that these genes play a role in chemosensation [6], [25]. However, the close contact between males and females during the courtship ritual suggests that mechanosensation might be involved as well [26].
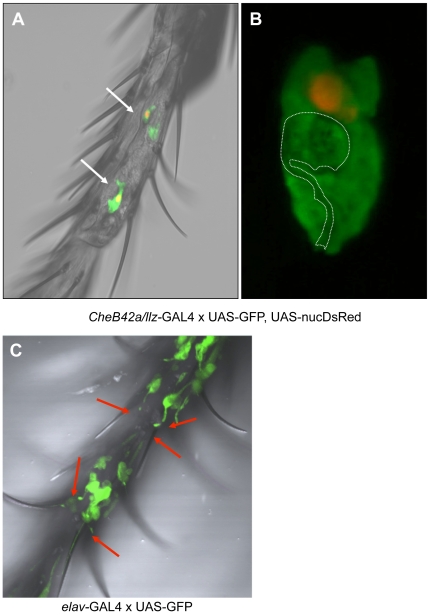
To identify specific cells expressing the CheB42a/llz locus, we drove a GFP reporter with a CheB42a/llz promoter, using the UAS/GAL4 system [27]. Adults showed expression in male front legs (Fig. 2A), consistent with previous work showing enrichment in male appendages [6], [25]. Because the GFP signal appeared larger than we anticipated for a single cell, we co-expressed GFP with DsRed containing a nuclear localization signal [28]. Each GFP-positive spot included only one labeled nucleus, indicating expression in large, single cells rather than cell clusters (Fig. 2B). A careful morphological analysis suggested the labeled cells were probably not neurons because they lacked any detectable sensory cilia or neurites as were readily apparent in leg sensory neurons when the pan-neuronal elav promoter drove GFP expression (Fig. 2C). Furthermore, high-resolution confocal 3-D reconstruction (Movies S1 and S2) suggested the CheB42a/llz-expressing cells might be support cells. Support cells are thought to enwrap sensory neurons in the fly, although their role in sensory transduction is not well-understood [29]. These data are consistent with recent work suggesting that CheB42a-expressing cells are non-neuronal, and seem to be associated with cells expressing the putative pheromone receptor Gr68a [25]. They are also consistent with the recent discovery that ACD-1, another DEG/ENaC channel expressed in C. elegans and involved in sensing, is required in sheath, glia-like cells rather than neurons [30].
Figure 2. The CheB42a/llz locus is preferentially expressed in non-neuronal sensory structures.
A–B. Driving expression of GFP with the CheB42a/llz promoter revealed expression in cells in the front legs of males. Co-expression of GFP and DsRed containing a nuclear localization signal revealed expression in relatively large cells with a single labeled nucleus. Morphology of the CheB42a/llz-expressing cells suggested the cells might enwrap another cell type; white dotted line represents boundaries of a potentially enwrapped cell with neuronal morphology (see Movies S1 and S2 for 3-D reconstruction of typical CheB42a/llz cells). C. Pan-neuronal elav promoter driving GFP expression in the same male leg segment as shown in panel A. Typical neuronal sensory morphologies such as sensory cilia extending to the sensory hairs are apparent.
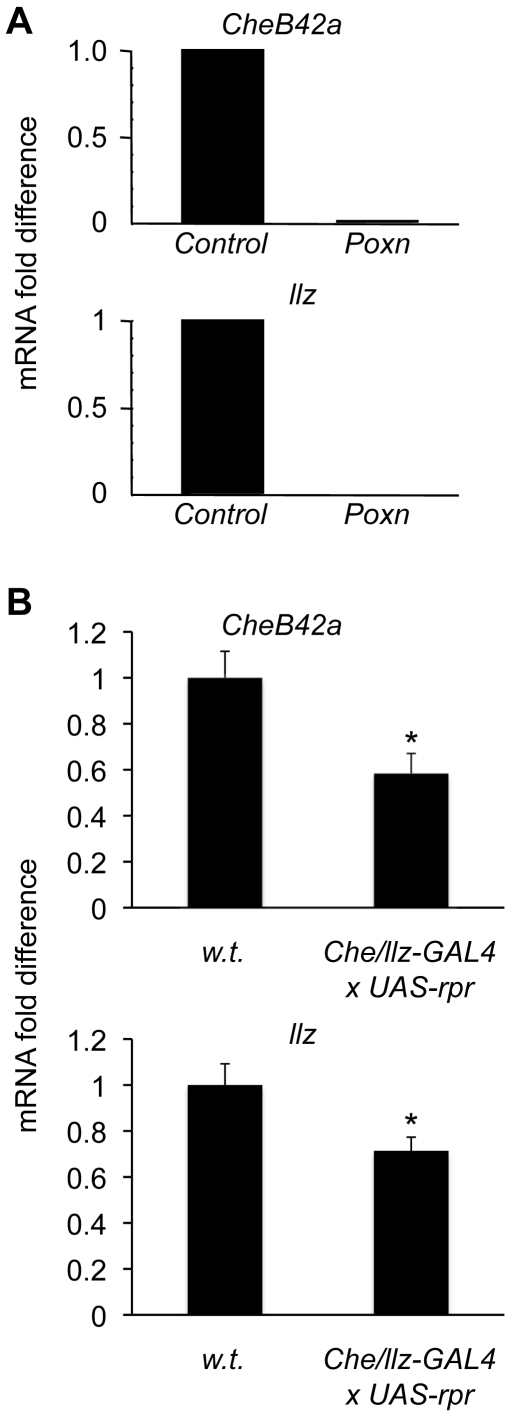
As an additional test of whether CheB42a/llz expressing cells are chemosensory in adults, we examined the expression of both genes in the Poxn mutant; this mutant converts most external chemosensory hairs into pure mechanosensory hairs [31]. The Poxn mutant reduced both CheB42a and llz transcripts (Fig. 3A). We also used the CheB42a/llz promoter and the UAS/GAL4 system [27] to drive the apoptotic gene rpr [32], thereby genetically ablating cells expressing the locus. In these flies, levels of both transcripts fell (Fig. 3B), consistent with expression of both genes in the same cells. Involvement of a chemosensory system in non-neuronal cells bears similarity to vertebrate gustatory taste buds and the gustatory system in insects. Both systems have essential non-neuronal components that are involved in transmitting chemical signals [33].
Figure 3. CheB42a and llz are expressed in the same chemosensory-related cells.
A. The expression levels of both CheB42a and llz were reduced in homozygous Poxn mutants relative to heterozygote controls. Total RNA was extracted from male appendages and was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. Data are mRNA in Poxn relative to wild-type control. Expression levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene rp49. y-axis represents arbitrary mRNA fold-difference units, with control expression levels designated as 1 unit. B. Genetic ablationCheB42a/llz-expressing cells reduced expression of both transcripts. The CheB42a promoter-GAL4 line was crossed to UAS-rpr, which induces cell-death [29]. Analysis as in panel A.
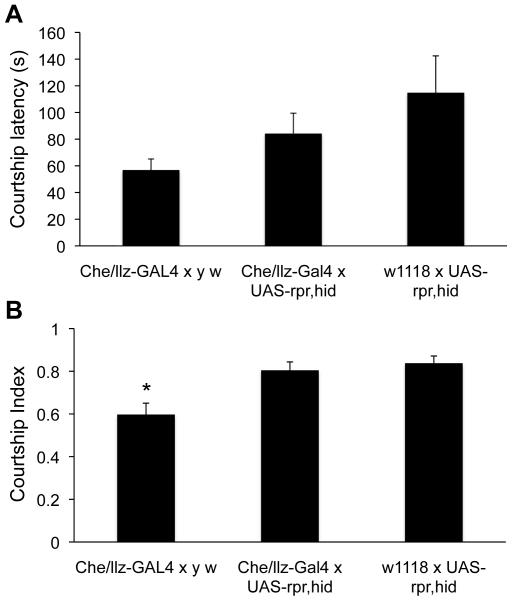
Two previous studies suggested that llz and CheB42a might contribute to male courtship behavior, albeit with opposing effects on male-female interactions [7], [8]. Because our genetic ablation studies with transgenic expression of proapoptotic genes suggested that this technique reduced expression of the CheB42a/llz locus, we examined the effects of ablations on male courtship behavior. In contrast to previous reports [7], [8], our data suggested that ablating CheB42a/llz-expressing cells did not significantly change male courtship latency (Fig. 4A). However, we did observe a small effect on male courtship index, although the difference was significant only relative to one of the parental control crosses (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4. Genetic ablation of CheB42a/llz expressing cells does not affect male courtship behavior.
A. Expression of the proapoptotic genes hid and rpr in CheB42a/llz-expressing cells using the UAS-GAL4 system did not affect male courtship latency (time from female introduction until the male shows any courtship related behaviors). Parental lines crossed to the reciprocal wild-type genetic background were used as controls. Although there were significant differences between the two parental controls, neither control line was statistically different from the focal cross (ANOVA). N = (Che/llz-GAL4 x yw, 33; Che/llz-GAL4 x UAS-rpr, hid, 52; w1118 x UAS-rpr, hid, 27). B. Genetic ablation of Che/llz-expressing cells resulted in a mild effect on male courtship index (the proportion of time a male spends courting once courting started). Genotypes and sample sizes as in A. *, P<0.05.
CHEB42A Associates with LLZ
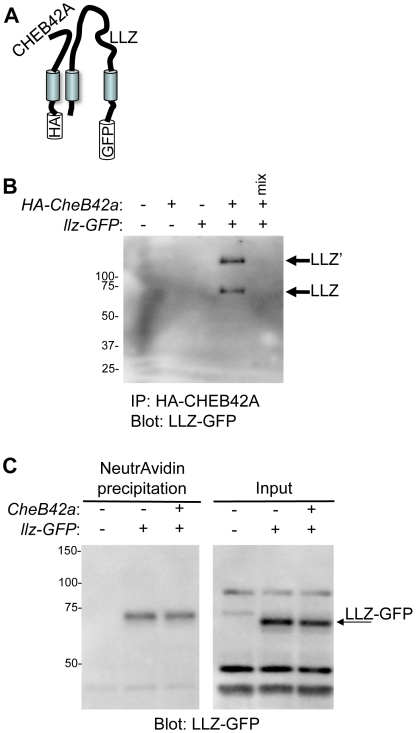
Since both llz and CheB42a are expressed in the same tissues and affect similar behavioral processes, we asked whether they are parts of the same protein complex. We tested whether CHEB42A could interact with LLZ by expressing tagged versions of both proteins in COS-7 cells. We then immunoprecipitated CHEB42A and found that LLZ co-precipitated (Fig. 5A,B). This result suggested that the two proteins could form a complex.
Figure 5. CHEB42A and LLZ can form a protein complex.
A. Schematic of transfected proteins. B. Co-expression of tagged CHEB42A-HA and LLZ-GFP proteins. Immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody co-precipitated LLZ. “mix” indicates an experiment in which equal amounts of protein from the singly-transfected cells were mixed prior to immunoprecipitation as a control for non-specific interactions. Expression of llz produced two protein bands, the expected lower molecular mass band, plus a band of higher molecular mass. We do not know the identity of the more slowly migrating band; it might represent an LLZ-containing multiunit complex that is resistant to SDS denaturation or might represent post-translational modifications of LLZ [45]. We also attempted to detect HA-CHEB42A after immunoprecipitating LLZ-GFP, but were not successful. C. CHEB42A did not affect LLZ surface expression. COS7 cells were transfected with llz and either GFP or CheB42a. Surface expression level was estimated with biotinylation of surface proteins followed by neutravidin precipitation. To estimate total protein, protein input was directly blotted with anti-GFP antibody (right panel). We did not observe the larger LLZ' band in the surface expression study. We speculate that differences in sample processing protocols between the IP and surface expression studies could affect solubility and detection of larger protein complexes.
To test whether LLZ alone or together with CHEB42a forms an ion channel, we expressed them alone and together in Xenopus oocytes and in CHO cells and measured current with two-electrode voltage clamp or patch-clamp, respectively. These experiments failed to reveal llz-dependent currents (not shown). Mutations in the residue preceding the second transmembrane domain of some DEG/ENaC subunit can generate a constitutively open channel (a “DEG” mutation) [34]. Interestingly, LLZ contains a methionine at this position (M409), which would predict that LLZ might have a “natural” DEG mutation and hence should behave as a constitutively open channel. Yet, adding amiloride (up to 100 µM), which inhibits some DEG/ENaC channels, did not reduce current. Moreover, extracellular addition of acid, hyper- and hypotonic solutions, FMRFamide, or proteases did not generate currents in cells expressing llz alone or with CheB42a. Because llz and CheB42a were both speculated to function in pheromone sensing pathways, we also tested whether LLZ might be gated directly by virgin female pheromonal hexane extracts, but we were not able to observe any llz-dependent currents. These electrophysiological experiments failed to induce current irrespective of expression in oocytes or CHO cells and regardless of whether llz was expressed alone or with CheB42a.
We considered that these experiments may have been negative because we do not know the appropriate ligand to activate LLZ and/or CHEB42a, or because LLZ must heteromultimerize with another as yet unknown DEG/ENaC subunit to generate current. Alternatively, it is possible that our expression constructs did not express enough llz transcripts to detect currents in oocytes. However, the same constructs expressed well in mammalian cells, but likewise did not elicit llz-dependent currents there. In addition, the same vectors were used to express ASIC1a in oocytes. Together, these data suggested that lack of llz expression is an unlikely explanation for the absence of llz-dependent currents in oocytes.
Because LLZ and CheB42a can associate, we asked if CHEB42A alters the presence of LLZ in the cell membrane. To test this possibility we biotinylated cell membrane proteins and precipitated with neutravidin. LLZ was precipitated, indicating its presence on the cell surface. However, co-expressing CheB42a did not alter the amount of biotinylated and precipitated LLZ (Fig. 5C). Thus, despite the interaction of the two proteins, CHEB42A did not induce LLZ channel activation or alter the relative amount of protein on the cells surface.
CHEB42A Modifies the Current of Mammalian ASIC1a Channels
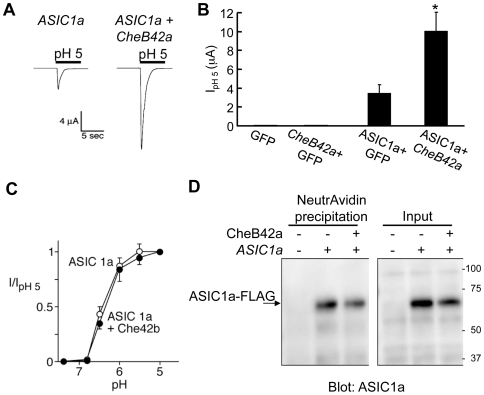
While we do not know the ligand for LLZ, we do know the ligand for some other DEG/ENaC channels. For example, extracellular protons activate another Deg/ENaC channel, the acid-sensing ion channel-1a (ASIC1a) [35]. Therefore, we asked whether CHEB42A might affect the activity of ASIC1a. As previously described [36], [37], ASIC1a produced acid-evoked currents when expressed in Xenopus oocytes (Fig. 6A,B). However, when we co-expressed CHEB42A with ASIC1a, acid-evoked currents increased three-fold. CHEB42a did not alter the pH-sensitivity of ASIC1a current (Fig. 6C). As we had observed with LLZ, CHEB42a did not increase the amount of ASIC1a on the cell surface (Fig. 6D). These results are similar to the report that the C. elegans DEG/ENaC accessory subunit MEC-6 increases current of the Deg/ENaC channel MEC-4/MEC-10 without altering the cell surface expression of either subunit [17], [21].
Figure 6. CHEB42A increases current from the mammalian DEG/ENaC protein ASIC1a.
A–C. Effect of CHEB42A on H+-gated ASIC1a currents. Xenopus oocytes were injected with ASIC1a, GFP or CheB42a cDNAs alone or in combinations indicated. Bathing solution pH was reduced to 5 during time indicated. A. example of H+-gated currents from the ASIC1a channel. B. CHEB42A increases ASIC1a H+-gated currents. Asterisk indicates P<0.01 (two-tail t-test). Number of oocytes studied: 9 GFP, 9 CheB42a and GFP, 20 ASIC1a and GFP, and 27 ASIC1a and CheB42a. Data are mean ± SEM. C. CHEB42A did not affect the pH dependence of ASIC1a current. Closed symbols indicate ASIC1a and CHEB42A (n = 15) and open symbols indicate ASICla + GFP (n = 12). D. CHEB42A did not affect ASIC1a surface expression. Experiment was done as in Fig. 5B.
CheB42a Encodes a Secreted Peptide
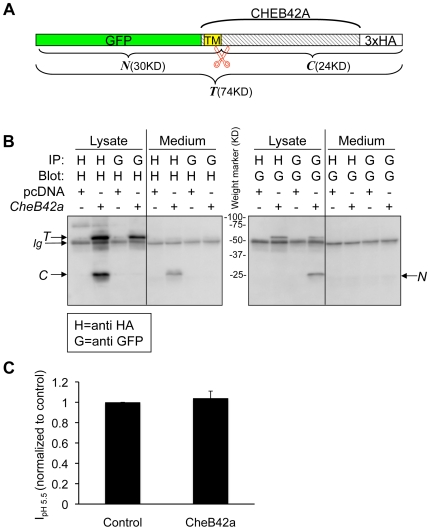
Sequence analysis of CHEB42A with the SignalIP algorithm suggested that the transmembrane domain might function as a signal peptide [38], raising the possibility that the extracellular domain of the protein might be secreted. To test the hypothesis that CHEB42A might generate a secreted peptide, we constructed a CheB42a cDNA that carried a GFP at its predicted intracellular N-terminus and a 3xHA tag at its predicted extracellular C-terminus (Fig. 7A).
Figure 7. CHEB42A produces a secreted peptide.
A. Schematic of the construct used to study CHEB42A. CheB42a cDNA was tagged with GFP at the 5′ end and 3xHA tags at the 3′ end and was cloned into the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1 (Invitrogen). TM, transmembrane peptide as predicted by the SignalP 3.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/). predicted transmembrane domain.  Predicted signal peptide cleavage site. T, N, and C represent the predicted full length and cleaved products. B. CHEB42A is a secreted protein. Cells were transfected with tagged cDNA (CheB42a) or pcDNA3.1 as a control. Proteins from cell lysates or cell media were immunoprecipitated (IP) with either anti-GFP (G) or anti-HA (H) antibodies, and then blotted for either tag. T, N, and C indicate the predicted peptides from Fig. 7A. C. Effects of CheB42a-conditioned media on ASIC1a currents. ASIC1a was expressed in Xenopus oocytes as in Fig. 6. Four ASIC1a-expressing oocytes were tested for pH-dependent currents with and without conditioned media from CheB42a-expressing cells. The same oocytes (N = 4) were stimulated with unconditioned medium (pH 5.5), followed by stimulation with CheB42a-conditioned medium. There was no obvious effect of the conditioned media on pH-activation of ASIC1a channels. Currents were normalized in the conditioned state relative to the control media. All oocytes showed significant ASIC1a-dependent currents in response to pH 5.5, which does not elicit any currents in non-injected oocytes.
Predicted signal peptide cleavage site. T, N, and C represent the predicted full length and cleaved products. B. CHEB42A is a secreted protein. Cells were transfected with tagged cDNA (CheB42a) or pcDNA3.1 as a control. Proteins from cell lysates or cell media were immunoprecipitated (IP) with either anti-GFP (G) or anti-HA (H) antibodies, and then blotted for either tag. T, N, and C indicate the predicted peptides from Fig. 7A. C. Effects of CheB42a-conditioned media on ASIC1a currents. ASIC1a was expressed in Xenopus oocytes as in Fig. 6. Four ASIC1a-expressing oocytes were tested for pH-dependent currents with and without conditioned media from CheB42a-expressing cells. The same oocytes (N = 4) were stimulated with unconditioned medium (pH 5.5), followed by stimulation with CheB42a-conditioned medium. There was no obvious effect of the conditioned media on pH-activation of ASIC1a channels. Currents were normalized in the conditioned state relative to the control media. All oocytes showed significant ASIC1a-dependent currents in response to pH 5.5, which does not elicit any currents in non-injected oocytes.
We expressed these constructs and tested for the tagged protein fragments in both the cellular fraction and the cell culture medium. The cell lysate contained the full-length protein plus N- and C-terminal fragments (Fig. 7B). In addition, we detected the C-terminal extracellular portion of CHEB42A in medium covering the cells. In contrast, the N-terminal fragment was detected only in the cell lysate. These results suggest that the extracellular domain of CHEB42A can be secreted. These data also indicate that the cleavage of CHEB42A occurs intracellularly since we were able to detect both N- and C-terminal fragments in cell lysates.
Because CheB42a can generate a secreted protein, we asked whether the secreted form might alter ASIC1a-dependent currents. We examined ASIC1a activation in response to lowered extracellular pH in the presence or absence of conditioned media from CheB42a-expressing cells. The conditioned media had no effect on pH-dependent currents (Fig. 7C), suggesting that the modulatory effect of CHEB42A was not mediated by the secreted peptide, but rather required physical interaction with the full-length, membrane bound protein.
Discussion
We previously identified operon-like cotranscription of the CheB42a and llz loci [4]. In addition, earlier studies suggested that CheB42a and llz are expressed in similar tissues and they might contribute to male courtship behavior [5], [6], [25], [39]. Here we show that as with other operons, the two gene products biochemically interact and may be functionally related.
Our data suggest that CHEB42A may function as an accessory subunit for DEG/ENaC channels. Although we were not able to elicit current from LLZ, we found that CHEB42A increased the current amplitude from another DEG/ENaC channel, ASIC1a, for which the ligand is known [14], [40]. In addition, CHEB42A associated with both LLZ and ASIC1a. How CHEB42a influences ASIC1a current remains uncertain, but our data suggest that CHEB42A does not increase the amount of LLZ or ASIC1a at the cell surface, nor did it change the pH-sensitivity of ASIC1a. Furthermore, although CHEB42A can be secreted, the modulatory effects on DEG/ENaC currents were not affected by the secreted peptide alone, suggesting that CHEB42A may have multiple, distinct physiological roles. These results are similar to the finding that the C. elegans MEC-6 protein increases current amplitude through the DEG/ENaC channel MEC-4/MEC-10 without altering its surface-expression, and all three proteins are required for mechanosensation [21]. It is also interesting that both CHEB42A and MEC-6 have extracellular domains with sequence similarities to enzymes; CHEB42A shares limited sequence similarity to aryl sulfotransferases of the SULT1A subfamily, and MEC-6 shows similarity to paraoxonases [21]. However, neither CHEB42a nor MEC-6 is known to have enzymatic activity. The fly genome contains 30 DEG/ENaC genes and 12 CheB genes. Our data raise the interesting possibility that CHEB42A or other members of the CheB family could regulate other channels. Perhaps combinatorial expression of members of the two families is a mechanism to increase receptor diversity and function.
Finding that CHEB42A is cleaved and the extracellular domain is released into the medium suggests that CHEB42A might have a function in addition to that of an accessory subunit. In this regard, CHEB42A is similar to several odorant-binding proteins, which are also expressed in and secreted from non-neuronal chemosensory accessory cells [41]. We speculate that it might interact with a chemical ligand produced by female flies and passed by physical contact to male front legs, where it could influence LLZ channel function, or possibly other sensory receptors. Interestingly, a recent study suggested that CheB genes might encode proteins that are homologs of the mammalian Tay-Sachs GM2-activator protein, a lysosomal soluble co-factor involved in the degradation of the ganglioside GM2 [19]. Our data did not support this hypothesis since we find that CHEB42A is a secreted rather than a soluble lysosomal protein. Yet, it is possible that some of the effects of CHEB42A on Deg/ENaC functions are to enzymatically modify external ligands, which can modulate channel function.
How the CheB42a/llz locus influences courtship behavior remains uncertain. There are several considerations. First, both genes were expressed in the forelegs of males, consistent with a role in male courtship behavior. Second, previous studies suggested that both genes can influence male courtship behavior, but unexpectedly, llz mutations delayed and CheB42a mutations enhanced courtship behavior [7], [8]. Third, rather than neurons, the CheB42a/llz locus was expressed in support cells enwrapping sensory neurons [29]. This localization is interesting given the recent surprising discovery that a C. elegans DEG/ENaC channel is required in glia rather than neurons to influence sensory function [30]. Fourth, our data suggested that genetic ablation of CheB42a/llz-expressing cells had little effect on male courtship behavior. Thus, we speculate that CheB42a and llz modulate chemosensory neuron function from a location in support cells. Thus, the support cells may not be required for the chemosensation, but through CheB42a and llz, they can modify the function of the neurons they enwrap.
Our current results further support the conclusion that the CheB42a/llz locus has operon-like transcription. In addition, a recent report suggested that another chemosensory-related locus in the fly genome is transcribed as a polycistronic mRNA [42]; the Gr64a-f locus encodes several sugar receptors. Finding that sensory-related loci are co-transcribed suggests an evolutionary solution for finely controlling the spatial, temporal and quantitative aspects of chemosensation. Tight control on the expression of membrane-bound complexes is probably essential in many eukaryotic systems. Hence, these results also raise the intriguing possibility that operon-like transcription may be more common in eukaryotes than has previously been appreciated, including organisms outside the Drosophila lineage. We speculate that identification of other co-transcribed genes may reveal novel protein interactions and pathways.
Materials and Methods
Drosophila Stocks and Cultures
Fly stocks and crosses were maintained according to standard Drosophila culture procedures and were housed in a 25 °C incubator under 12∶12 light:dark cycle. A CheB42a promoter-GAL4 line was a gift from C.W. Pikielny. We generated additional CheB42a/llz promoter-GAL4 lines by PCR amplifying a ∼2.5 kb fragment which included upstream sequences and the first intron of CheB42a subcloned into a pPTGAL4 vector (a gift from D. Eberl). The elav-GAL4, UAS-EGFP, UAS-rpr, and UAS-stinger (nuclear DsRed) were obtained from the Bloomington Fly Stock Center (IN). The UAS-hid, UAS-rpr line was from P. Taghert. The Poxn Δm flies were a gift from M. Noll.
RNA Analysis
Flies were separated by sex under CO2 and kept at −80°C until processing. To separate body parts, microcentrifuge tubes with flies were dipped in liquid nitrogen and then separated by repeated vortexing. Total RNA was extracted with the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) or TRizol reagent (Invitrogen) according to manufacturer instructions. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR assays were performed on an “ABI7500 fast” with pre-designed real-time FAM-labeled probe-based assays from ABI according to manufacturer instructions. For analysis, expression levels of the housekeeping gene rp49 were used as an RNA loading control. Data were transformed according to the ΔΔCt method and are represented as relative values [43]. Fold difference was calculated relative to lowest-expressing sample, which represented 1 arbitrary unit of expression.
ABI assays used were: rp49, Dm02151827_g1; CheB42a, Dm01794214_g1; llz, Dm01794217_g1.
Co-Immunoprecipitation and Cell Surface Expression of Protein
COS-7 or HEK293T cells were electroporated with 12 µg of either control pEGFPN1, pcDNA3.1[CheB42a-HA], pEGFPN1[llz], or both pcDNA3.1[CheB42a-HA] and pEGFP[llz] (6 µg each), and were then maintained in standard medium in a 37°C incubator for 48 h. For co-immunoprecipitation, cells were lysed in RIPA buffer containing 1% NP-40 (Pierce). Extracted protein was first incubated with either anti-HA or anti-GFP antibodies for 3 h followed by 1 h incubation with protein A sepharose (Pierce). Bound protein was released from pelleted protein A by direct incubation with 2% SDS loading buffer and analyzed according to standard western blotting techniques. Total cell protein was measured using the BCA assay (Pierce). Analysis of expression of proteins on the cell surface was done with the EZ-Link-NHS-Biotin reagent according to manufacturer instructions (Pierce). Total protein for surface expression normalization was measured by western blotting of total protein input.
To measure CHEB42A secretion, the full-length CheB42a cDNA minus the STOP codon was amplified using gene specific primers. The reverse primer included the sequence for 3xHA tag such that the expressed protein will be tagged with a 3xHA on its C' terminus. The PCR product was then cloned into a pEGFP-C vector which resulted in a final expressed protein that has a GFP tag on its N' terminus (intracellular) and 3xHA tag on it C' terminus (extracellular). The construct was transfected into HEK293-T cells and proteins were extracted according to standard protocols as described above. To harvest secreted protein in the conditioned media, medium from cells expressing the pEGFP-CheB42a-3xHA construct were concentrated using Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filters according to manufacturer instructions.
Electrophysiology
To test the effect of CHEB42A on LLZ and ASIC1a, we injected nuclei of albino Xenopus laevis oocytes with 20 nl of water containing cDNAs (in pMT3-Swick [44]) encoding ASIC1a (0.02 mg/ml) or LLZ (0.02 mg/ml) and CHEB42A or GFP (0.04 mg/ml). Following incubation for 16–24 hrs in modified Barth's solution at 18°C, we measured whole-cell current by two-electrode voltage-clamp at −60 mV. Oocytes were bathed in pH = 7.4 NaCl Ringer (116 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 0.4 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM Hepes). Maximal H+-activated current was measured by perfusing cells with pH = 5 NaCl Ringer. We also expressed llz alone and with CheB42a in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and measured current with the whole-cell, patch-clamp technique as we have previously described [37].
Supporting Information
A 3D movie of a confocal z-stack reconstruction of a single Che/llz positive cell in a male foreleg. Flies expressed simultaneously a nuclear localized DsRed and cytoplasmic GFP proteins.
(1.62 MB AVI)
A 3D movie of a confocal z-stack reconstruction of a single Che/llz positive cell in a male foreleg. Flies expressed simultaneously a nuclear localized DsRed and cytoplasmic GFP proteins. Images in Movies S1 and S2 were recorded from two independent cells in a single male.
(0.69 MB AVI)
Acknowledgments
We thank Mariana Mata and Sarah Pedigo for help with fly maintenance and general laboratory assistance at Iowa. We thank Mahmod Panahi and Judith Tigah for help with experiments at Washington University. We thank Yuhong Li, and Nicholas Heiniger for help with experiments. We thank the University of Iowa In Vitro Models and Cell Culture Core for cell maintenance.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: The University of Iowa In Vitro Models and Cell Culture Core is supported in part by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (R458-CR02 and ENGLH9850), and the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (DK54759)]. Y.B.S. was an Associate and M.J.W. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Lawrence JG. Gene organization: selection, selfishness, and serendipity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:419–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blumenthal T, Gleason KS. Caenorhabditis elegans operons: form and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:112–120. doi: 10.1038/nrg995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lawrence JG. Shared strategies in gene organization among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Cell. 2002;110:407–413. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00900-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ben-Shahar Y, Nannapaneni K, Casavant TL, Scheetz TE, Welsh MJ. Eukaryotic operon-like transcription of functionally related genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:222–227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609683104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Starostina E, Xu A, Lin H, Pikielny CW. A Drosophila protein family implicated in pheromone perception is related to Tay-Sachs GM2-activator protein. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:585–594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806474200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Xu A, Park SK, D'Mello S, Kim E, Wang Q, et al. Novel genes expressed in subsets of chemosensory sensilla on the front legs of male Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;307:381–392. doi: 10.1007/s00441-002-0524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lin H, Mann KJ, Starostina E, Kinser RD, Pikielny CW. A Drosophila DEG/ENaC channel subunit is required for male response to female pheromones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506420102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park SK, Mann KJ, Lin H, Starostina E, Kolski-Andreaco A, et al. A Drosophila protein specific to pheromone-sensing gustatory hairs delays males' copulation attempts. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1154–1159. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bray S, Amrein H. A putative Drosophila pheromone receptor expressed in male-specific taste neurons is required for efficient courtship. Neuron. 2003;39:1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mano I, Driscoll M. DEG/ENaC channels: a touchy superfamily that watches its salt. Bioessays. 1999;21:568–578. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199907)21:7<568::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wemmie JA, Price MP, Welsh MJ. Acid-sensing ion channels: advances, questions and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:578–586. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schild L. The epithelial sodium channel: from molecule to disease. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;151:93–107. doi: 10.1007/s10254-004-0023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jasti J, Furukawa H, Gonzales EB, Gouaux E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 A resolution and low pH. Nature. 2007;449:316–323. doi: 10.1038/nature06163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wemmie JA, Chen J, Askwith CC, Hruska-Hageman AM, Price MP, et al. The acid-activated ion channel ASIC contributes to synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Neuron. 2002;34:463–477. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00661-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lingueglia E, Champigny G, Lazdunski M, Barbry P. Cloning of the amiloride-sensitive FMRFamide peptide-gated sodium channel. Nature. 1995;378:730–733. doi: 10.1038/378730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu L, Leonard AS, Motto DG, Feller MA, Price MP, et al. Contribution of Drosophila DEG/ENaC genes to salt taste. Neuron. 2003;39:133–146. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O'Hagan R, Chalfie M, Goodman MB. The MEC-4 DEG/ENaC channel of Caenorhabditis elegans touch receptor neurons transduces mechanical signals. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:43–50. doi: 10.1038/nn1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Price MP, McIllwrath SL, Xie J, Cheng C, Qiao J, et al. The DRASIC cation channel contributes to the detection of cutaneous touch and acid stimuli in mice. Neuron. 2001;32:1071–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00547-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shimada Y, Li YT, Li SC. Effect of GM2 activator protein on the enzymatic hydrolysis of phospholipids and sphingomyelin. J Lipid Res. 2003;44:342–348. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M200234-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Abbott GW, Sesti F, Splawski I, Buck ME, Lehmann MH, et al. MiRP1 forms IKr potassium channels with HERG and is associated with cardiac arrhythmia. Cell. 1999;97:175–187. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80728-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chelur DS, Ernstrom GG, Goodman MB, Yao CA, Chen L, et al. The mechanosensory protein MEC-6 is a subunit of the C. elegans touch- cell degenerin channel. Nature. 2002;420:669–673. doi: 10.1038/nature01205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hanlon MR, Wallace BA. Structure and function of voltage-dependent ion channel regulatory beta subunits. Biochemistry. 2002;41:2886–2894. doi: 10.1021/bi0119565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heusser K, Schwappach B. Trafficking of potassium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:364–369. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2005.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sakaguchi M. Eukaryotic protein secretion. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1997;8:595–601. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(97)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Park SK, Mann KJ, Lin H, Starostina E, Kolski-Andreaco A, et al. A Drosophila protein specific to pheromone-sensing gustatory hairs delays males' copulation attempts. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1154–1159. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Greenspan RJ, Ferveur JF. Courtship in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 2000;34:205–232. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Phelps CB, Brand AH. Ectopic gene expression in Drosophila using GAL4 system. Methods. 1998;14:367–379. doi: 10.1006/meth.1998.0592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barolo S, Castro B, Posakony JW. New Drosophila transgenic reporters: insulated P-element vectors expressing fast-maturing RFP. Biotechniques 36: 436-440, 2004;442 doi: 10.2144/04363ST03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lai EC, Orgogozo V. A hidden program in Drosophila peripheral neurogenesis revealed: fundamental principles underlying sensory organ diversity. Dev Biol. 2004;269:1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, Apicella A, Jr, Lee SK, Ezcurra M, Slone RD, et al. A glial DEG/ENaC channel functions with neuronal channel DEG-1 to mediate specific sensory functions in C. elegans. EMBO J. 2008;27:2388–2399. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boll W, Noll M. The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection of all enhancers. Development. 2002;129:5667–5681. doi: 10.1242/dev.00157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.White K, Tahaoglu E, Steller H. Cell killing by the Drosophila gene reaper. Science. 1996;271:805–807. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5250.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Matsunami H, Amrein H. Taste and pheromone perception in mammals and flies. Genome Biol. 2003;4:220. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-7-220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Adams CM, Anderson MG, Motto DG, Price MP, Johnson WA, et al. Ripped pocket and pickpocket, novel Drosophila DEG/ENaC subunits expressed in early development and in mechanosensory neurons. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M. A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature. 1997;386:173–177. doi: 10.1038/386173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Askwith CC, Benson CJ, Welsh MJ, Snyder PM. DEG/ENaC ion channels involved in sensory transduction are modulated by cold temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:6459–6463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111155398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Askwith CC, Cheng C, Ikuma M, Benson CJ, Price MP, et al. Neuropeptide FF and FMRFamide potentiate acid-evoked currents from sensory neurons and proton-gated DEG/ENaC channels. Neuron. 2000;26:133–141. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wolfe MS, Kopan R. Intramembrane proteolysis: theme and variations. Science. 2004;305:1119–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.1096187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lin H, Mann KJ, Starostina E, Kinser RD, Pikielny CW. A Drosophila DEG/ENaC channel subunit is required for male response to female pheromones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:12831–12836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506420102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Xiong ZG, Zhu XM, Chu XP, Minami M, Hey J, et al. Neuroprotection in ischemia: blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channels. Cell. 2004;118:687–698. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Xu P, Atkinson R, Jones DN, Smith DP. Drosophila OBP LUSH is required for activity of pheromone-sensitive neurons. Neuron. 2005;45:193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Slone J, Daniels J, Amrein H. Sugar receptors in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1809–1816. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.09.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ben-Shahar Y, Robichon A, Sokolowski MB, Robinson GE. Influence of gene action across different time scales on behavior. Science. 2002;296:741–744. doi: 10.1126/science.1069911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Swick AG, Janicot M, Cheneval-Kastelic T, McLenithan JC, Lane MD. Promoter-cDNA-directed heterologous protein expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:1812–1816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zha XM, Wang R, Collier DM, Snyder PM, Wemmie JA, et al. Oxidant regulated inter-subunit disulfide bond formation between ASIC1a subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3573–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813402106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
A 3D movie of a confocal z-stack reconstruction of a single Che/llz positive cell in a male foreleg. Flies expressed simultaneously a nuclear localized DsRed and cytoplasmic GFP proteins.
(1.62 MB AVI)
A 3D movie of a confocal z-stack reconstruction of a single Che/llz positive cell in a male foreleg. Flies expressed simultaneously a nuclear localized DsRed and cytoplasmic GFP proteins. Images in Movies S1 and S2 were recorded from two independent cells in a single male.
(0.69 MB AVI)