Abstract
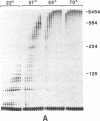
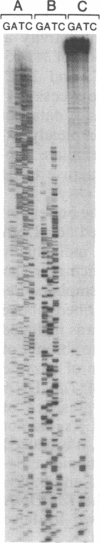
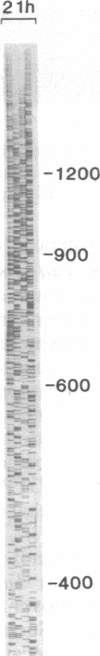
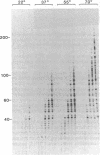
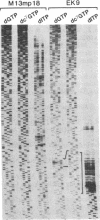
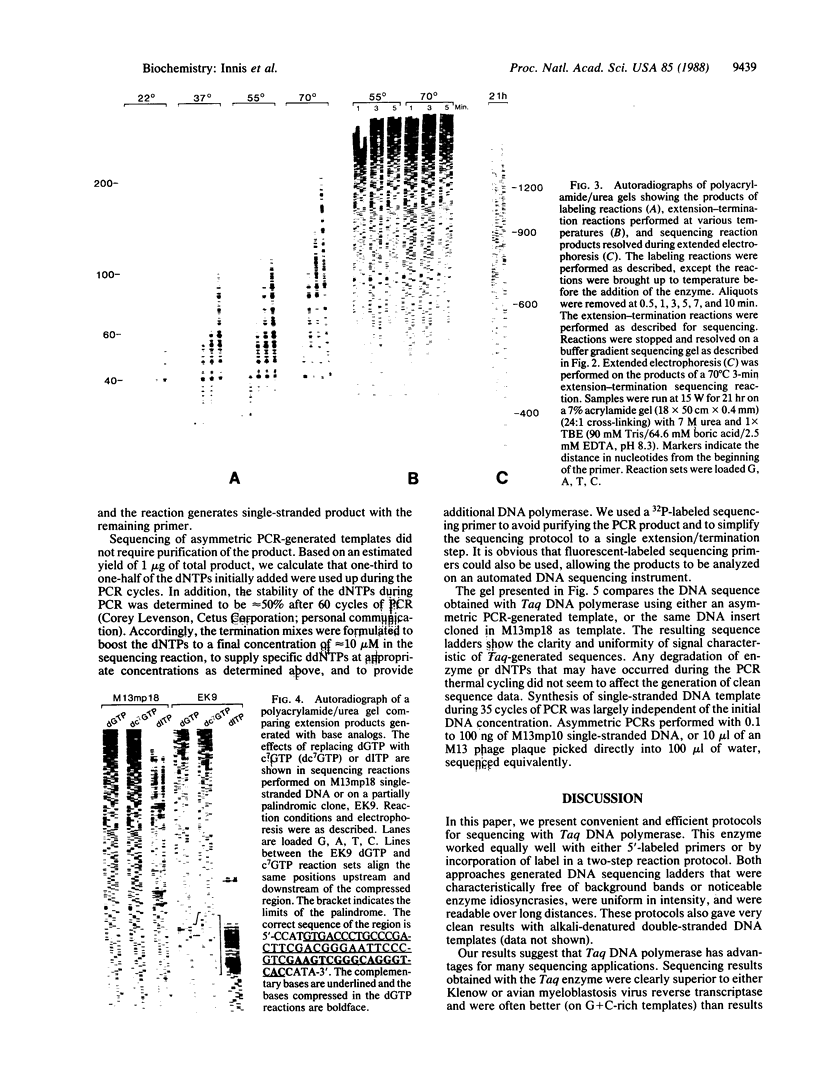
The highly thermostable DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus (Taq) is ideal for both manual and automated DNA sequencing because it is fast, highly processive, has little or no 3'-exonuclease activity, and is active over a broad range of temperatures. Sequencing protocols are presented that produce readable extension products greater than 1000 bases having uniform band intensities. A combination of high reaction temperatures and the base analog 7-deaza-2'-deoxyguanosine was used to sequence through G + C-rich DNA and to resolve gel compressions. We modified the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) conditions for direct DNA sequencing of asymmetric PCR products without intermediate purification by using Taq DNA polymerase. The coupling of template preparation by asymmetric PCR and direct sequencing should facilitate automation for large-scale sequencing projects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Hoener P. A., Collins F. S. Direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified human genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):544–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Boeke J. D. The filamentous phage (Ff) as vectors for recombinant DNA--a review. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]