Abstract
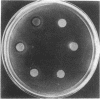
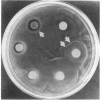
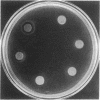
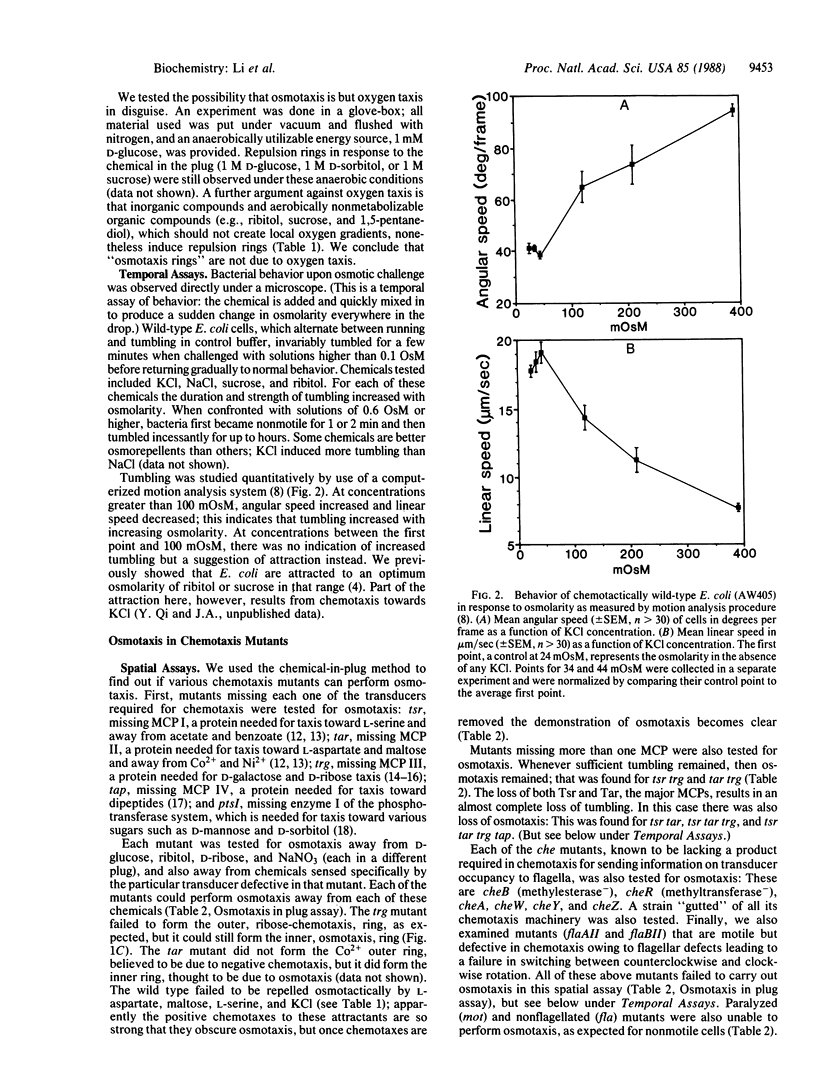
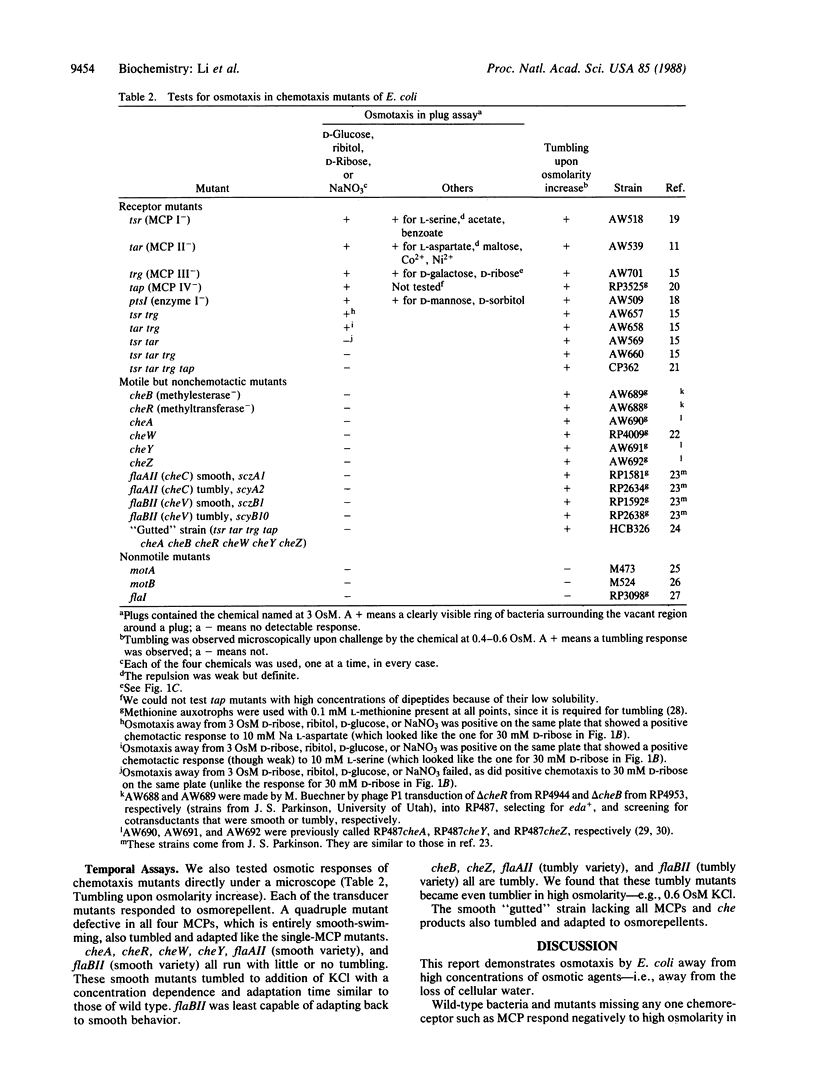
The escape of motile organisms from high concentrations of chemicals was studied in Escherichia coli. We have found all chemicals tested to be osmorepellents. It was shown in both a spatial assay and a temporal assay that the known sensory receptors for chemotaxis are not used for osmotaxis, so a different sensory mechanism appears to be employed. According to the temporal assay, the mechanism between sensory receptors and flagella is also not used for tumbling response (at least in solutions above 0.4 osmolar).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Epstein W. Phosphotransferase-system enzymes as chemoreceptors for certain sugars in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Hazelbauer G. L., Dahl M. M. Chemotaxis toward sugars in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):824–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.824-847.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. How motile bacteria are attracted and repelled by chemicals: an approach to neurobiology. Lecture held on the occasion of the receipt of the Otto-Warburg-Medaille 1986. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Mar;368(3):163–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Li C., Boileau A. J., Qi Y., Kung C. Osmotaxis in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):19–22. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J. Genetics of motility in Escherichia coli: complementation of paralysed mutants. Genetics. 1967 Jul;56(3):363–373. doi: 10.1093/genetics/56.3.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin W. W., Sheu M. J., Bankston P. W., Woldringh C. L. Changes in buoyant density and cell size of Escherichia coli in response to osmotic shocks. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):452–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.452-455.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett S., Taylor R. K., Silhavy T. J., Berman M. L. Isolation and characterization of delta ompB strains of Escherichia coli by a general method based on gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):840–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.840-844.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Failure of sensory adaptation in bacterial mutants that are defective in a protein methylation reaction. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Mutants in transmission of chemotactic signals from two independent receptors of E. coli. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Paul B. R., Howe M. M. Use of lambda pMu bacteriophages to isolate lambda specialized transducing bacteriophages carrying genes for bacterial chemotaxis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.619-628.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Strom A. R., Dandekar A. M., Smith L. T., Valentine R. C. Molecular biology of osmoregulation. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1064–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4653.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Blank V., Brade G., Higgins C. F. Peptide chemotaxis in E. coli involves the Tap signal transducer and the dipeptide permease. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):253–256. doi: 10.1038/321253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinac B., Buechner M., Delcour A. H., Adler J., Kung C. Pressure-sensitive ion channel in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2297–2301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N. Osmotic adaptation by gram-negative bacteria: possible role for periplasmic oligosaccharides. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.3941890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Imae Y. Glycerol and ethylene glycol: members of a new class of repellents of Escherichia coli chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):104–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.104-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Adler J. Properties of mutants in galactose taxis and transport. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):517–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.517-526.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Mutations specifically affecting ligand interaction of the Trg chemosensory transducer. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager B. M., Sekelsky J. J., Matsumura P., Adler J. Use of a computer to assay motility in bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: methylation of che gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocum M. K., Parkinson J. S. Genetics of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli: null phenotypes of the tar and tap genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):586–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.586-594.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Parkinson J. S. Overlapping genes at the cheA locus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5370–5374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Adler J. Change in membrane potential during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4387–4391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szupica C. J., Adler J. Cell envelopes of chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli rotate their flagella counterclockwise. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):451–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.451-453.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Kramer T. J., Berg H. C. Reconstitution of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1878-1885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonekawa H., Hayashi H., Parkinson J. S. Requirement of the cheB function for sensory adaptation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1228–1235. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1228-1235.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]