Abstract
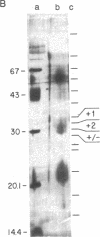
We purified a factor that induces bone formation greater than 300,000-fold from guanidinium chloride extracts of demineralized bone. Fifty nanograms of highly purified protein was active in an in vivo cartilage and bone-formation assay. The activity resided in a single gel band, corresponding to a molecular mass of approximately 30 kDa, which yielded proteins of 30, 18, and 16 kDa on reduction. The partial amino acid sequence obtained from these proteins confirmed our identification of specific factors that induce new bone formation in vivo.
Full text
PDF
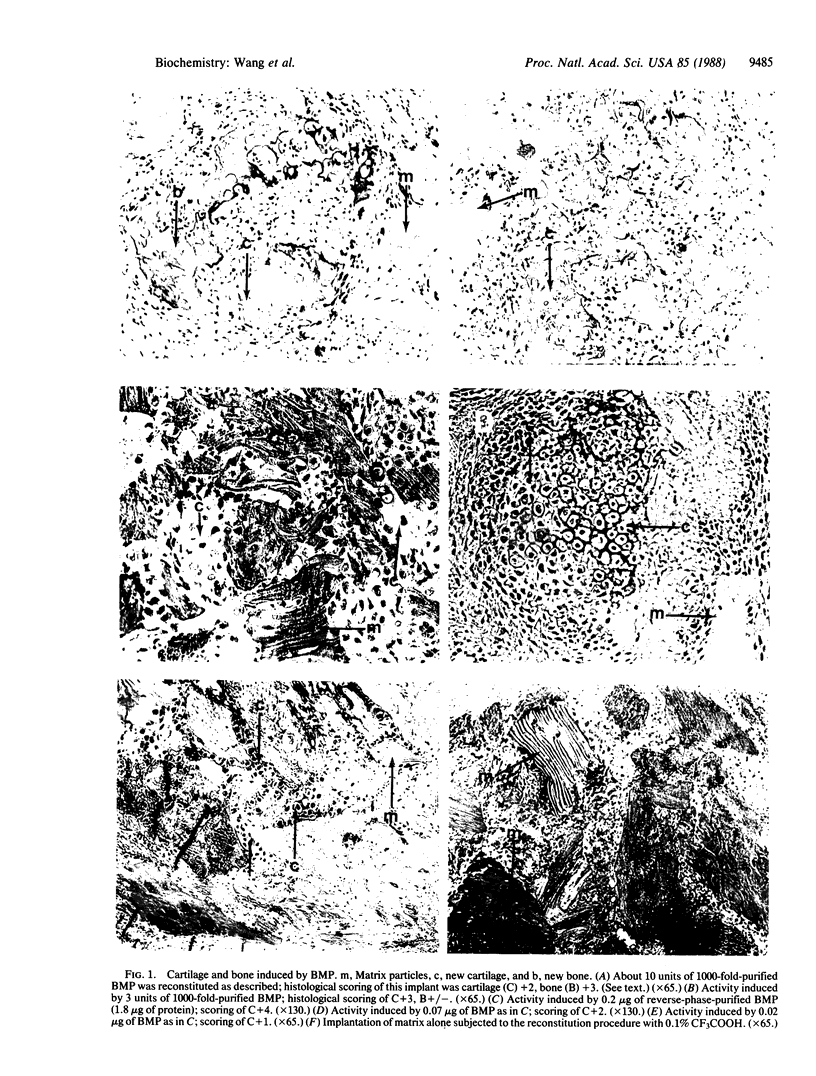

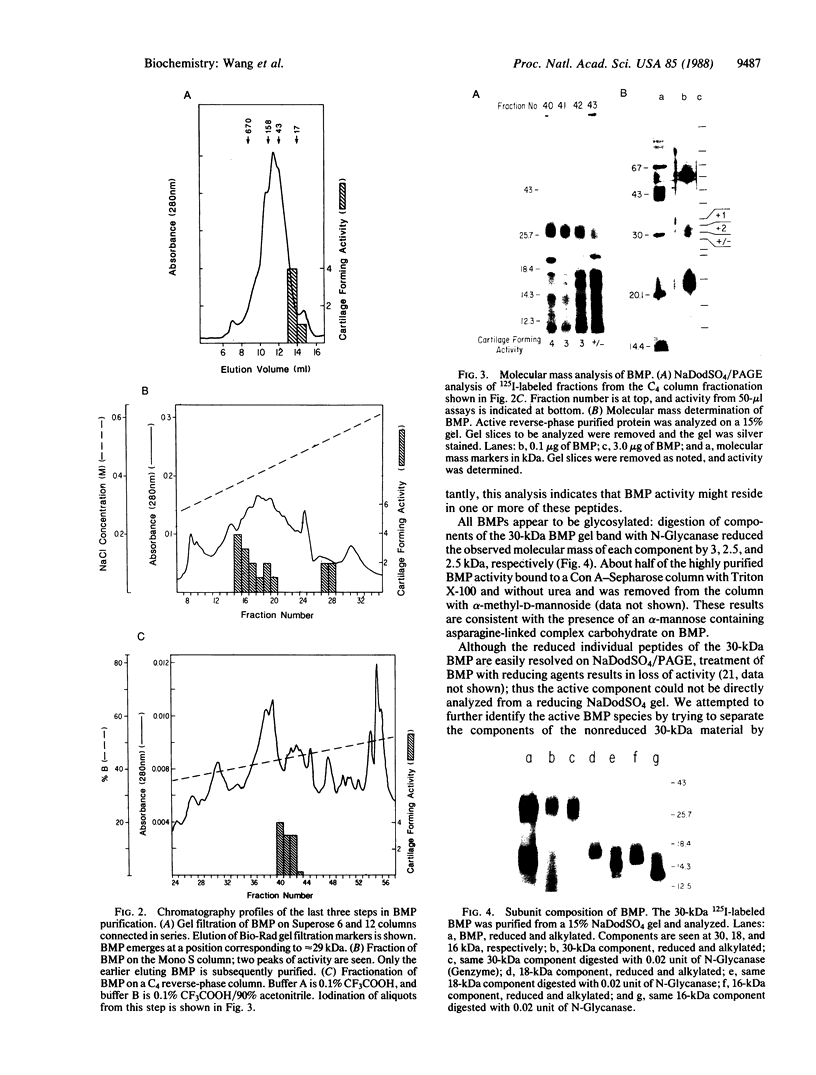

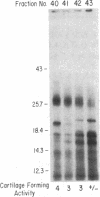
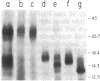
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., Canalis E. Local regulators of skeletal growth: a perspective. Endocr Rev. 1985 Fall;6(4):544–551. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-4-544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firschein H. E., Urist M. R. Enzyme induction, accumulation of collagen, and calcification in implants of bone matrix. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972 May;84:263–275. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197205000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Mavrakos A. E., Iafrati M. D., Doleman S. E., Klagsbrun M. Growth factors in bone matrix. Isolation of multiple types by affinity chromatography on heparin-Sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12665–12674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Huggins C. Biochemical sequences in the transformation of normal fibroblasts in adolescent rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1601–1605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Muthukumaran N., Reddi A. H. Isolation of osteogenin, an extracellular matrix-associated, bone-inductive protein, by heparin affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7109–7113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Reddi A. H. Homology of bone-inductive proteins from human, monkey, bovine, and rat extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6591–6595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Chang J. J., Lietze A., Huo Y. K., Brownell A. G., DeLange R. J. Preparation and bioassay of bone morphogenetic protein and polypeptide fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:294–312. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Huo Y. K., Brownell A. G., Hohl W. M., Buyske J., Lietze A., Tempst P., Hunkapiller M., DeLange R. J. Purification of bovine bone morphogenetic protein by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Iwata H., Ceccotti P. L., Dorfman R. L., Boyd S. D., McDowell R. M., Chien C. Bone morphogenesis in implants of insoluble bone gelatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Jurist J. M., Jr, Dubuc F. L., Strates B. S. Quantitation of new bone formation in intramuscular implants of bone matrix in rabbits. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970 Jan-Feb;68:279–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Lietze A., Dawson E. Beta-tricalcium phosphate delivery system for bone morphogenetic protein. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984 Jul-Aug;(187):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Lietze A., Mizutani H., Takagi K., Triffitt J. T., Amstutz J., DeLange R., Termine J., Finerman G. A. A bovine low molecular weight bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) fraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Jan-Feb;(162):219–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]