Abstract
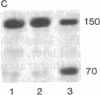
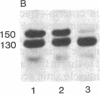
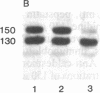
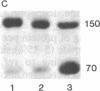
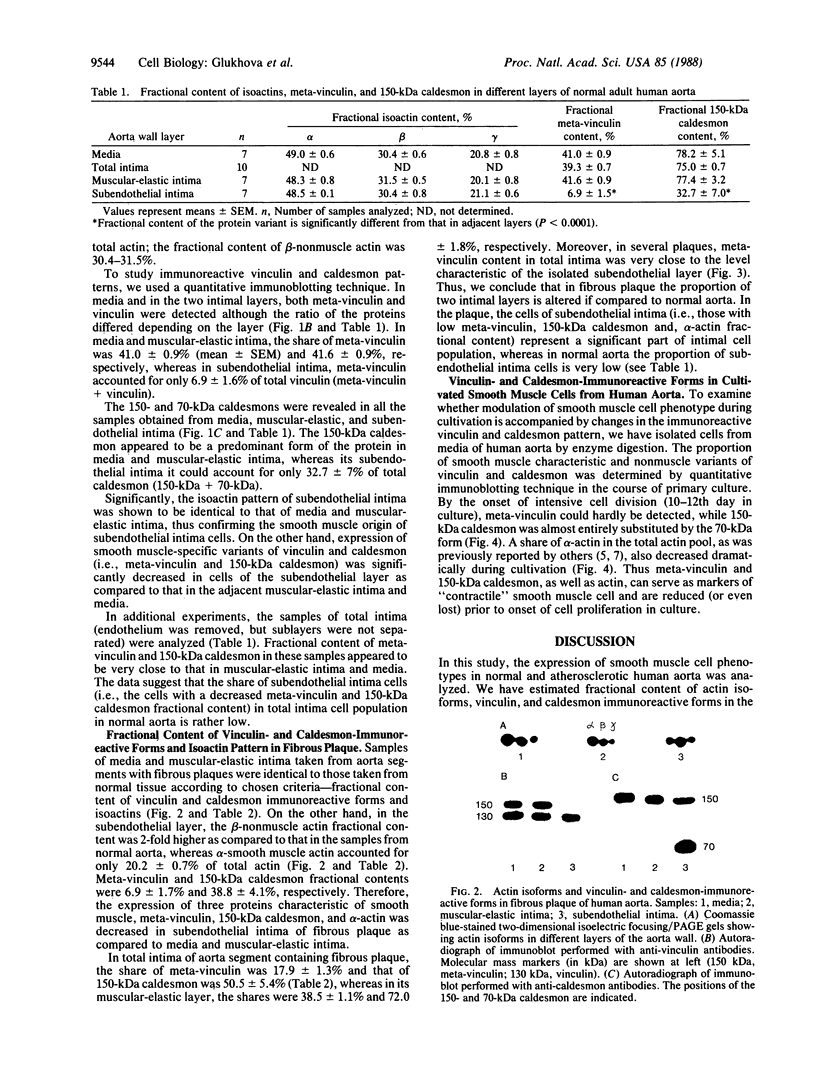
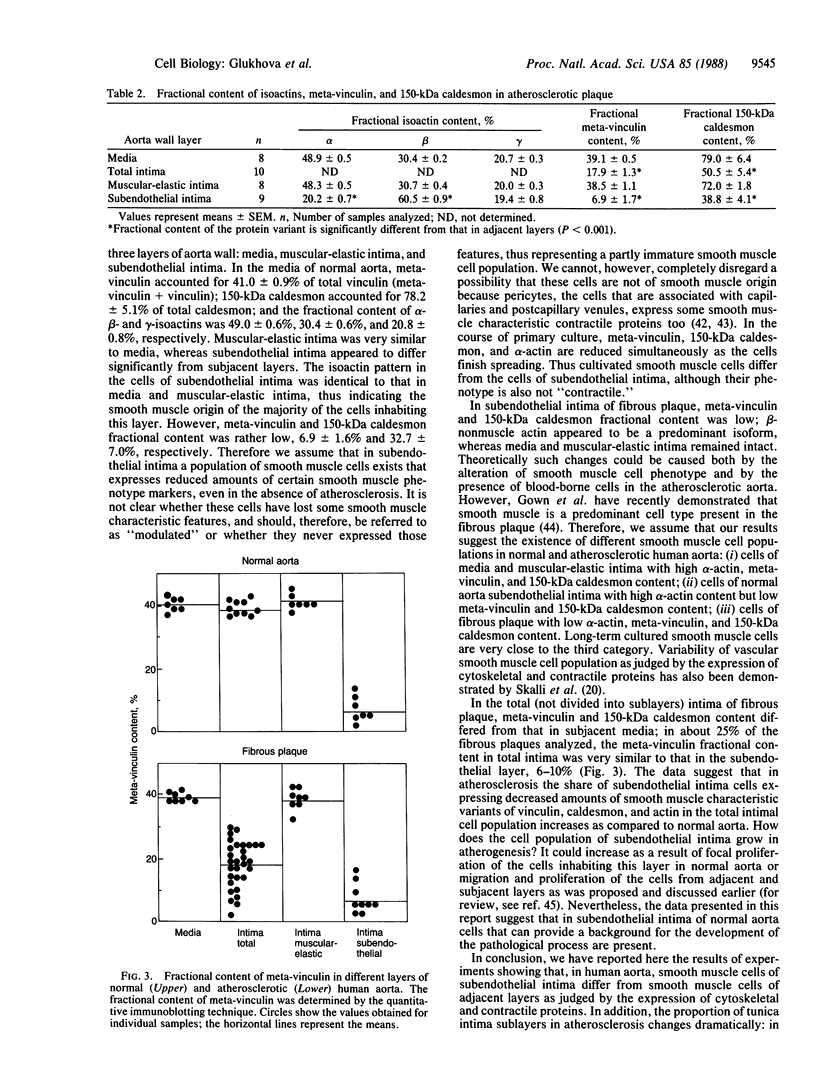
Vinculin- and caldesmon-immunoreactive forms and actin isoform patterns were studied in samples of normal and atherosclerotic human aorta. After removal of adventitia and endothelium, the remaining tissue was divided into three layers: media, muscular-elastic (adjacent to media) intima, and subendothelial (juxtaluminal) intima. In media of normal aorta, meta-vinculin accounted for 41.0 +/- 0.9% (mean +/- SEM) of total immunoreactive vinculin (meta-vinculin + vinculin); 150-kDa caldesmon accounted for 78.2 +/- 5.1% of immunoreactive caldesmon (150-kDa + 70-kDa); the fractional contents of alpha-smooth muscle actin, beta-nonmuscle, and gamma-isoactins were 49.0 +/- 0.6%, 30.4 +/- 0.6%, and 20.8 +/- 0.8%, respectively. Muscular-elastic intima was very similar to media by these criteria. In subendothelial intima, the fractional content of meta-vinculin and 150-kDa caldesmon was significantly lower (6.9 +/- 1.5% and 32.7 +/- 7.0%, respectively) than in muscular-elastic intima and media, whereas the isoactin pattern was identical to that in adjacent layers, demonstrating the smooth muscle origin of subendothelial intima cells. In atherosclerotic fibrous plaque, the fractional content of alpha-actin was decreased in subendothelial intima, rather than in media and muscular-elastic intima. Additionally, the proportion of subendothelial intima cells [i.e., the cells that express low amounts of smooth muscle phenotype markers (meta-vinculin, 150-kDa caldesmon, and alpha-actin)] in the total intima cell population increased dramatically in atherosclerotic fibrous plaque. The results suggest that changes in the relative content of meta-vinculin and 150-kDa caldesmon as well as alpha-actin in human aortic intima are associated with atherosclerosis although, in subendothelial intima of normal aorta, a certain smooth muscle cell population exists that expresses reduced amounts of "contractile" phenotype markers, even in the absence of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barja F., Coughlin C., Belin D., Gabbiani G. Actin isoform synthesis and mRNA levels in quiescent and proliferating rat aortic smooth muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1986 Aug;55(2):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Lynch W. Identification and localization of immunoreactive forms of caldesmon in smooth and nonmuscle cells: a comparison with the distributions of tropomyosin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1656–1663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Smooth muscle caldesmon. Rapid purification and F-actin cross-linking properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12873–12880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Thin filament regulatory proteins of smooth- and non-muscle cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):726–727. doi: 10.1038/321726b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J. H., Campbell G. R., Ross R. Phenotype-dependent response of cultured aortic smooth muscle to serum mitogens. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):379–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J. H., Campbell G. R. What controls smooth muscle phenotype? Atherosclerosis. 1981 Nov-Dec;40(3-4):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T., Ngai P. K., Sutherland C., Gröschel-Stewart U., Walsh M. P. Vascular smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8028–8035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatigati V., Murphy R. A. Actin and tropomyosin variants in smooth muscles. Dependence on tissue type. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14383–14388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner C., Traut R. R., Mason D. T., Wikman-Coffelt J. Quantification of Coomassie Blue stained proteins in polyacrylamide gels based on analyses of eluted dye. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Burridge K. A rapid purification of alpha-actinin, filamin, and a 130,000-dalton protein from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Smart J. E., Burridge K., Helfman D. M., Thomas G. P. Co-existence of vinculin and a vinculin-like protein of higher molecular weight in smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11024–11031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E. D., Warren L. Aortic smooth muscle cells contain vimentin instead of desmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Cross R. A., De Mey J., Small J. V. Caldesmon is an elongated, flexible molecule localized in the actomyosin domains of smooth muscle. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):251–257. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Kocher O., Bloom W. S., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin expression in smooth muscle cells of rat aortic intimal thickening, human atheromatous plaque, and cultured rat aortic media. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):148–152. doi: 10.1172/JCI111185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Schmid E., Winter S., Chaponnier C., de Ckhastonay C., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K., Franke W. W. Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific alpha-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geer J. C. Fine structure of human aortic intimal thickening and fatty streaks. Lab Invest. 1965 Oct;14(10):1764–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glukhova M. A., Kabakov A. E., Belkin A. M., Frid M. G., Ornatsky O. I., Zhidkova N. I., Koteliansky V. E. Meta-vinculin distribution in adult human tissues and cultured cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., D'Amore P. A. Microvascular pericytes contain muscle and nonmuscle actins. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):43–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce N. C., Haire M. F., Palade G. E. Contractile proteins in pericytes. II. Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence of two isomyosins in graded concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1387–1395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Adelstein R. S. Characterization of myosin heavy chains in cultured aorta smooth muscle cells. A comparative study. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7282–7288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeletal features of normal and atheromatous human arterial smooth muscle cells. Hum Pathol. 1986 Sep;17(9):875–880. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80637-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Skalli O., Bloom W. S., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeleton of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Normal conditions and experimental intimal thickening. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Skalli O., Cerutti D., Gabbiani F., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeletal features of rat aortic cells during development. An electron microscopic, immunohistochemical, and biochemical study. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):829–838. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M. Change of actin isomers during differentiation of smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 13;843(3):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Walsh M. P. Detection of caldesmon in muscle and non-muscle tissues of the chicken using polyclonal antibodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):533–539. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orekhov A. N., Andreeva E. R., Tertov V. V., Krushinsky A. V. Dissociated cells from different layers of adult human aortic wall. Acta Anat (Basel) 1984;119(2):99–105. doi: 10.1159/000145868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orekhov A. N., Kosykh V. A., Repin V. S., Smirnov V. N. Cell proliferation in normal and atherosclerotic human aorta. II. Autoradiographic observation on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in primary cell culture. Lab Invest. 1983 Jun;48(6):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Caselitz J., Weber K. Heterogeneity of intermediate filament expression in vascular smooth muscle: a gradient in desmin positive cells from the rat aortic arch to the level of the arteria iliaca communis. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):196–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owada M. K., Hakura A., Iida K., Yahara I., Sobue K., Kakiuchi S. Occurrence of caldesmon (a calmodulin-binding protein) in cultured cells: comparison of normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K., Loeb A., Gordon D., Thompson M. M. Expression of smooth muscle-specific alpha-isoactin in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: relationship between growth and cytodifferentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):343–352. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K., Thompson M. M. Developmental changes in isoactin expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells in vivo. Relationship between growth and cytodifferentiation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13373–13380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovner A. S., Murphy R. A., Owens G. K. Expression of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin heavy chains in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14740–14745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga S., Hamaguchi M., Hoshino M., Kojima K. Expression of meta-vinculin associated with differentiation of chicken embryonal muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jan;156(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E., Osborn M., Rungger-Brändle E., Gabbiani G., Weber K., Franke W. W. Distribution of vimentin and desmin filaments in smooth muscle tissue of mammalian and avian aorta. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Campbell G. R., Campbell J. H. Replication of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):427–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano J. D., Craig S. W. Meta-vinculin--a vinculin-related protein with solubility properties of a membrane protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):533–535. doi: 10.1038/300533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Pritchard K., Marston S. B. The mechanism of Ca2+ regulation of vascular smooth muscle thin filaments by caldesmon and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of actins from bovine aorta, bovine heart, bovine fast skeletal muscle, and rabbit slow skeletal muscle. A protein-chemical analysis of muscle actin differentiation. Differentiation. 1979;14(3):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]