Abstract
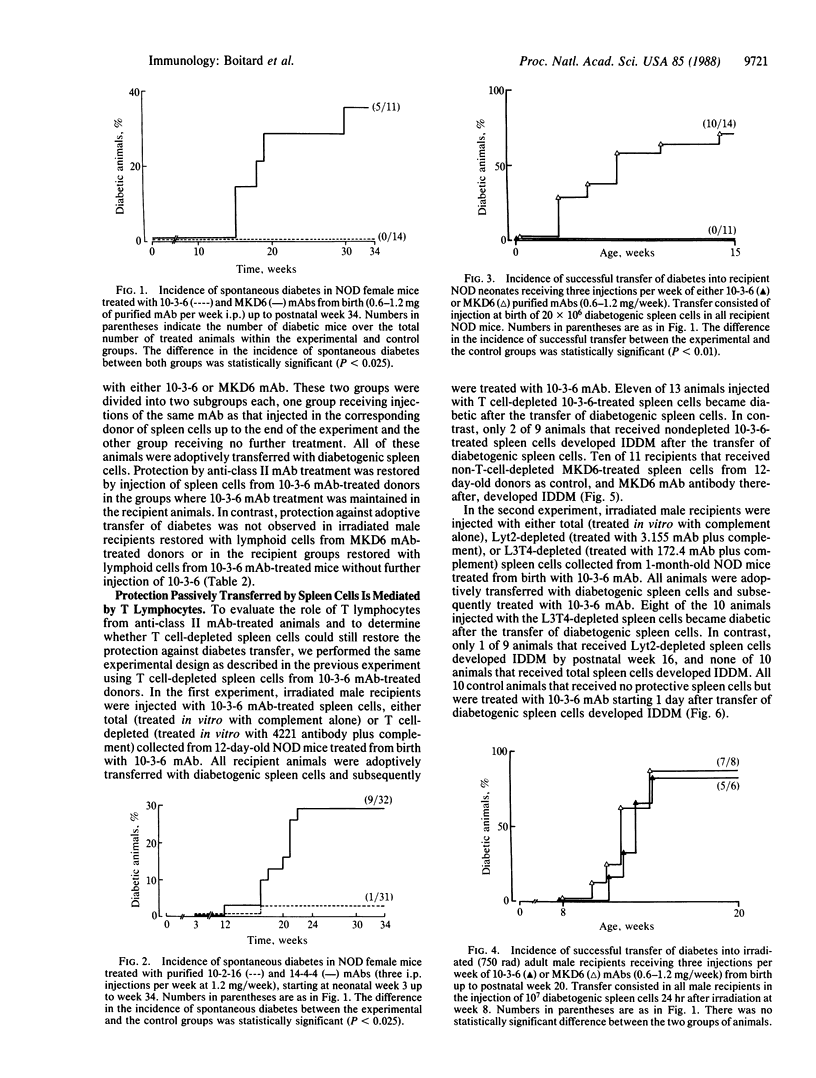
The nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse has been developed as a model for insulin-dependent diabetes. One gene required for the development of diabetes is associated with the major histocompatibility complex. This gene possibly could be linked to class II genes, which show a unique pattern in NOD mice. To evaluate the role of the I-A class II antigen expressed in NOD mice, we studied the effect of anti-I-A monoclonal antibodies on disease onset in vivo. Long-term treatment with anti-class II IgG2a antibodies specific for NOD I-A antigen prevented the spontaneous development of diabetes, as opposed to control antibodies shown not to react with NOD I-A antigen. Anti-class II antibodies apparently elicited active immune suppression, requiring a fully immunocompetent host, rather than passive blockade of class II antigen. Treatment with anti-class II antibody effectively prevented the adoptive transfer of diabetes produced by splenocytes from diabetic NOD mice into newborn mice but failed to prevent adoptive transfer into irradiated adult NOD recipients. Direct evidence for the induction of suppressor cells was obtained from the passive transfer of spleen cells from anti-class II antibody-treated NOD donors. The injection of anti-class II antibody-treated spleen cells collected from NOD donors prevented the development of diabetes, which normally follows transfer of diabetogenic spleen cells into irradiated 8-week-old male NOD recipients. Depletion experiments indicate that CD4+ cells are responsible for anti-class II-induced protection transferred by spleen cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., McDevitt H. O. The first external domain of the nonobese diabetic mouse class II I-A beta chain is unique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2435–2439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelman N. E., Watling D. L., McDevitt H. O. Treatment of (NZB x NZW)F1 disease with anti-I-A monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1350–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki I., Ishii N., Minami M., Nagashima Y., Misugi K., Okuda K. Induction of suppressor T cells by intravenous administration of monoclonal anti-I-A antibody. Transplantation. 1987 Sep;44(3):421–425. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198709000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Carnaud C., Boitard C., Bach J. F. Syngeneic transfer of autoimmune diabetes from diabetic NOD mice to healthy neonates. Requirement for both L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):823–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Richman L. K. Genetic control of the immune response to myoglobins. IV. Inhibition of determinant-specific Ir gene-controlled antigen presentation and induction of suppression by pretreatment of presenting cells with anti-Ia antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1898–1904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boitard C., Michie S., Serrurier P., Butcher G. W., Larkins A. P., McDevitt H. O. In vivo prevention of thyroid and pancreatic autoimmunity in the BB rat by antibody to class II major histocompatibility complex gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Mann D. L., Waldmann T. A. Participation of suppressor T cells in the immunosuppressive activity of a heteroantiserum to human Ia-like antigens (p23,30). J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):257–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz M. J., Scher I., Finkelman F. D., Kincade P., Mond J. J. Neonatal suppression with anti-Ia antibody. I. Suppression of murine B lymphocyte development. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):992–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz M., Finkelman F. D., Mond J. J. In vivo administration of anti-I-A antibody induces the internalization of B cell surface I-A and I-E without affecting the expression of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):91–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Levinson J. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with murine teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):377–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Fujino-Kurihara H., Miyazaki A., Yamada K., Nakajima H., Miyagawa J., Kono N., Tarui S. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on pancreatic B cells in the NOD mouse. Diabetologia. 1987 Feb;30(2):104–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00274580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Makino S. Promotion of spontaneous diabetes in non-obese diabetes-prone mice by cyclophosphamide. Diabetologia. 1984 Dec;27(6):604–606. doi: 10.1007/BF00276978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Buse J. B., Jackson R. A., Glimcher L., Dorf M. E., Minami M., Makino S., Moriwaki K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):733–735. doi: 10.1126/science.3003909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Skidmore B., White J., Marrack P. Antigen-inducible, H-2-restricted, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridomas. Lack of independent antigen and H-2 recognition. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1198–1214. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Itoh Y., Ishii T., Ito I., Takabayashi K., Maruyama N., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Preventive effect of monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibody on development of diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):539–541. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Fultz M. J., Sharrow S. O., Singer A., Mond J. J. Early development of the T cell repertoire. In vivo treatment of neonatal mice with anti-Ia antibodies interferes with differentiation of I-restricted T cells but not K/D-restricted T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1932–1946. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Mond J. J., Fowlkes B. J., Carmen J. A., Bridges S., Longo D. L. Absence of the Lyt-2-,L3T4+ lineage of T cells in mice treated neonatally with anti-I-A correlates with absence of intrathymic I-A-bearing antigen-presenting cell function. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1029–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Titus J. A., Stephany D. A., Gause B. L., Longo D. L. In vivo treatment with monoclonal anti-I-A antibodies: disappearance of splenic antigen-presenting cell function concomitant with modulation of splenic cell surface I-A and I-E antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3605–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Eckels D. D., Ketterer E. A., Sell T. W., Woody J. N. Antigen-specific human T lymphocyte clones: mechanisms of inhibition of proliferative responses by xenoantiserum to human nonpolymorphic HLA-DR antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Kunimoto K., Muraoka Y., Mizushima Y., Katagiri K., Tochino Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–13. doi: 10.1538/expanim1978.29.1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. J., Appel M. C., O'Neil J. J., Wicker L. S. Both the Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ T cell subsets are required for the transfer of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki A., Hanafusa T., Yamada K., Miyagawa J., Fujino-Kurihara H., Nakajima H., Nonaka K., Tarui S. Predominance of T lymphocytes in pancreatic islets and spleen of pre-diabetic non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice: a longitudinal study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):622–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Suko M., Okudaira H., Matsuba I., Tsuruoka A., Sasaki A., Yokoyama H., Tanase T., Shida T., Nishimura M. Preventive effects of cyclosporin on diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 1986 Apr;29(4):244–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00454884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Regulation of immune response to tumor antigen: interference with syngeneic tumor immunity by anti-IA alloantisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):920–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Greene M. I. Conversion of immunity to suppression by in vivo administration of I-A subregion-specific antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):480–491. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Williams I. R. Regulation of transplantation immunity in vivo by monoclonal antibodies recognizing host class II restriction elements. I. Genetics and specificity of anti-Ia immunotherapy in murine skin allograft recipients. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2935–2941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Leiter E. H., Serreze D. V., Coleman D. L. Three recessive loci required for insulin-dependent diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.2885918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Adelman N. E., McDevitt H. O. In vivo effects of antibodies to immune response gene products. I. Haplotype-specific suppression of humoral immune responses with a monoclonal anti-I-A. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1694–1702. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signore A., Cooke A., Pozzilli P., Butcher G., Simpson E., Beverley P. C. Class-II and IL2 receptor positive cells in the pancreas of NOD mice. Diabetologia. 1987 Nov;30(11):902–905. doi: 10.1007/BF00274802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Steinman L. Anti I-A antibody suppresses active encephalomyelitis: treatment model for diseases linked to IR genes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1362–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Steinman L., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Disappearance and reappearance of B cells after in vivo treatment with monoclonal anti-I-A antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2855–2858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. In vivo therapy with monoclonal anti-I-A antibody suppresses immune responses to acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Hao L., Gill R. G., Lafferty K. J. Autoimmune diabetes in NOD mouse is L3T4 T-lymphocyte dependent. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):535–538. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Mullen Y. Transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus with splenocytes from nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):855–860. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. R., Perry L. L. Regulation of transplantation immunity in vivo by monoclonal antibodies recognizing host class II restriction elements. II. Effects of anti-Ia immunotherapy on host T cell responses to graft alloantigens. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2942–2947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Lafuse W. P., Huse A., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. III. Suppression of arthritis by using monoclonal and polyclonal anti-Ia antisera. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2366–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



