Abstract
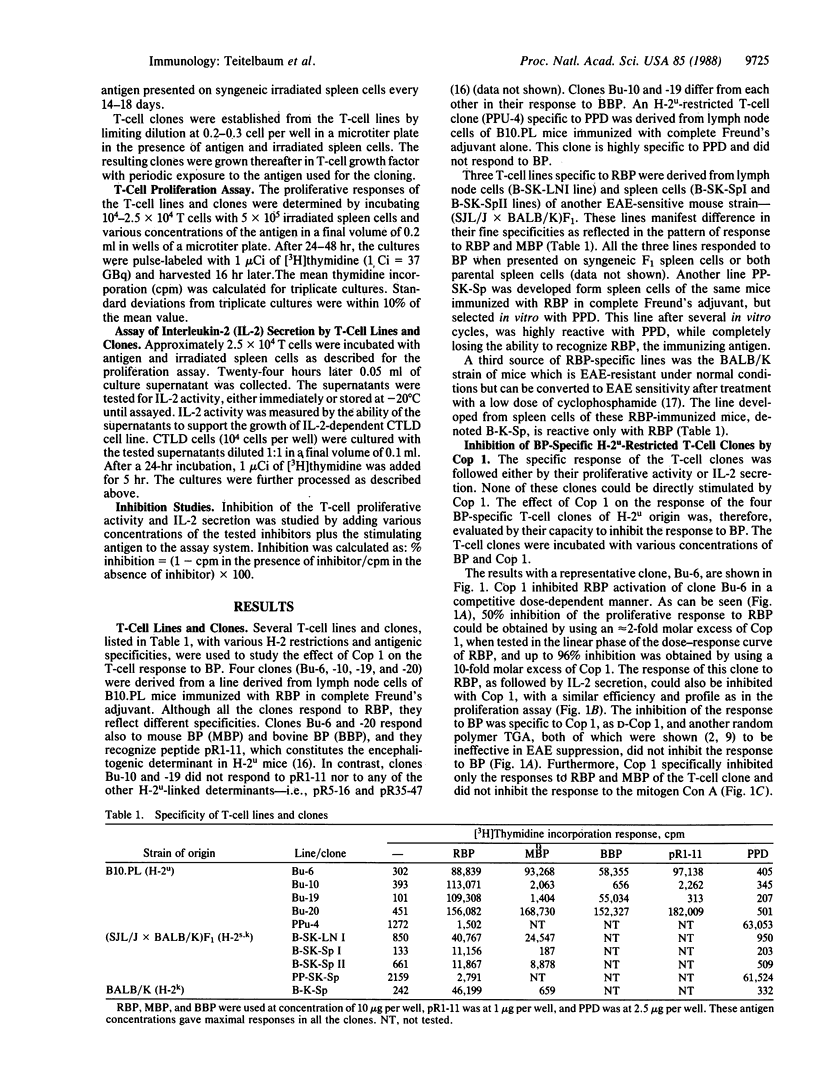
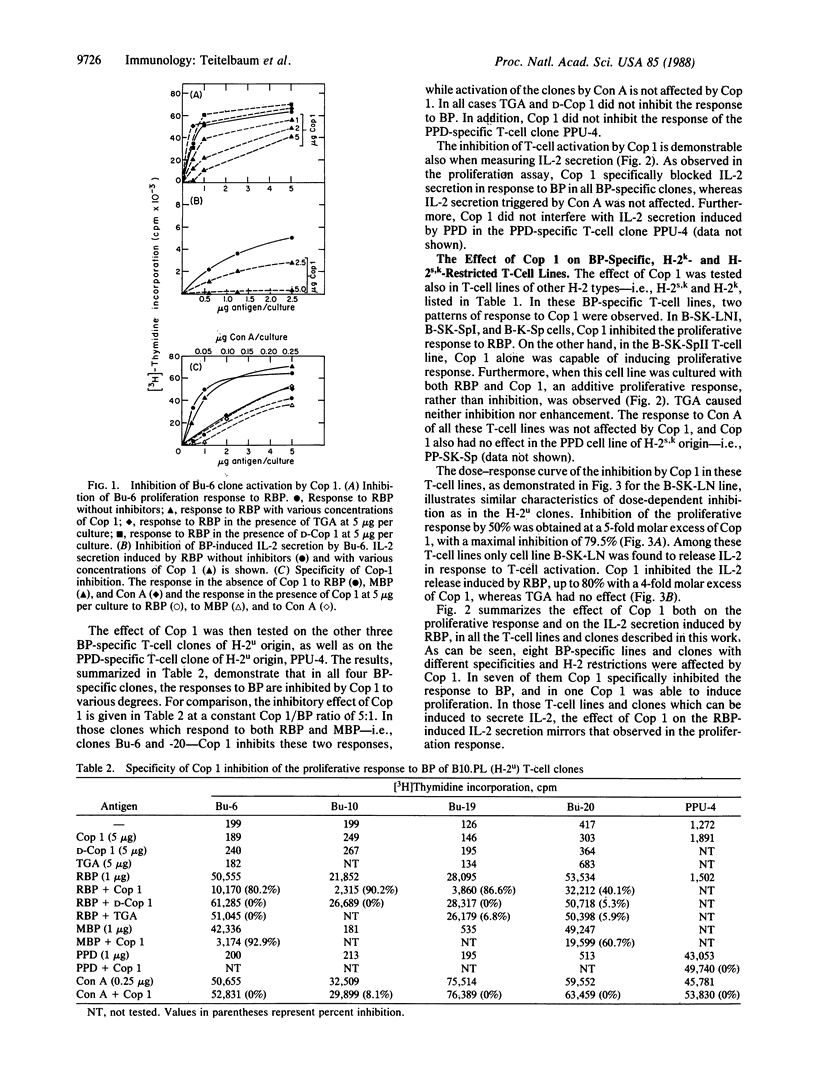
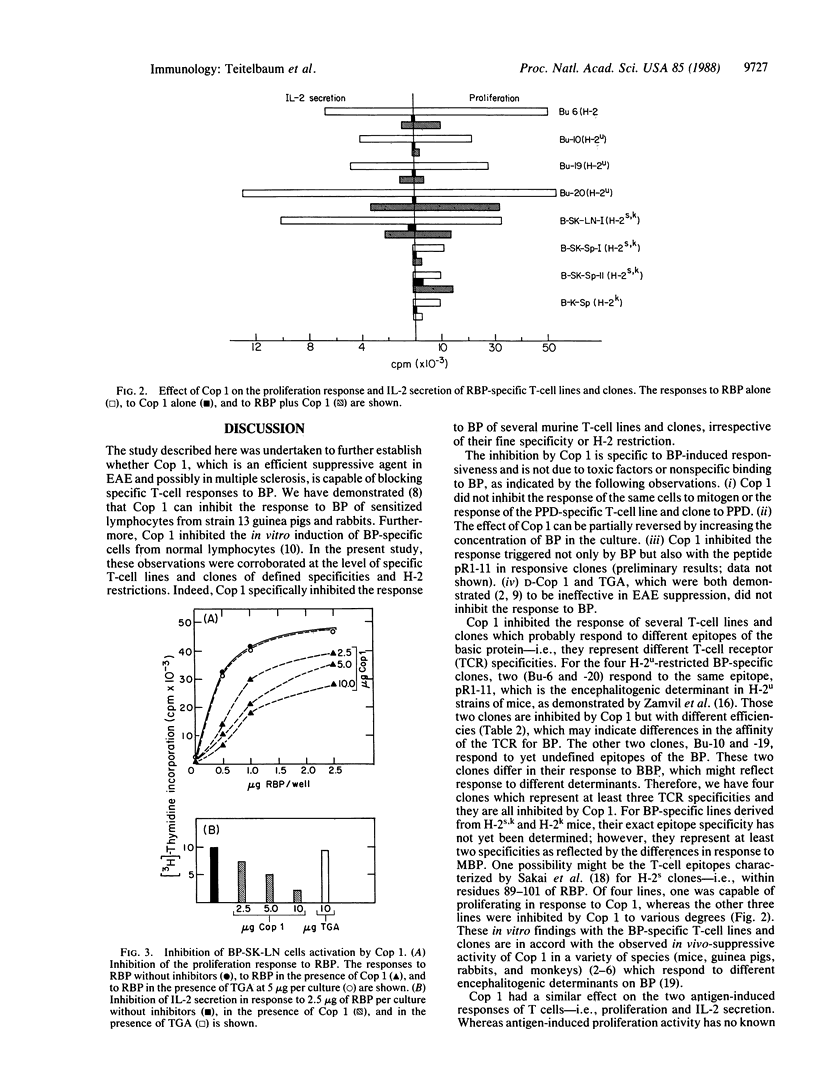
Cop 1 is a synthetic basic random copolymer of L-alanine, L-glutamic acid, L-lysine, and L-tyrosine in a residue molar ratio of 6.0:1.9:4.7:1.0 and with a molecular weight of 21,000 which proved to be effective in specific suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and has been proposed as a candidate drug against multiple sclerosis. In the present study we further investigated the mechanism of Cop 1 suppressive activity and tested whether Cop 1 could inhibit the specific T-cell response to myelin basic protein (BP). Eight BP-specific T-cell lines and clones with various H-2 restrictions and antigenic specificities were used. The responses of all these lines and clones to BP, as followed by both cell proliferation and interleukin 2 secretion assays, were affected by Cop 1. For one line, a direct cross proliferation with Cop 1 was observed, whereas in the other seven lines and clones, Cop 1 specifically inhibited the responses to BP in a competitive dose-dependent manner. The inhibition of the response to BP is specific to Cop 1, as D-Cop 1 and another random acidic polymer, poly(Tyr,Glu,Ala) (TGA), both of which were previously demonstrated to be ineffective in suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, did not inhibit the response to BP. Furthermore, Cop 1 specifically inhibited only the response of the T-cell lines and clones to BP. It did not inhibit their response to the mitogen Con A, nor did it inhibit the responses of the purified protein derivative-specific T-cell line and clone. These results suggest that Cop 1 may be effective in suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, not only because of the selective stimulation of suppressor T cells, as we have previously demonstrated, but also by specific inhibition of BP-specific effector T cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Nun A., Lando Z. Detection of autoimmune cells proliferating to myelin basic protein and selection of T cell lines that mediate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Miller A., Slagle S., Weitzman M., Crystal H., Drexler E., Keilson M., Merriam A., Wassertheil-Smoller S., Spada V. A pilot trial of Cop 1 in exacerbating-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 13;317(7):408–414. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708133170703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Krasner L. J., Guerrero F. Human cellular immune response to copolymer I and myelin basic protein. Neurology. 1986 Jan;36(1):92–94. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Regulation of autoimmune disease physiological and therapeutic. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:5–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Lai M. Z., Briner T. J., Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Immunological self, nonself discrimination. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):865–870. doi: 10.1126/science.2433769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Lai M. Z., Briner T. J., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Interaction of peptide antigens and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):260–262. doi: 10.1038/324260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshfeld H., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R., Sela M. Basic encephalitogenic protein: A simplified purification on sulphoethyl-sephadex. FEBS Lett. 1970 May 1;7(4):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando Z., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Effect of cyclophosphamide on suppressor cell activity in mice unresponsive to EAE. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2156–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando Z., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in genetically resistant strains of mice. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):551–552. doi: 10.1038/287551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozes E., Apte R. N. Nature and function of antigen-specific T-cell lines and their products. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):653–709. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Day E. D. Current perspectives of neuroimmunologic disease: multiple sclerosis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (1,2). Clin Immunol Rev. 1981;1(4):581–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELA M., FUCHS S., ARNON R. Studies on the chemical basis of the antigenicity of proteins. 5. Synthesis, characterization and immunogenicity of some multichain and linear polypeptides containing tyrosine. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85:223–235. doi: 10.1042/bj0850223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Sinha A. A., Mitchell D. J., Zamvil S. S., Rothbard J. B., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Involvement of distinct murine T-cell receptors in the autoimmune encephalitogenic response to nested epitopes of myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8608–8612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum D., Meshorer A., Hirshfeld T., Arnon R., Sela M. Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by a synthetic polypeptide. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Aug;1(4):242–248. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum D., Webb C., Bree M., Meshorer A., Arnon R., Sela M. Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Rhesus monkeys by a synthetic basic copolymer. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Nov;3(2):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum D., Webb C., Meshorer A., Arnon R., Sela M. Suppression by several synthetic polypeptides of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced in guinea pigs and rabbits with bovine and human basic encephalitogen. Eur J Immunol. 1973 May;3(5):273–279. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R., Sela M. In vivo and in vitro immunological cross-reactions between basic encephalitogen and synthetic basic polypeptides capable of suppressing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1973 May;3(5):279–286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C., Teitelbaum D., Herz A., Arnon R., Sela M. Molecular requirements involved in suppression of EAE by synthetic basic copolymers of amino acids. Immunochemistry. 1976 Apr;13(4):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



