Abstract
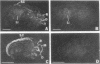
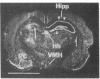
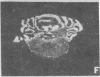
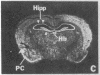
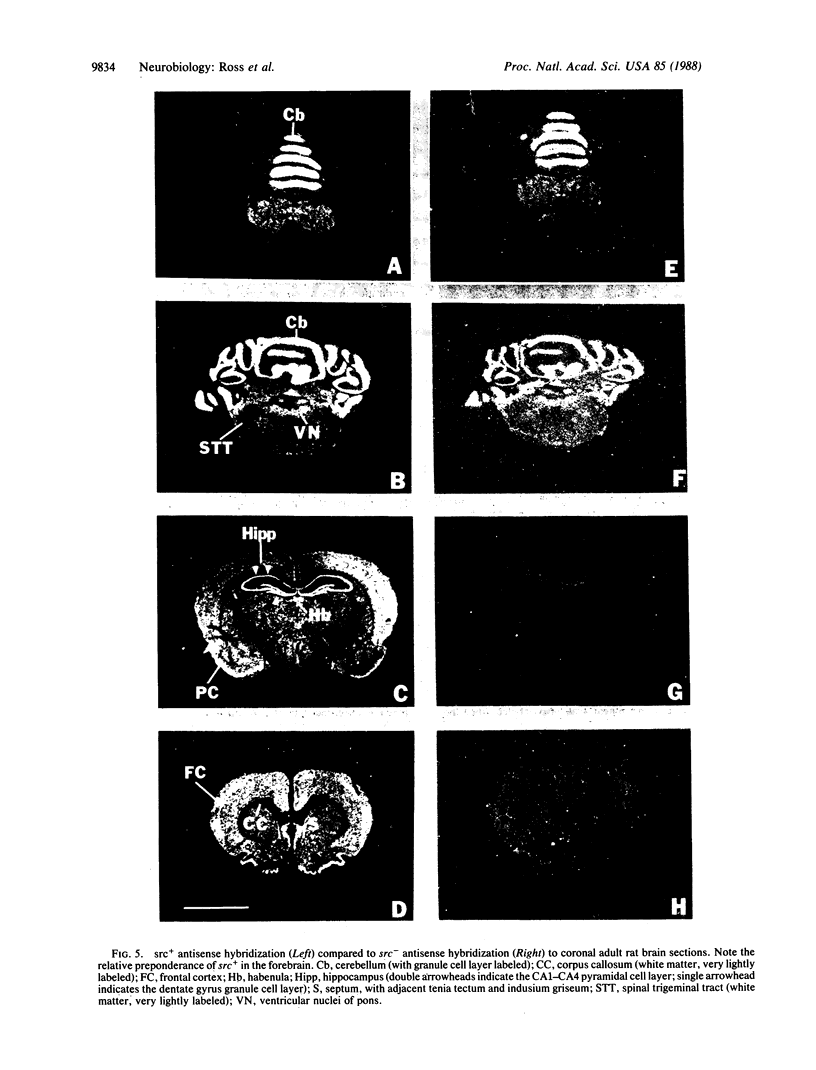
Brain src protooncogene is expressed in two forms, one identical to message in other tissues, and one containing an 18-nucleotide insert specific to brain. We have mapped mRNA for the two forms of src in rat brain with selective antisense oligonucleotide probes to the brain (src+) and peripheral (src-) forms. Fetal rat src mRNA levels were much higher in the central nervous system than any peripheral organ. In adult brain, src+ mRNA level was highest in the internal granular layer of the olfactory bulb, pyramidal cells of the hippocampus, granule cells of the dentate gyrus, and cerebellar granule cells. src+ and src- levels were similar in hindbrain, but src+ levels were higher than those of src- in forebrain. These distributions suggest that src+ may play roles in a number of neural processes, possibly including neuronal plasticity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azarnia R., Reddy S., Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D., Loewenstein W. R. The cellular src gene product regulates junctional cell-to-cell communication. Science. 1988 Jan 22;239(4838):398–401. doi: 10.1126/science.2447651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Simantov R., Cowan W. M., Hunter T., Eckhart W. pp60c-src expression in the developing rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3348–3352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Simantov R., Kaplan P. L., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Alterations in pp60c-src accompany differentiation of neurons from rat embryo striatum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1830–1840. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziadei P. P., Graziadei G. A. Neurogenesis and neuron regeneration in the olfactory system of mammals. I. Morphological aspects of differentiation and structural organization of the olfactory sensory neurons. J Neurocytol. 1979 Feb;8(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01206454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R. Proto-oncogenes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A. A., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Protein tyrosine kinase activity and its endogenous substrates in rat brain: a subcellular and regional survey. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs C., Rübsamen H. Expression of pp60c-src protein kinase in adult and fetal human tissue: high activities in some sarcomas and mammary carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1696–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Jones D. T., Reed R. R., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. G protein mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Bar-Eli M., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Antibodies to two defined regions of the transforming protein pp60src interact specifically with the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5911–5915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau J. M., Wiestler O. D., Walter G. An altered form of pp60c-src is expressed primarily in the central nervous system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4115–4117. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B. T., Sorge L. K., Meymandi A., Maness P. F. pp60c-src Kinase is in chick and human embryonic tissues. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. A., Brugge J. S., Levine J. M. Induction of altered c-src product during neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):873–876. doi: 10.1126/science.3095923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Aubry M., Shores C. G., Frame L., Pfenninger K. H. c-src gene product in developing rat brain is enriched in nerve growth cone membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5001–5005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Erikson R. L. Highly specific antibody to Rous sarcoma virus src gene product recognizes a novel population of pp60v-src and pp60c-src molecules. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):409–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J. P., Sorge L. K., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is expressed in human fetal and adult brain. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):151–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. F. The neurobiology of learning and memory. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):941–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3738519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Lustig A., Greengard P., Brugge J. S. Widespread distribution of the c-src gene product in nerve cells and axon terminals in the adult rat brain. Brain Res. 1988 Jun;427(3):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The action of oncogenes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.2997917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Beyond receptors: multiple second-messenger systems in brain. Ann Neurol. 1987 Mar;21(3):217–229. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Vasopressin and oxytocin mRNAs in adrenalectomized and Brattleboro rats: analysis by quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]