Abstract
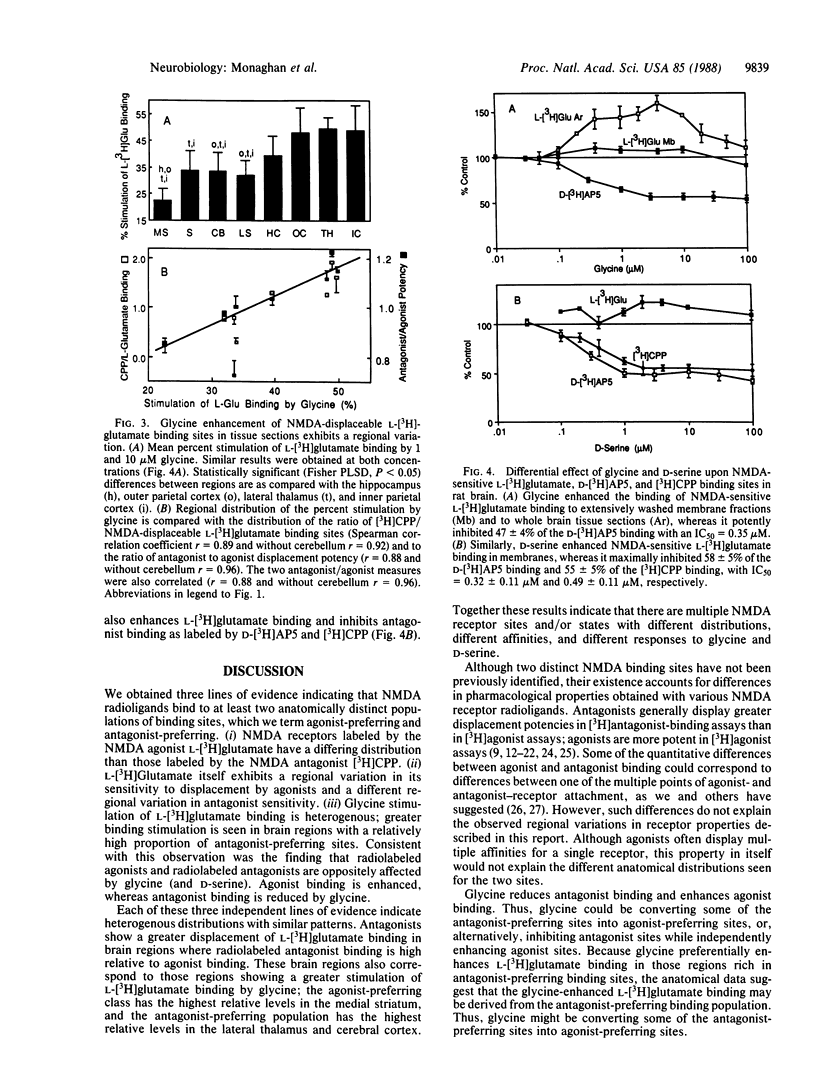
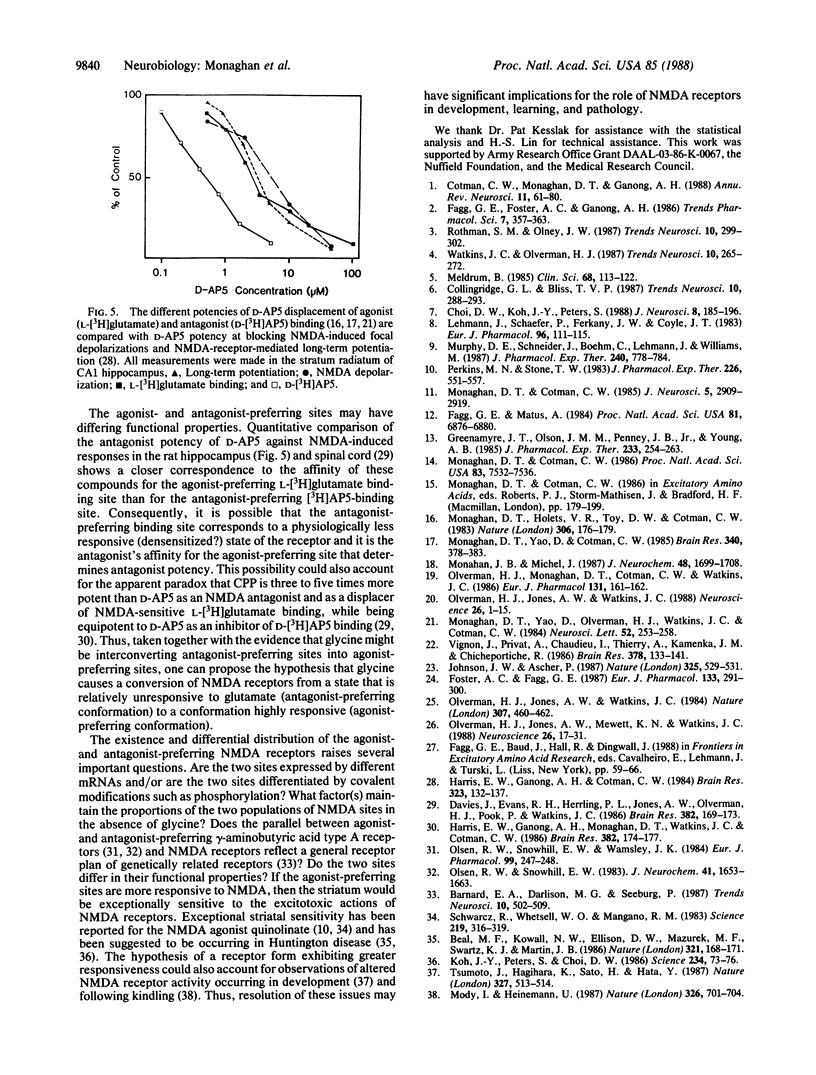
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a subtype of excitatory amino acid receptor, mediates synaptic responses in many regions of the central nervous system. This receptor plays a critical role in the mechanisms of both synaptic plasticity and excitotoxicity. Although these receptors were generally thought to be a single homogeneous receptor population, we report observations indicating that two anatomically distinct forms of the NMDA-receptor complex exist. (i) The distribution of NMDA receptors, as labeled by the NMDA agonist L-[3H]glutamate, differs from that obtained with the radiolabeled antagonist 3H-labeled 3-[(+/-)2-carboxypiperazine-4-yl]propyl-1-phosphonic acid [( 3H]CPP). Relative to L-[3H]glutamate, [3H]CPP binding is low in the striatum and septum and high in the thalamus and inner cerebral cortex. (ii) NMDA antagonists are relatively more potent than agonists at displacing L-[3H]glutamate binding in the thalamus and cerebral cortex; agonists are relatively more potent in the striatum and cerebellum. (iii) Glycine, which potentiates NMDA-receptor responses to glutamate, causes a greater percentage increase in L-[3H]glutamate binding to NMDA receptors in the thalamus and cerebral cortex than in the striatum, septum, and cerebellum. Radiolabeled NMDA-antagonist binding, in contrast, is inhibited by glycine. Thus, as observed for gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors, NMDA receptors have an agonist-preferring binding-site population and an antagonist-preferring binding site population. These may represent two distinct receptors and/or two interconverting forms. It could be of significant clinical importance if these two sites differ in their response to NMDA.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beal M. F., Kowall N. W., Ellison D. W., Mazurek M. F., Swartz K. J., Martin J. B. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington's disease by quinolinic acid. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):168–171. doi: 10.1038/321168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Koh J. Y., Peters S. Pharmacology of glutamate neurotoxicity in cortical cell culture: attenuation by NMDA antagonists. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):185–196. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00185.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Monaghan D. T., Ganong A. H. Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission: NMDA receptors and Hebb-type synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:61–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Herrling P. L., Jones A. W., Olverman H. J., Pook P., Watkins J. C. CPP, a new potent and selective NMDA antagonist. Depression of central neuron responses, affinity for [3H]D-AP5 binding sites on brain membranes and anticonvulsant activity. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Matus A. Selective association of N-methyl aspartate and quisqualate types of L-glutamate receptor with brain postsynaptic densities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6876–6880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Comparison of L-[3H]glutamate, D-[3H]aspartate, DL-[3H]AP5 and [3H]NMDA as ligands for NMDA receptors in crude postsynaptic densities from rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 20;133(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Olson J. M., Penney J. B., Jr, Young A. B. Autoradiographic characterization of N-methyl-D-aspartate-, quisqualate- and kainate-sensitive glutamate binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):254–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Ganong A. H., Cotman C. W. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus involves activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 3;323(1):132–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Ganong A. H., Monaghan D. T., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Action of 3-((+/-)-2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)-propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP): a new and highly potent antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Peters S., Choi D. W. Neurons containing NADPH-diaphorase are selectively resistant to quinolinate toxicity. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):73–76. doi: 10.1126/science.2875522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Schaefer P., Ferkany J. W., Coyle J. T. Quinolinic acid evokes [3H]acetylcholine release in striatal slices: mediation by NMDA-type excitatory amino acid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. Possible therapeutic applications of antagonists of excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Feb;68(2):113–122. doi: 10.1042/cs0680113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Heinemann U. NMDA receptors of dentate gyrus granule cells participate in synaptic transmission following kindling. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):701–704. doi: 10.1038/326701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
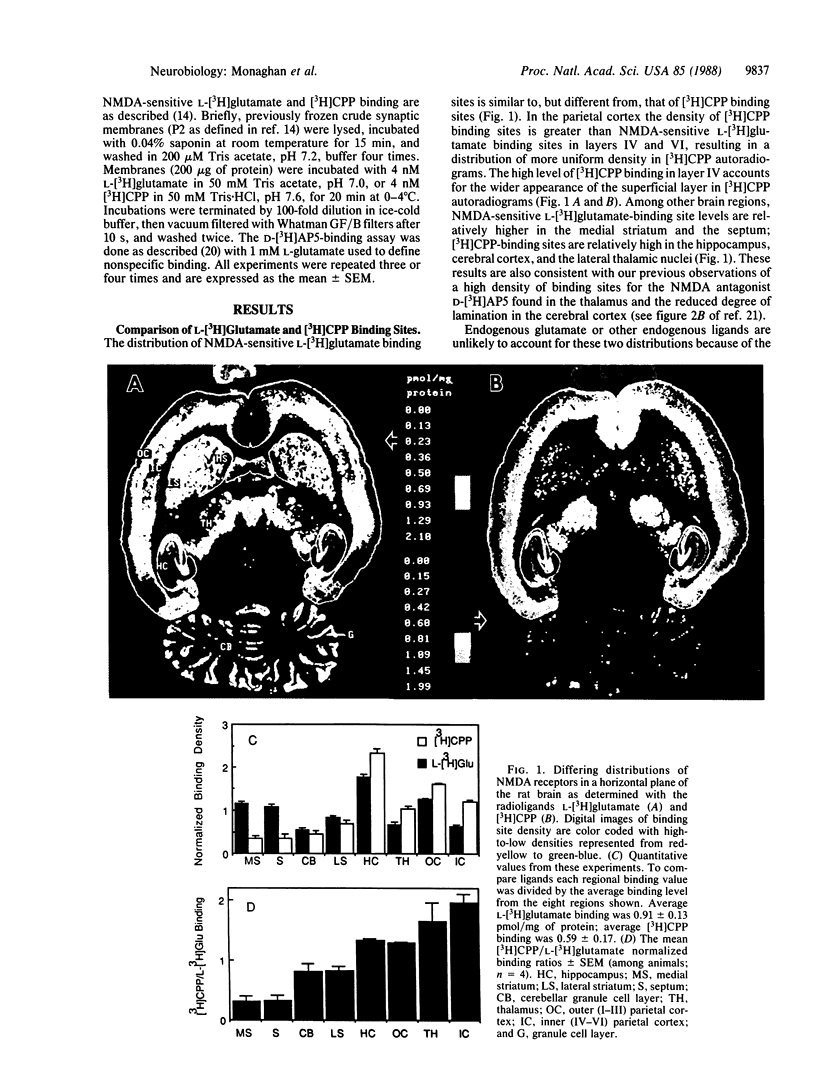
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Distribution of N-methyl-D-aspartate-sensitive L-[3H]glutamate-binding sites in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1985 Nov;5(11):2909–2919. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02909.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Identification and properties of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7532–7536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Holets V. R., Toy D. W., Cotman C. W. Anatomical distributions of four pharmacologically distinct 3H-L-glutamate binding sites. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):176–179. doi: 10.1038/306176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Cotman C. W. L-[3H]Glutamate binds to kainate-, NMDA- and AMPA-sensitive binding sites: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 12;340(2):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90936-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Olverman H. J., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Autoradiography of D-2-[3H]amino-5-phosphonopentanoate binding sites in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Dec 21;52(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. B., Michel J. Identification and characterization of an N-methyl-D-aspartate-specific L-[3H]glutamate recognition site in synaptic plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1987 Jun;48(6):1699–1708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
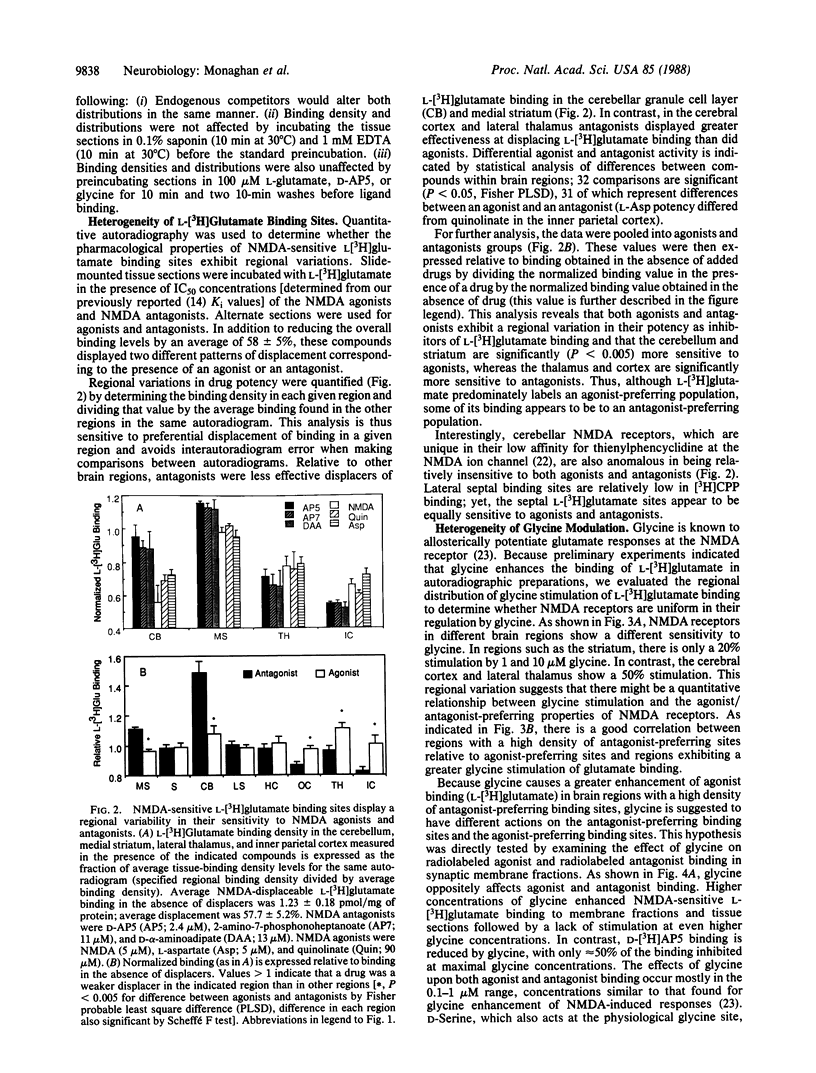
- Murphy D. E., Schneider J., Boehm C., Lehmann J., Williams M. Binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid to rat brain membranes: a selective, high-affinity ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):778–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Snowhill E. W., Wamsley J. K. Autoradiographic localization of low affinity GABA receptors with [3H]bicuculline methochloride. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 23;99(2-3):247–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Snowman A. M. [3H]bicuculline methochloride binding to low-affinity gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor sites. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1653–1663. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Mewett K. N., Watkins J. C. Structure/activity relations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands as studied by their inhibition of [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid binding in rat brain membranes. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate as a ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Watkins J. C. [3H]CPP, a new competitive ligand for NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 12;131(1):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. Pharmacology and regional variations of quinolinic acid-evoked excitations in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarcz R., Whetsell W. O., Jr, Mangano R. M. Quinolinic acid: an endogenous metabolite that produces axon-sparing lesions in rat brain. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):316–318. doi: 10.1126/science.6849138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumoto T., Hagihara K., Sato H., Hata Y. NMDA receptors in the visual cortex of young kittens are more effective than those of adult cats. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):513–514. doi: 10.1038/327513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignon J., Privat A., Chaudieu I., Thierry A., Kamenka J. M., Chicheportiche R. [3H]thienyl-phencyclidine ([3H]TCP) binds to two different sites in rat brain. Localization by autoradiographic and biochemical techniques. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]