Abstract
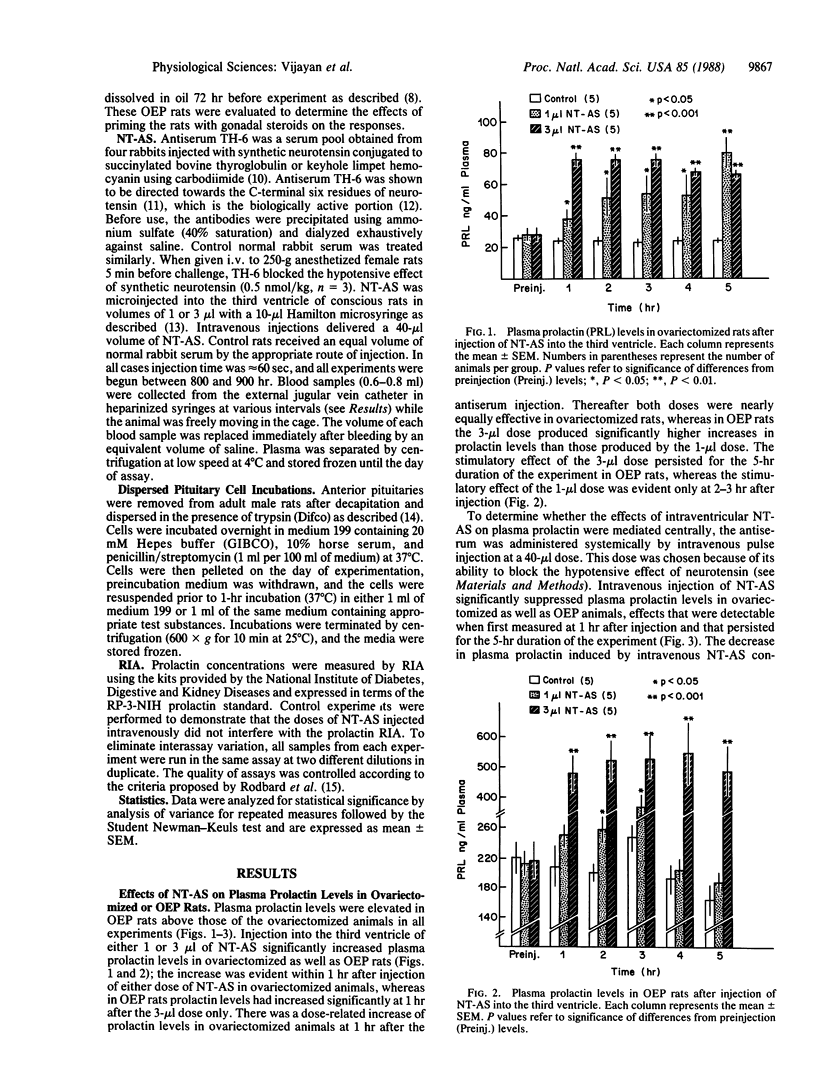
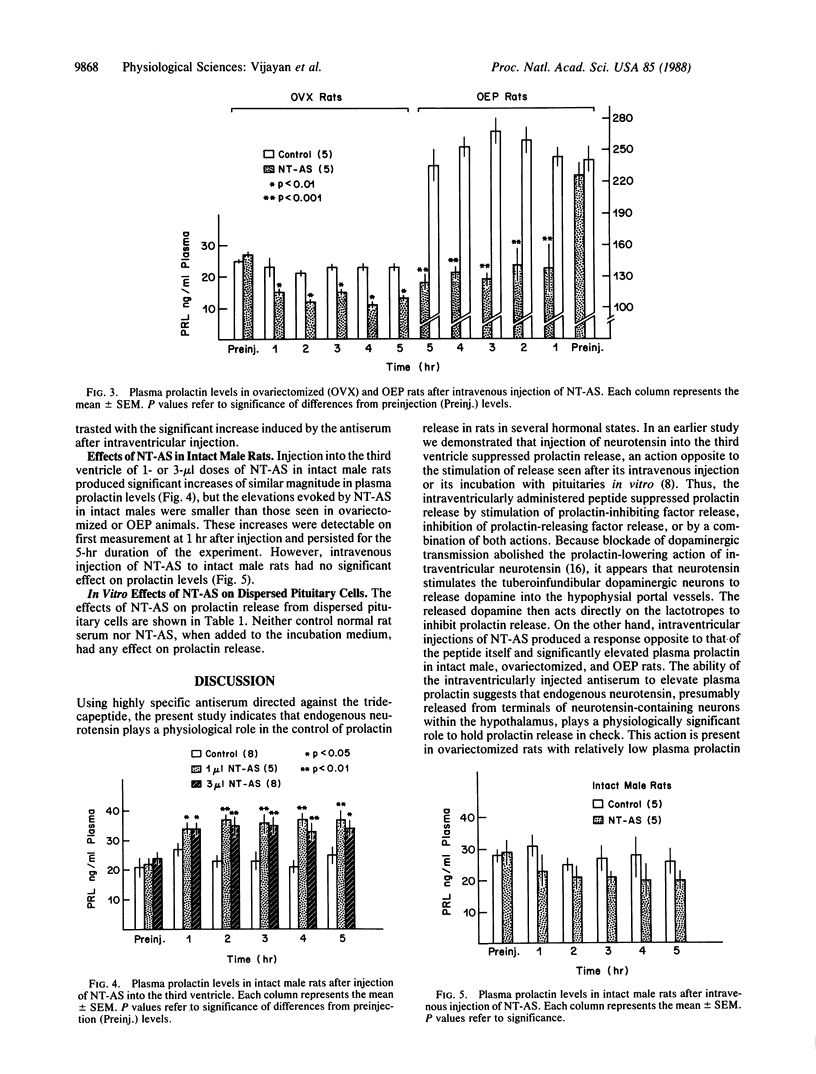
Previous studies have indicated that the brain peptide neurotensin can stimulate prolactin release by direct action on the pituitary gland, whereas its action within the hypothalamus is inhibitory. The inhibitory action is mediated by the release of dopamine into the hypophyseal portal veins, which deliver the neurotransmitter to the anterior pituitary gland to inhibit prolactin release. Our experiments were done to evaluate the physiologic significance of these neurotensin actions by injecting the globulin fraction of highly specific neurotensin antiserum either intravenously or intraventricularly. Injection into the third ventricle of either 1 or 3 microliter of neurotensin antiserum significantly increased plasma prolactin concentrations in (i) ovariectomized and (ii) ovariectomized estrogen- and progesterone-primed rats within 1 hr of injection. The response was more pronounced in the ovariectomized than in the ovariectomized estrogen- and progesterone-treated animals and was dose related. Intraventricular injection of these doses of neurotensin antiserum also evoked elevations in plasma prolactin in intact males, which were significant but smaller in magnitude than those seen in female rats. To evaluate the effect of the antiserum on the pituitary directly, the antiserum was injected intravenously at a dose of 40 microliter, which was sufficient to block the blood pressure-lowering effect of neurotensin. After the intravenous injection of antiserum, a highly significant suppression of plasma prolactin occurred, detectable when first measured at 1 hr after injection in both ovariectomized and ovariectomized estrogen- and progesterone-treated animals; however, the intravenous injection of antiserum had no significant effect on the prolactin release in males. These data indicate the physiological significance of the hypothalamic inhibitory actions of neurotensin on prolactin release, which are probably mediated by its stimulation of dopamine release that in turn, inhibits prolactin secretion by the lactotropes. The direct stimulatory effect of the peptide on prolactin release after its presumed release into portal vessels also appears to be physiologically significant in female but not in male rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carraway R., Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E. Neurotensin in plasma: immunochemical and chromatographic character of acid/acetone-soluble material. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):400–406. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Radioimmunoassay for neurotensin, a hypothalamic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7035–7044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennes L., Stumpf W. E., Kalivas P. W. Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Sep 20;210(3):211–224. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur F. B., St-Pierre S., Aubé C., Rivest R., Gagné M. A. Relationships between structure and duration of neurotensin's central action: emergence of long acting analogs. Neuropeptides. 1984 Nov;4(6):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Van Rietschoten J., Granier C., Morgat J. L., Menez A., Leeman S., Freychet P. Neurotensin: specific binding to synaptic membranes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. I., Mayfield M. A., McCann S. M., Krulich L. On the prolactin-inhibiting effect of neurotensin. The role of dopamine. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Oct;35(4):277–281. doi: 10.1159/000123394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin M. D., Samson W. K., McCann S. M. Hypothalamic and pituitary sites of action of oxytocin to alter prolactin secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1711–1717. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Frohman L. A. Neurotensin release by rat hypothalamic fragments in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 6;210(1-2):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90899-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak D. W., Carraway R. E., Ferris C. F. Characterization of immunoreactive substance P and neurotensin in the goldfish retina. Exp Eye Res. 1987 Jun;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(87)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Rayford P. L., Cooper J. A., Ross G. T. Statistical quality control of radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Oct;28(10):1412–1418. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-10-1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G., Hymer W. C. A short method for the isolation of somatotrophs from the rat pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):792–796. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan E., McCann S. M. In vivo and in vitro effects of substance P and neurotensin on gonadotropin and prolactin release. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):64–68. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan E., McCann S. M. Re-evaluation of the role of catecholamines in control of gonadotropin and prolactin release. Neuroendocrinology. 1978;25(3):150–165. doi: 10.1159/000122737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Neurotensin receptor localization by light microscopic autoradiography in rat brain. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


