Abstract
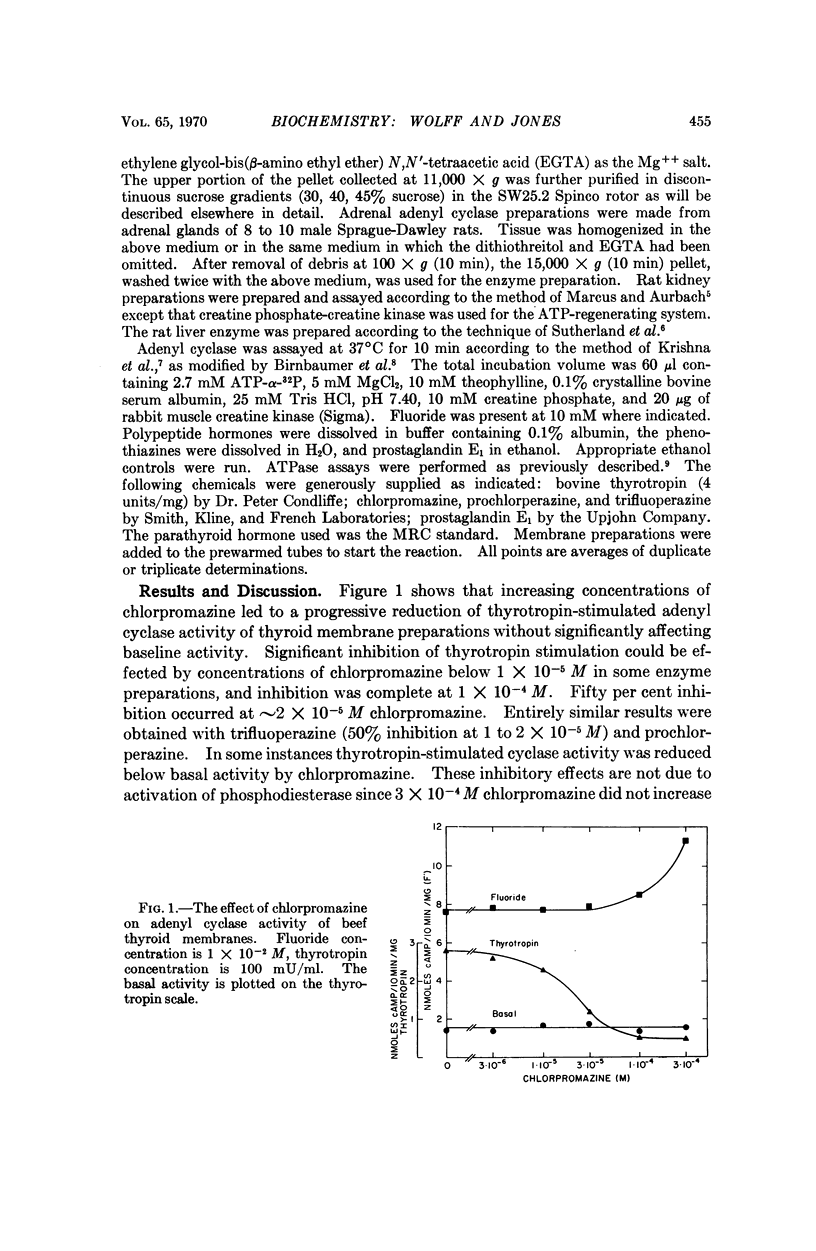
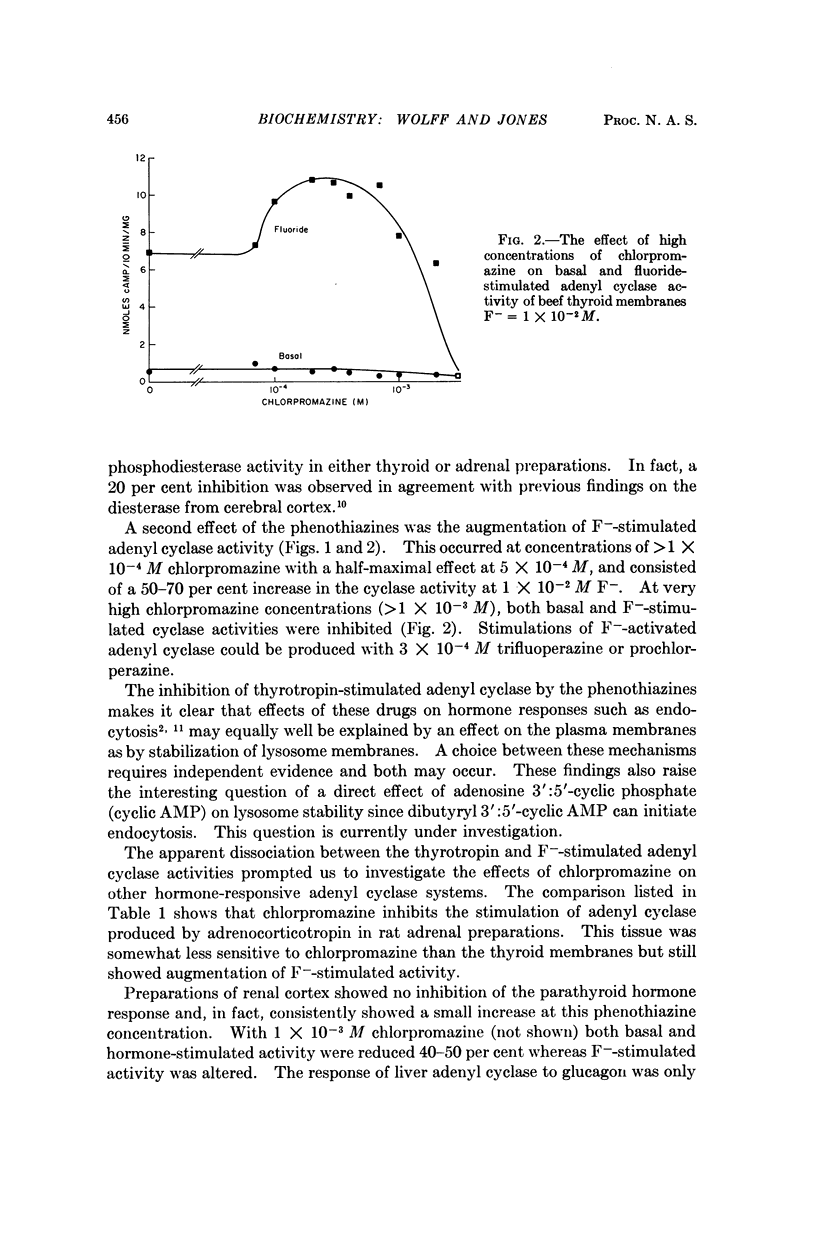
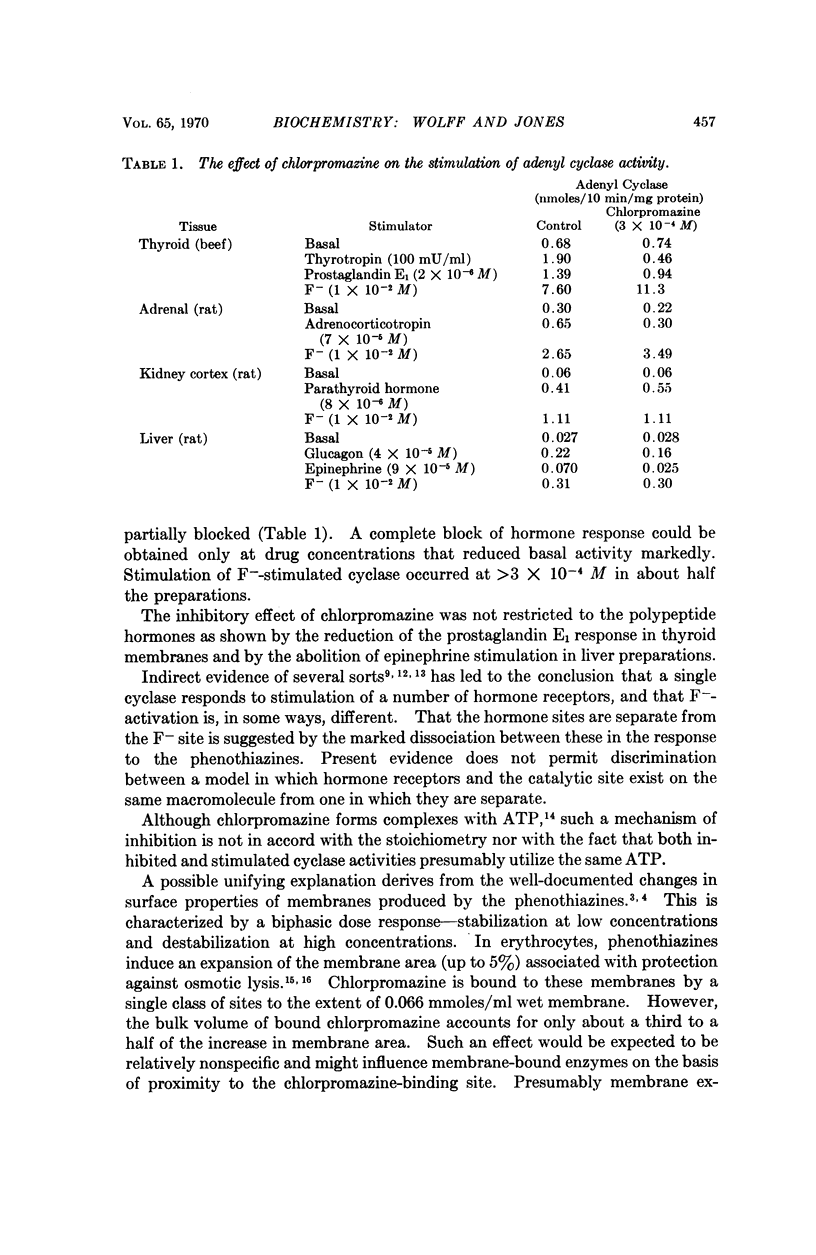
Chlorpromazine (3 × 10-4 M) prevents the stimulation of adenyl cyclase activity in thyroid membranes produced by thyrotropin and prostaglandin, ACTH stimulation of adenyl cyclase in adrenal tissue, and glucagon- and epinephrine-stimulation of adenyl cyclase activity in liver. Baseline activity is unaffected. Parathyroid hormone stimulation of kidney preparations was not inhibited under these conditions. At chlorpromazine concentrations >3 × 10-4 M F--stimulated cyclase activity of thyroid and adrenal tissue was increased. Other phenothiazines, trifluoperazine, and prochlorperazine, have similar effects on thyrotropin and F--stimulated cyclase activity of thyroid. Na+- K+-dependent ATPase of thyroid is also inhibited by chlorpromazine. Since thymol causes a similar dissociation of hormone- and F--stimulated adenyl cyclase, it is concluded that the surface properties of these agents best account for their effects on adenyl cyclase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Rodbell M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. 1. Properties and the effects of adrenocorticotropin and fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3468–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. II. Hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3477–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär H. P., Hechter O. Adenyl cyclase and hormone action. I. Effects of adrenocorticotropic hormone, glucagon, and epinephrine on the plasma membrane of rat fat cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):350–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. W., Brody T. M. Inhibition of Na+K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity in rat brain by substituted phenothiazines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Jun;15(6):703–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTH P. S., SPIRTES M. A. THE PHENOTHIAZINETRANQUILIZERS: BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL ACTIONS. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1964;7:231–278. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda F., Imamura H. Inhibition of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase by phenothiazine and reserpine derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwant W. O., Seeman P. The membrane concentration of a local anesthetic (chlorpromazine). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):530–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Bioassay of parathyroid hormone in vitro with a stable preparation of adenyl cyclase from rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1969 Nov;85(5):801–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-5-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onaya T., Solomon D. H., Davidson W. D. Effect of chlorpromazine on thyrotropin-stimulated endocytosis and glucose oxidation in canine thyroid slices. Endocrinology. 1969 Jul;85(1):150–154. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-1-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Wollman S. H. Colloid droplet formation in dog thyroid in vitro. Induction by dibutyrl cyclic-AMP. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):262–266. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., RALL T. W., MENON T. Adenyl cylase. I. Distribution, preparation, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. M. Membrane stabilization by drugs: tranquilizers, steroids, and anesthetics. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1966;9:145–221. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Kwant W. O., Sauks T., Argent W. Membrane expansion of intact erythrocytes by anesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):490–498. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J., HALMI N. S. Thyroidal iodide transport. V. The role of Na-K-activated, ouabain-sensitive adenosinetriphosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:847–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



