Abstract
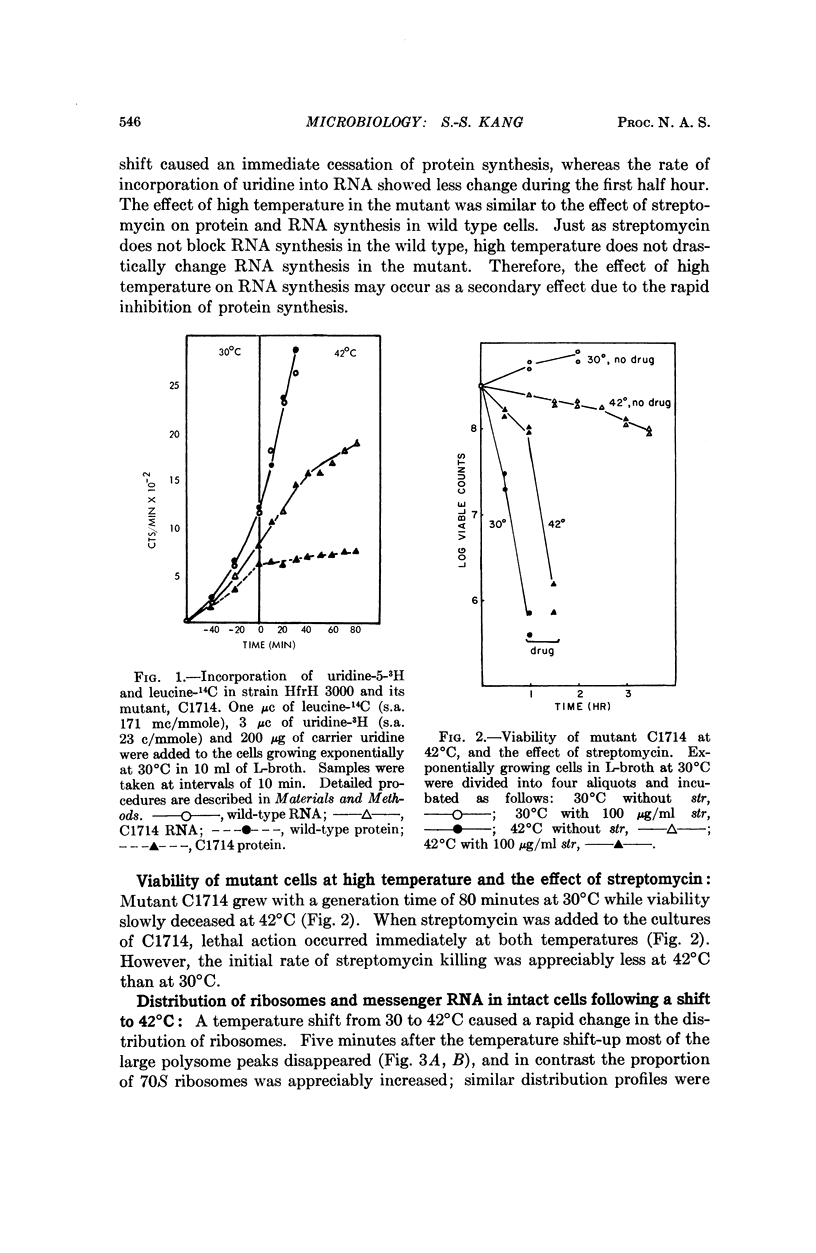
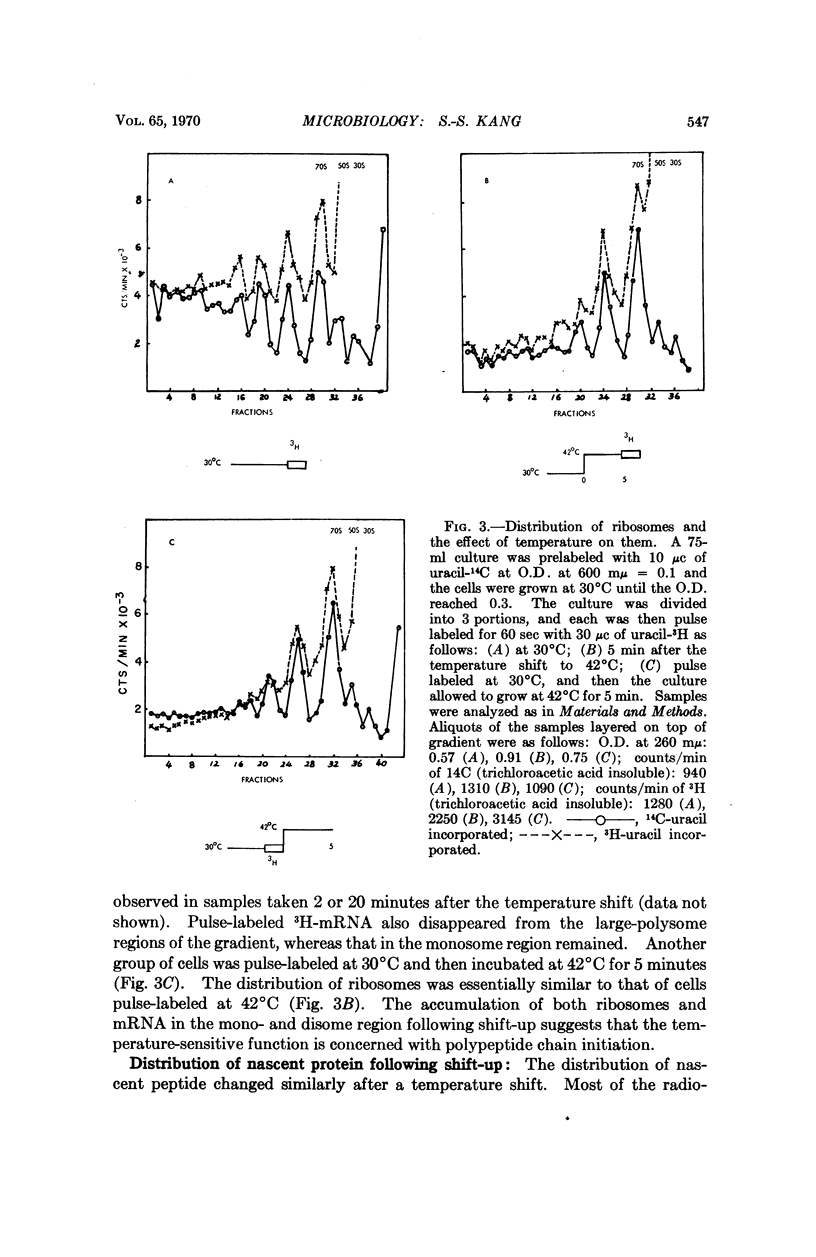
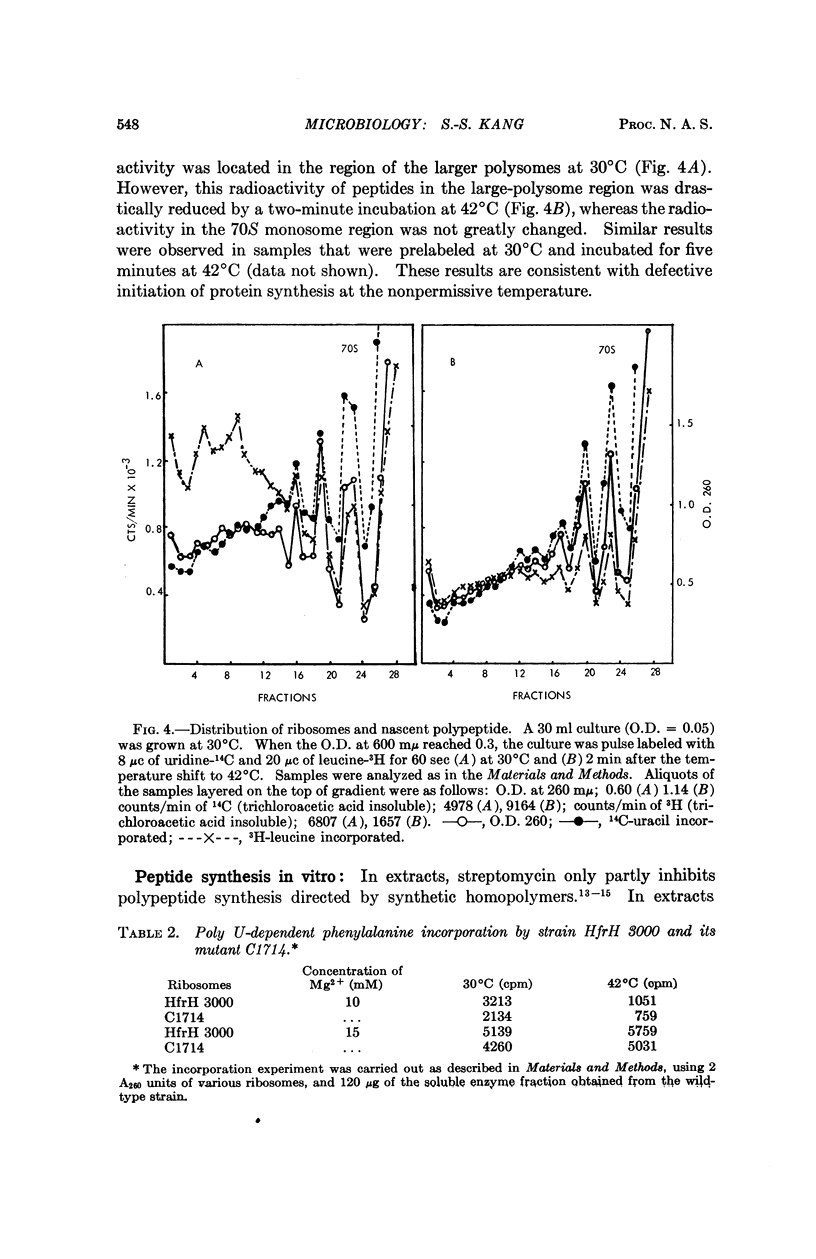
The temperature-sensitive mutation in our Escherichia coli strain C1714 appears to be in a ribosomal protein. The mutation maps at the streptomycin locus. Protein synthesis in intact cells stops immediately when the temperature is shifted from 30 to 42°C. Analysis of polyribosome distributions after shift-up suggests that initiation of protein synthesis is defective at the high temperature. In vitro protein synthesis in extracts from C1714 is temperature sensitive when directed by natural mRNA, but not when directed by poly U.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capecchi M. R. Cell-free protein synthesis programmed with R17 RNA: identification of two phage proteins. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coolsma J., Haselkorn R. In vitro synthesis of T4 proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 7;34(3):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90824-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J. E. STUDIES ON THE RIBOSOMES OF STREPTOMYCIN-SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:659–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WHITE J. R. Inhibition of polypeptide synthesis by streptomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:385–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flessel C. P., Ralph P., Rich A. Polyribosomes of growing bacteria. Science. 1967 Nov 3;158(3801):658–660. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3801.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Mechanism of action of streptomycin in E. coli: interruption of the ribosome cycle at the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):873–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Davis B. D. Rapid inhibition of polypeptide chain extension by streptomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C., CARLTON B. C., GUEST J. R., HELINSKI D. R., HENNING U. ON THE COLINEARITY OF GENE STRUCTURE AND PROTEIN STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:266–272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



