Abstract
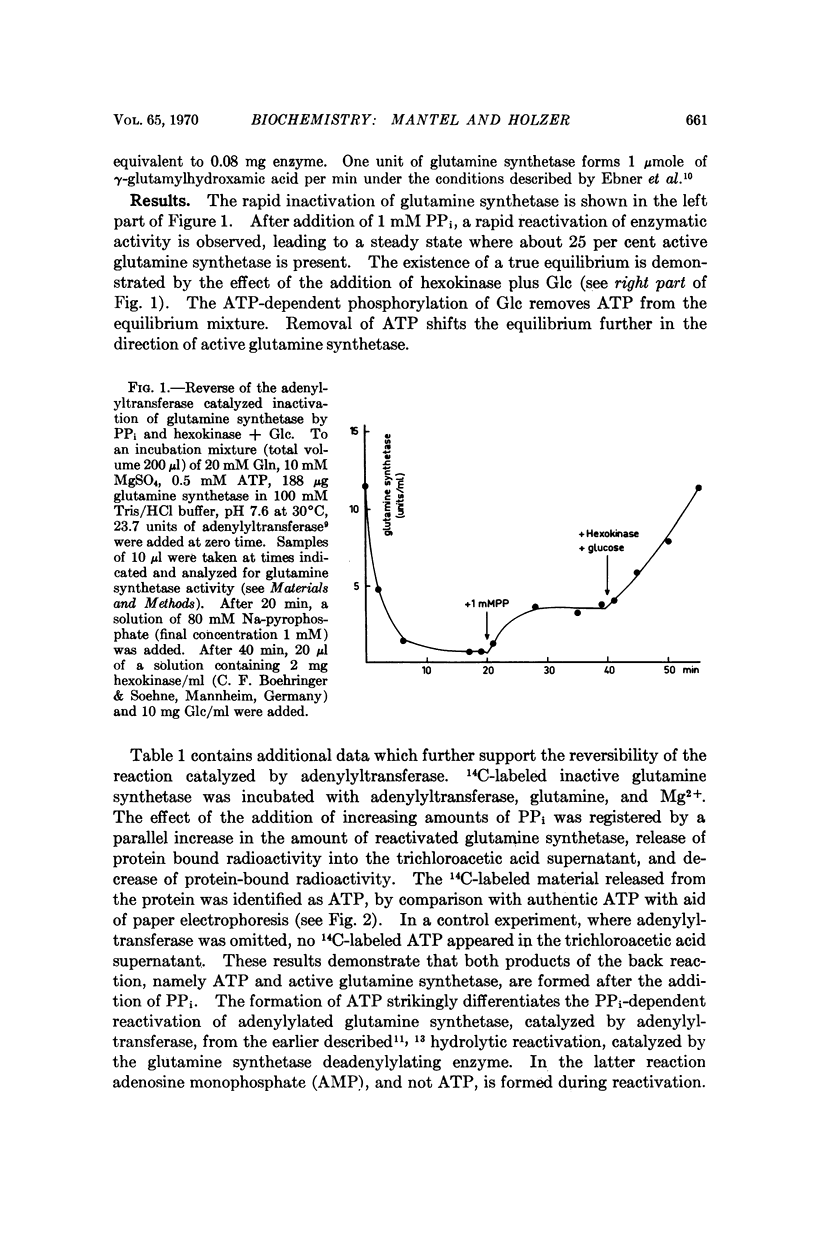
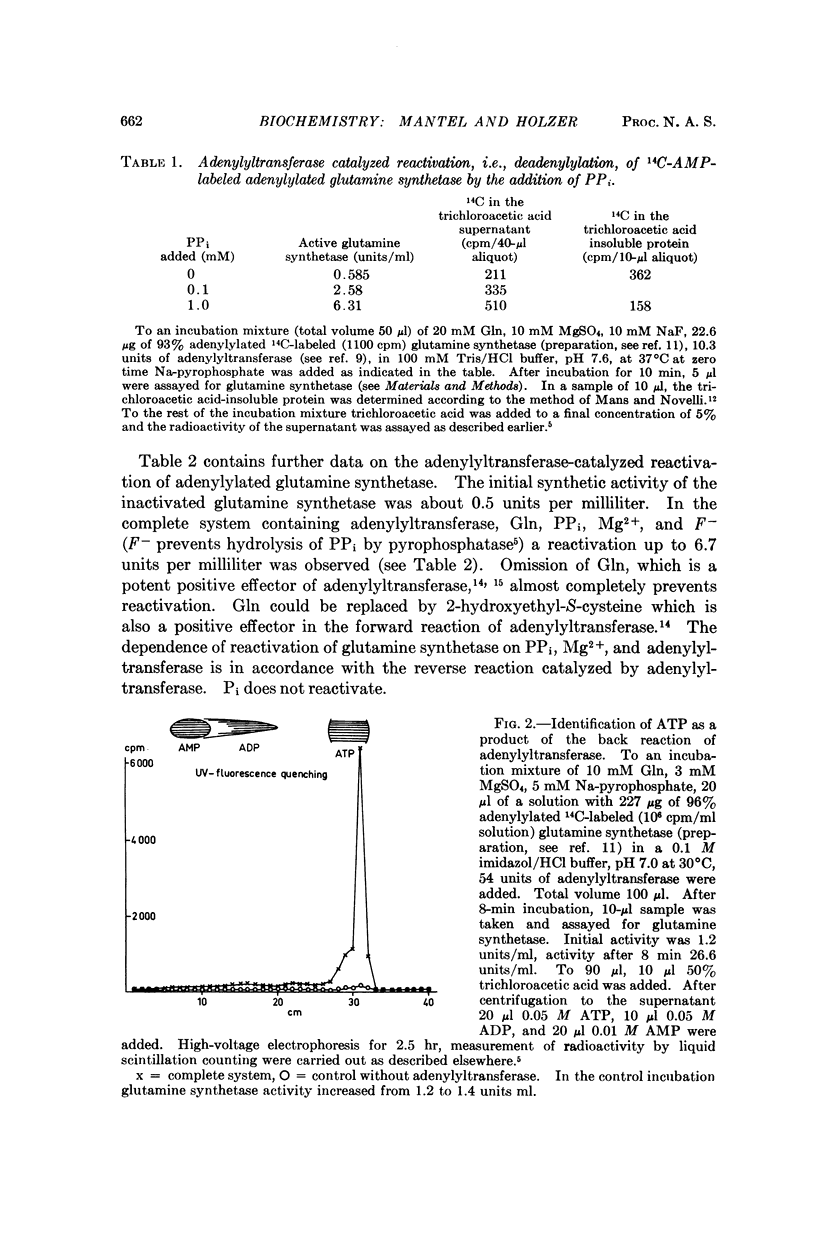
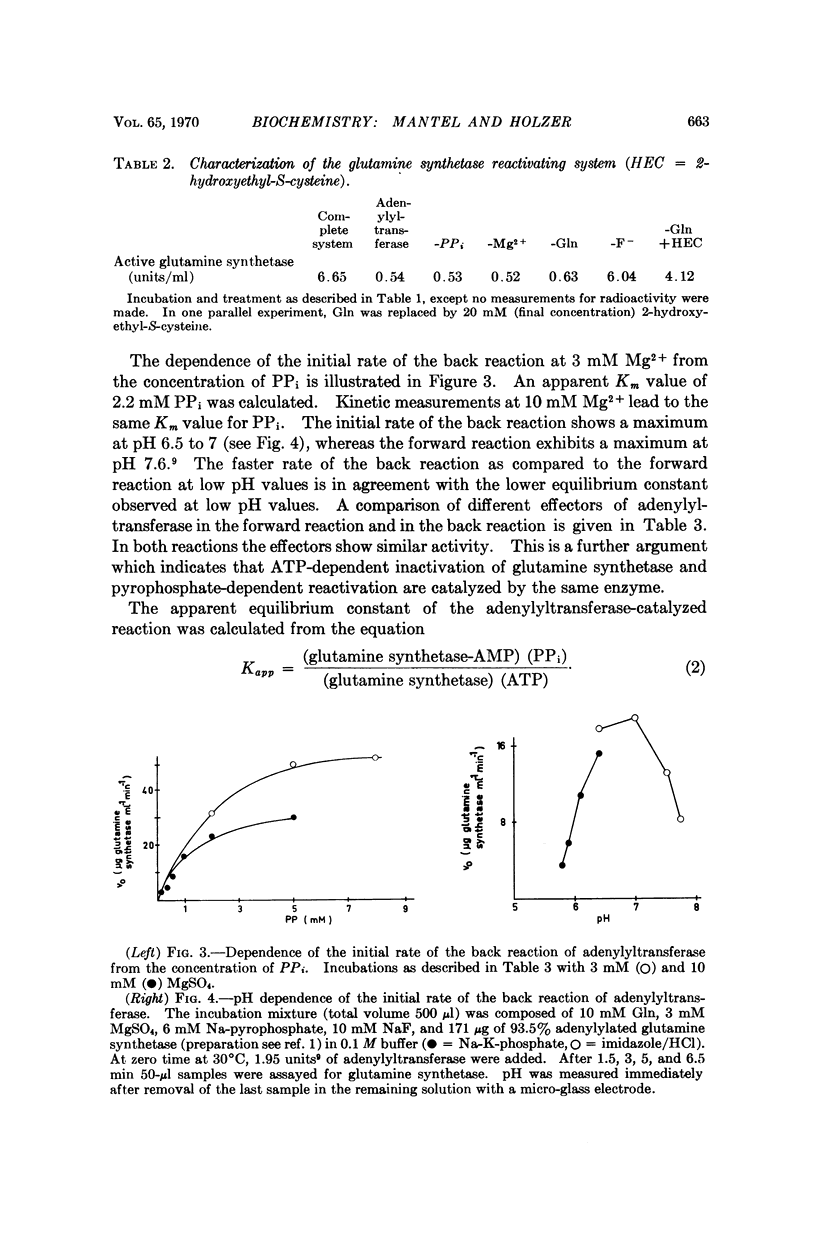
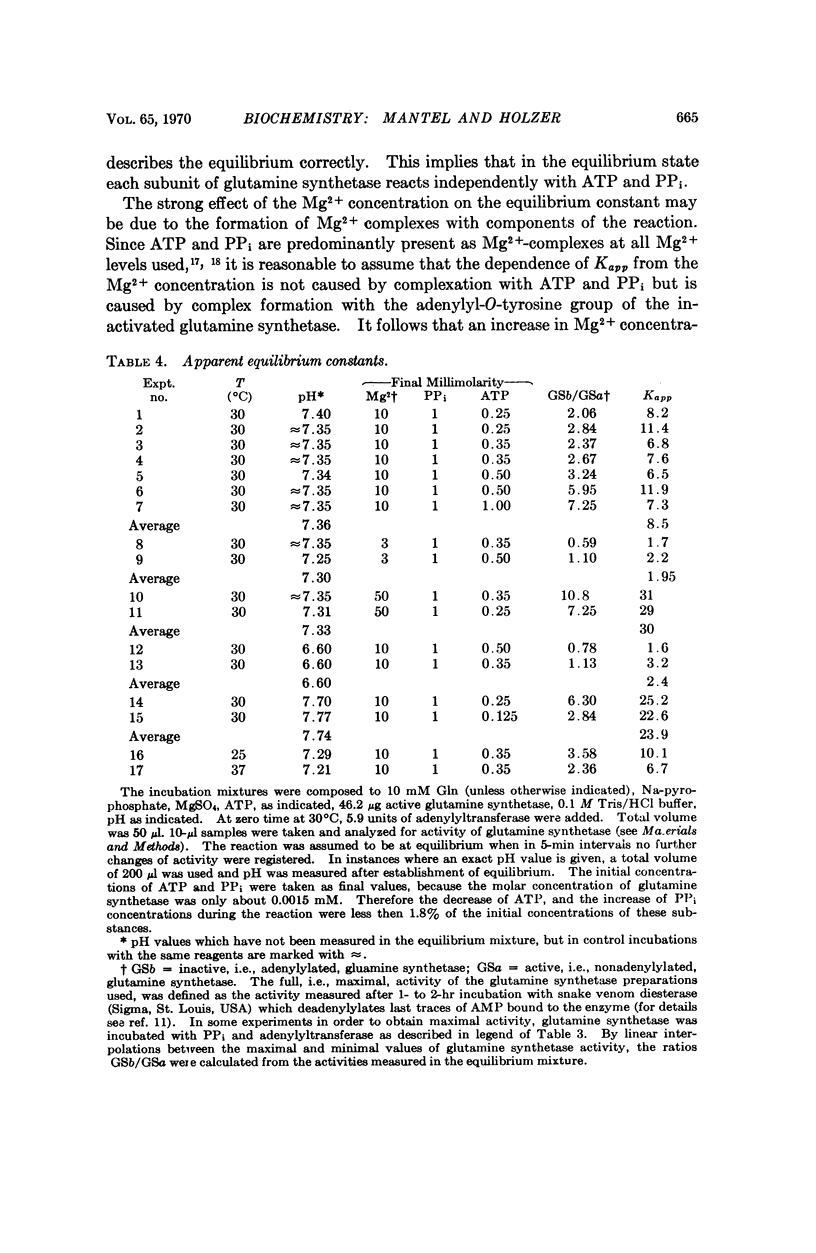
The reversibility of adenylylation of glutamine synthetase from E. coli by adenylyltransferase was demonstrated. Several positive effectors (Gln, 2-hydroxyethyl-S-cysteine, Trp and Met) stimulate the back reaction in the same manner as the forward reaction. The apparent Michaelis constant for PPi is 2.2 mM at pH 7.35. The pH optimum of the back reaction is 6.5-7 while the pH optimum of the forward reaction is 7.6. The apparent equilibrium constant in the presence of 10 mM Mg2+ at pH 7.36 is 8.5 in favor of adenylylated glutamine synthetase and PPi. The equilibrium constant is strongly dependent from pH and from Mg2+ concentration. There is a difference of about 0.5 to 1 kcal/mole free energy between the adenylyl-O-tyrosine bond and the pyrophosphate bond of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It follows from these considerations that the adenylyl-O-tyrosine bond is an „energy-rich phosphate bond.”
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberty R. A. Standard Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, and entropy changes as a function of pH and pMg for several reactions involving adenosine phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3290–3302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmeyer L., Jr, Battig F., Holzer H. Characterization of a glutamine synthetase b activating (deadenylylating) enzyme system in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):259–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H. Regulation of enzymes by enzyme-catalyzed chemical modification. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:297–326. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunan K. D., Mitchell H. K. The metabolism of tyrosine-O-phosphate in Drosophila. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jul;132(2):450–456. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecke D., Wulff K., Liess K., Holzer H. Characterization of a glutamine synthetase inactivating enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):452–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUEGRAF A., RATNER S., WARNER R. C. Free energy changes of the argininosuccinate synthetase reaction and of the hydrolysis of the inner pyrophosphate bond of adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3597–3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. 5'-adenylyl-O-tyrosine. The novel phosphodiester residue of adenylylated glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3769–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Shapiro B. M., Ginsburg A., Kingdon H. S., Denton M. D. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):378–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Thompson A., Richardson C. C. Ezymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VII. Properties of the enzyme-adenylate intermediate in the polynucleotide ligase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4556–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Shapiro B., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff K., Mecke D., Holzer H. Mechanism of the enzymatic inactivation of glutamine synthetase from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):740–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



