Abstract
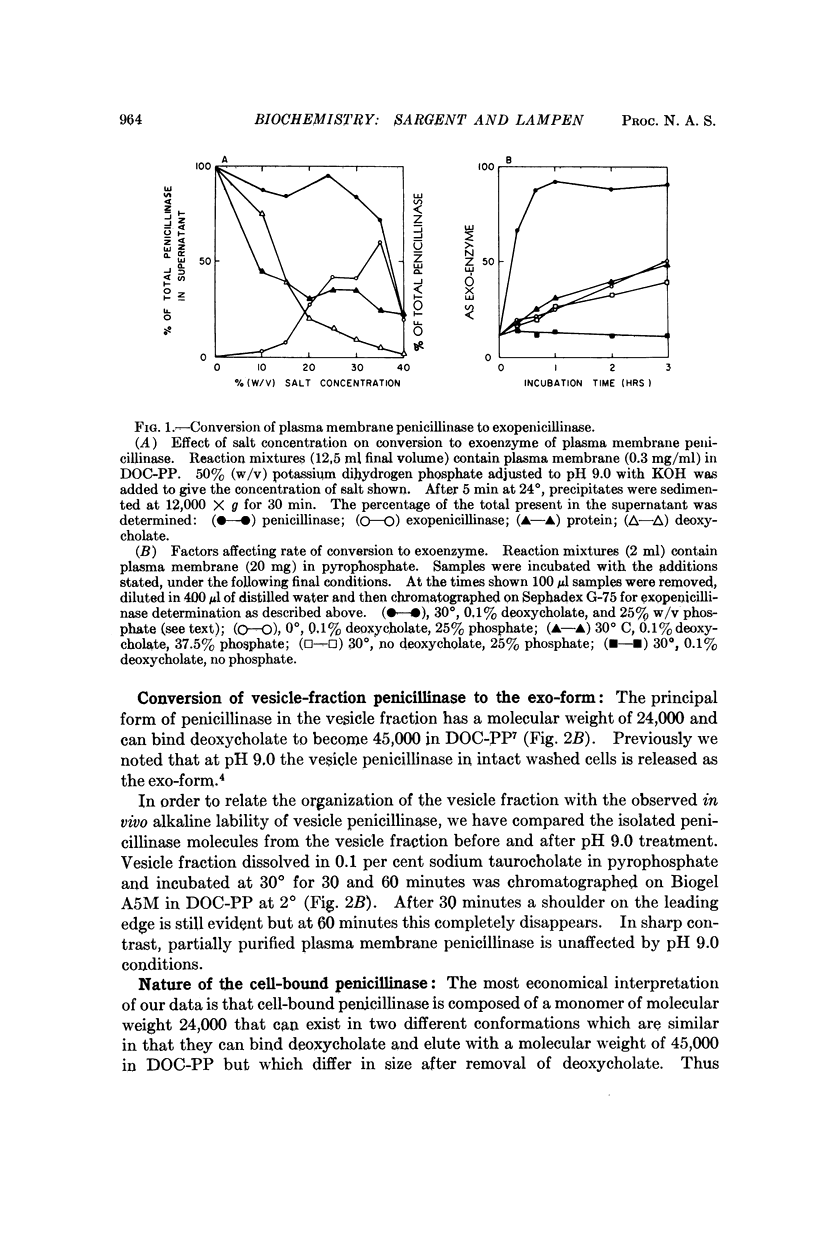
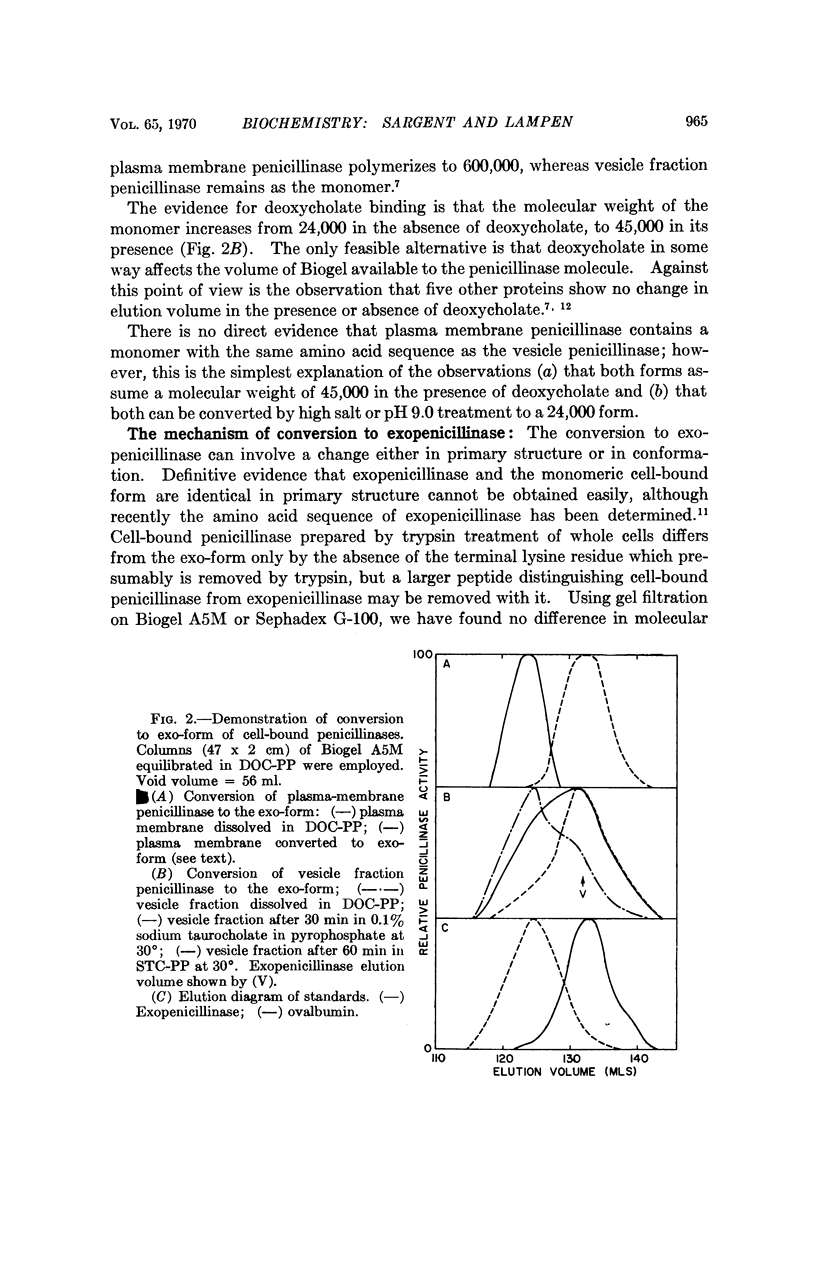
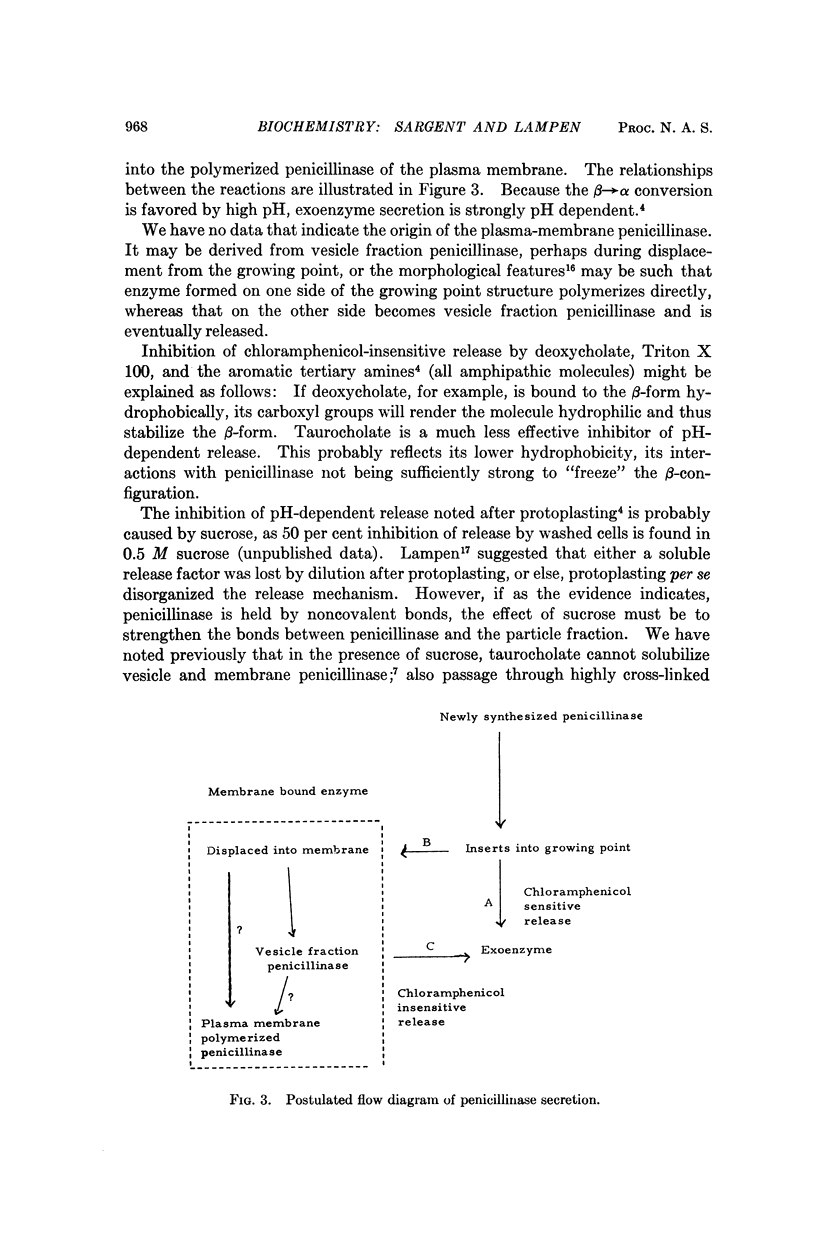
Cell-bound isozymes of penicillinase are distinguished from extracellular enzyme by their capacity to bind deoxycholate and to elute with an apparent molecular weight of 45,000 on gel filtration in its presence. By methods that are unlikely to involve changes in primary structure, the cell-bound forms (both from the plasma membrane and from the periplasmic vesicles) can be converted to forms that are very similar if not identical to the exo-form (i.e., eluting with a molecular weight of 24,000 in the presence and absence of deoxycholate). In the case of plasma membrane penicillinase, addition of 25 per cent potassium phosphate at pH 9.0 leads to a 65 per cent conversion in 20 minutes at 30°. Vesicle fraction penicillinase can be converted by pH 9.0 treatment alone. We suggest that the conversion involves a change from a hydrophobic to a hydrophilic conformational type, and that this is the crucial step for enzyme secretion in microorganisms. A model is presented to account for existing data in which we postulate that monomers of the newly synthesized penicillinase in an extended hydrophobic conformation are inserted into the membrane at special growing points where they may change to a hydrophilic exoform, or polymerize to the major plasma membrane type of penicillinase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Meadway R. J. Chemical structure of bacterial penicillinases. Nature. 1969 Apr 5;222(5188):24–26. doi: 10.1038/222024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITRI N., GARBER N., SELA M. The effect of urea and guanidine hydrochloride on activity and optical rotation of penicillinase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3454–3459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITRI N. Two antigenically different states of active penicillinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casas I. A., Zimmerman L. N. Dependence of protease secretion by Streptococcus faecalis var. liquefaciens on arginine and its possible relation to site of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):307–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.307-312.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. Exopenicillinase synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):659–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.659-661.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Sargent M. G., Lampen J. O. Morphological phenomena associated with penicillinase induction and secretion in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1314–1328. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1314-1328.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., POLLOCK M. R. The location of cell-bound penicillinase in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:255–265. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratohvil J. P., DelliColli H. T. Micellar properties of bile salts. Sodium taurodeoxycholate and sodium glycodeoxycholate. Can J Biochem. 1968 Aug;46(8):945–952. doi: 10.1139/o68-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Cell-bound penicillinase of Bacillus licheniformis; properties and purification. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Release of penicillinase by Bacillus licheniformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. K., Elliott W. H. Characteristics of extracellular protease formation by Bacillus subtilis and its control by amino acid repression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. G., Barrowman J., Borgström B. The effect of sodium taurodesoxycholate and pH on the gel filtration behavior of rat pancreatic protein and lipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 4;175(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. The mechanism of liberation of penicillinase from Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:267–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M. Studies on the transfer of incomplete polypeptide chains across rat liver microsomal membranes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):761–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Ghosh B. K., Lampen J. O. Characteristics of penicillinase secretion by growing cells and protoplasts of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.820-826.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Lampen J. O. Organization of the membrane-bound penicillinases of Bacillus licheniformis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Rapid fixed-time assay for penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1493–1494. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1493-1494.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Penkett S. A., Chapman D. Studies on simple and mixed bile salt micelles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):178–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



