Abstract
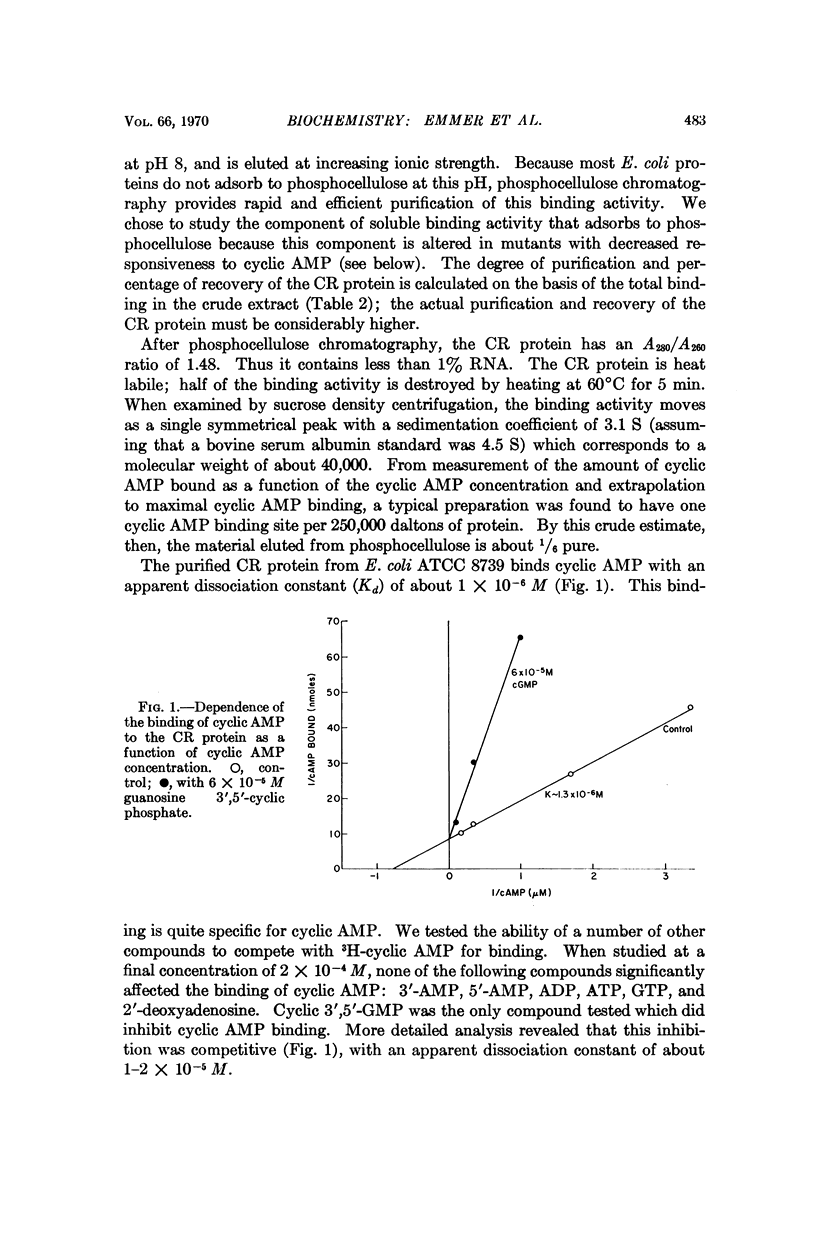
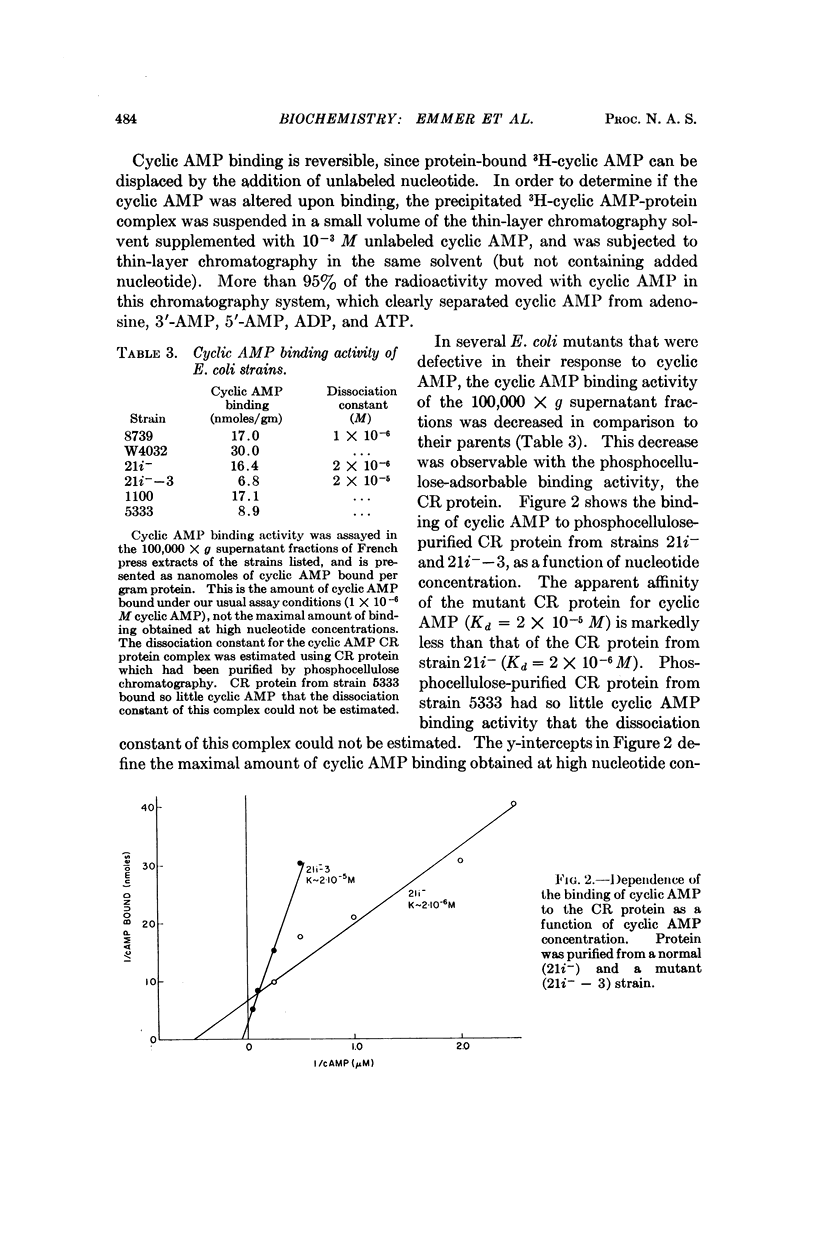
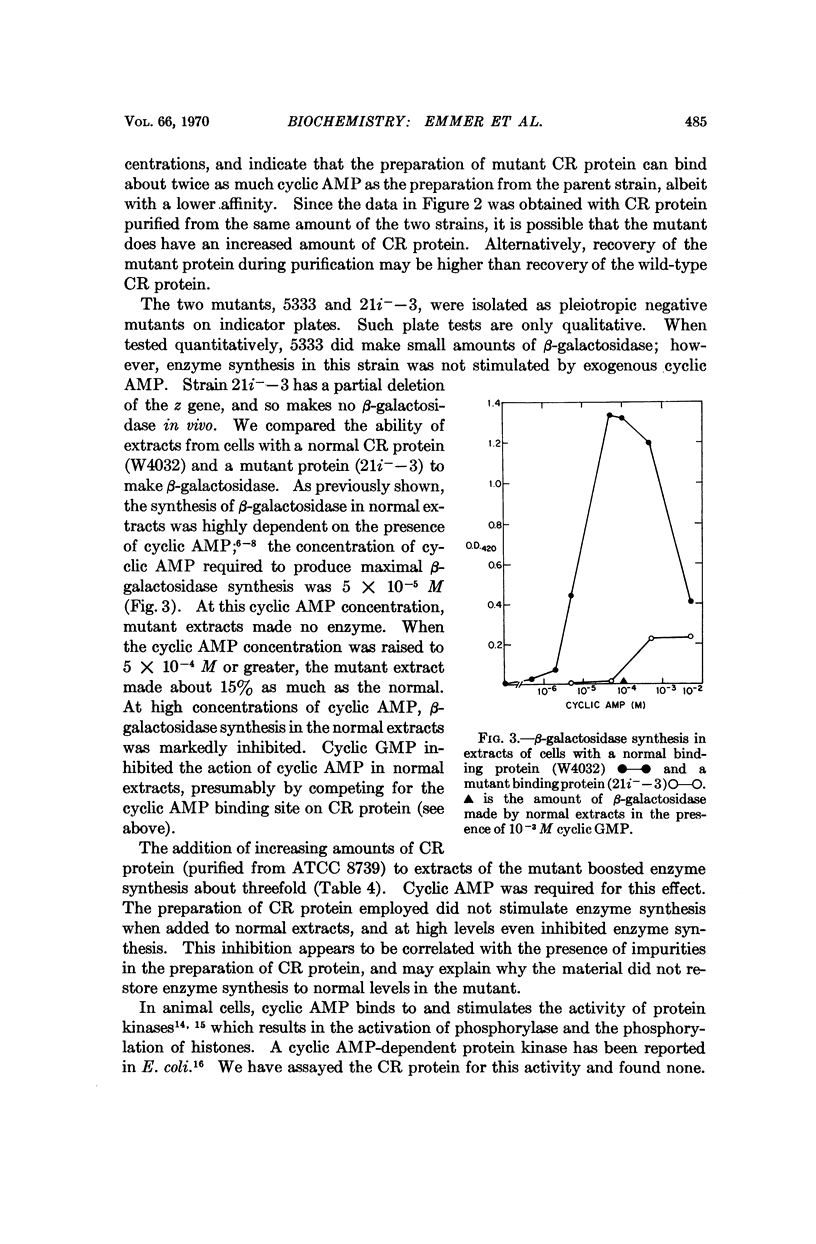
A cyclic AMP binding protein has been purified over 100-fold from E. coli extracts. Protein purified from wild-type strains binds cyclic AMP with an apparent dissociation constant of 1-2 × 10-6 M. Two mutant strains that are unresponsive to exogenous cyclic AMP have altered binding activity; the protein purified from one of these mutants has a decreased affinity for cyclic AMP (apparent dissociation constant = 2 × 10-5 M). Extracts of this mutant are deficient in their ability to support β-galactosidase synthesis in vitro. The addition of purified, wild-type binding protein to these extracts restores enzyme synthesis toward normal. Because this binding protein appears to be required for cyclic AMP action, we suggest it be called the cyclic AMP receptor protein (CR protein).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers D. A., Zubay G. The stimulatory effect of cyclic adenosine 3'5'-monophosphate on DNA-directed synthesis of beta-galactosidase in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Krebs E. G. A cyclic AMP--stimulated protein kinase in adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3417–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Schlessinger D. Binding of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic phosphate to G factor of Escherichia coli, and its effects on GTPase, RNase V, and protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):146–152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., De Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP regulates catabolite and transient repression in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):810–812. doi: 10.1038/223810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Pleiotropic deficiency of carbohydrate utilization in an adenyl cyclase deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90893-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5420–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Siegel R. B. Control of template specificity of E. coli RNA polymerase by a phage-coded protein. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1111–1113. doi: 10.1038/2231111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Bacteriophage sigma factor for RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1107–1110. doi: 10.1038/2231107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Monod J. Cyclic AMP as an antagonist of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLSON C., PERRIN D., COHN M., JACOB F., MONOD J. NON-INDUCIBLE MUTANTS OF THE REGULATOR GENE IN THE "LACTOSE" SYSTEM OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:582–592. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Lederman M. DNA-directed peptide synthesis. VI. Regulating the expression of the lac operon in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):550–557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



