Abstract
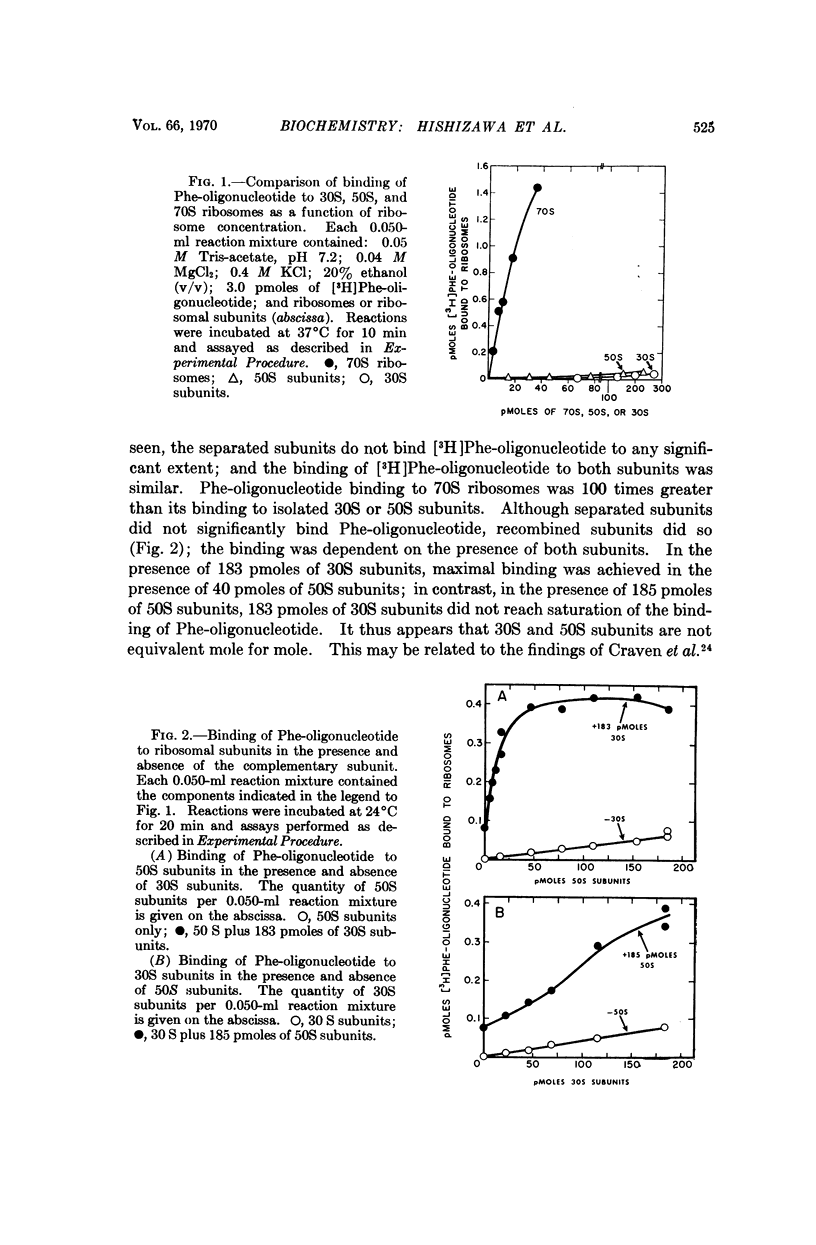
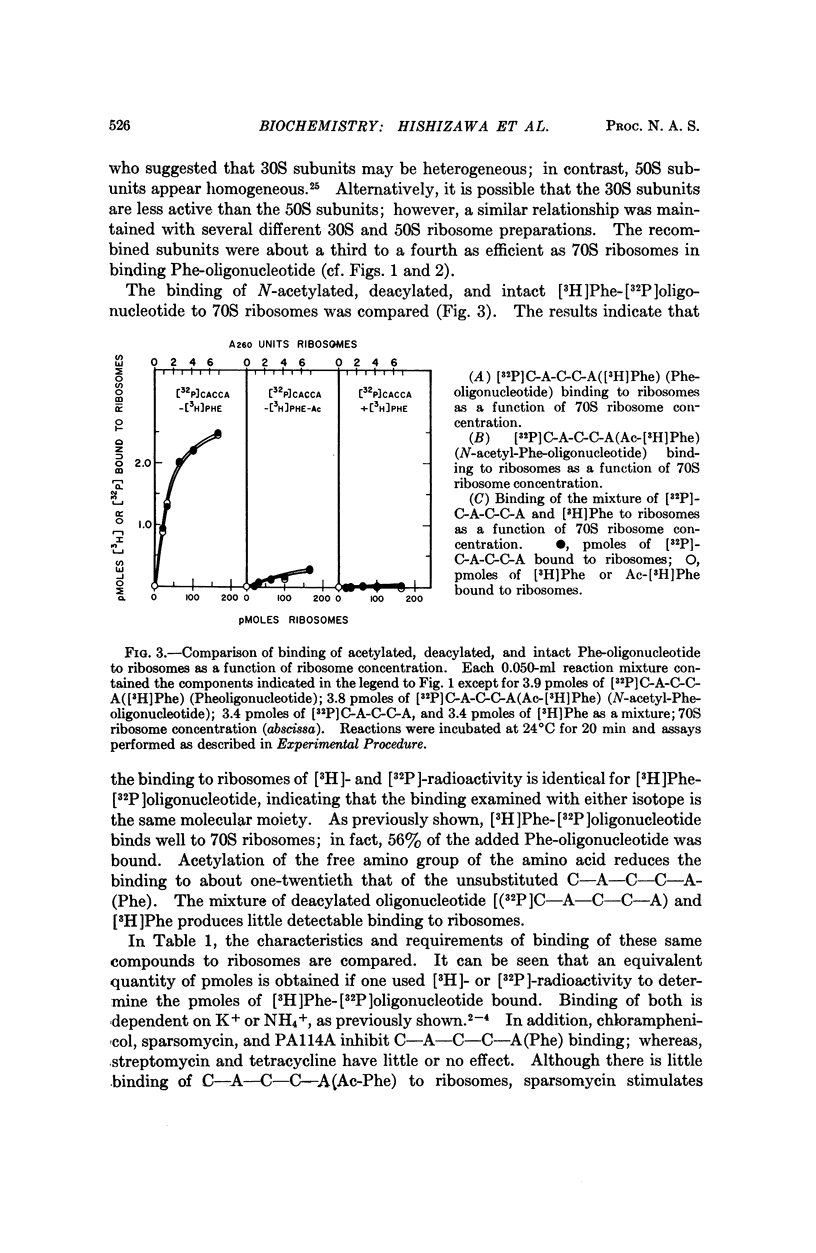
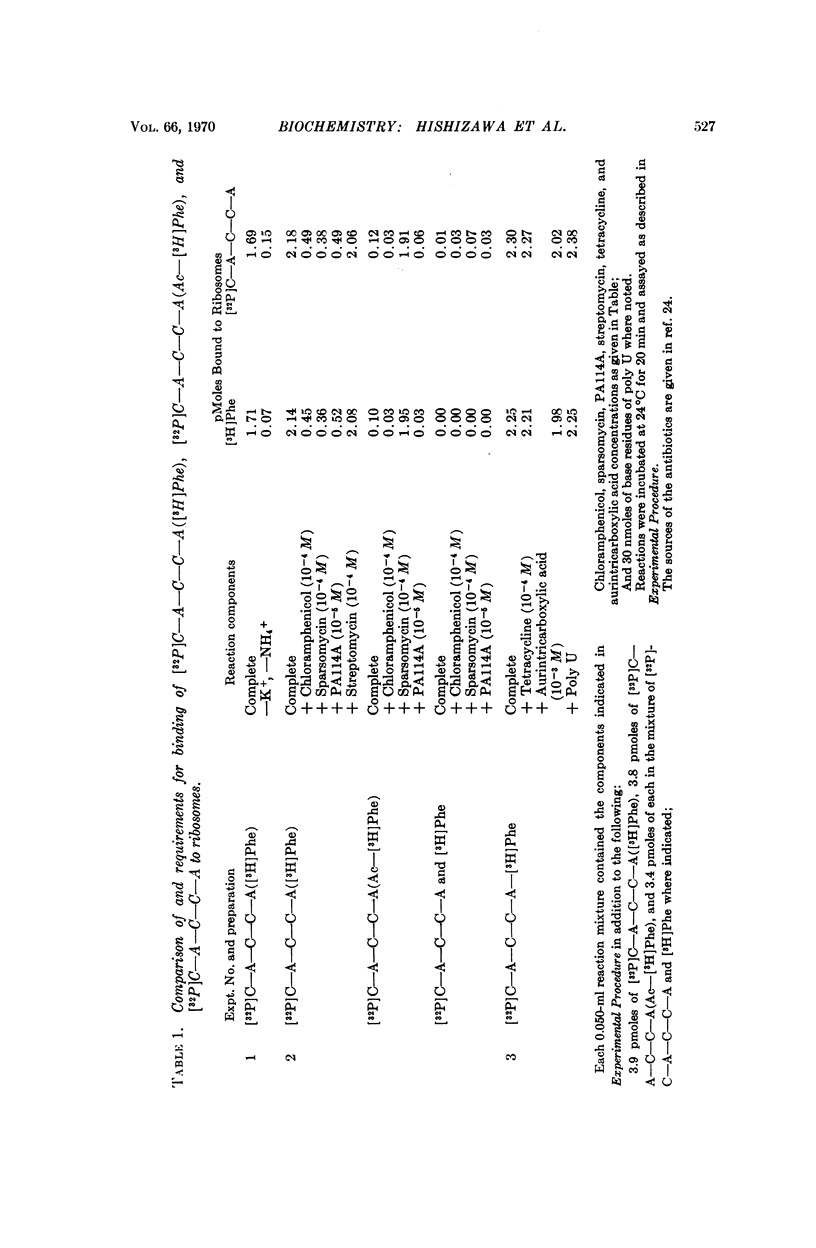
The binding of phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide, C-A-C-C-A-(Phe), to ribosomes requires the presence of a free amino group on the amino acid. Acetylation of the amino acid reduces the binding to ribosomes to about 1/20 of the binding observed with the intact Phe-oligonucleotide. Deacylation of the phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide eliminates binding of the free amino acid and markedly reduces the binding of the oligonucleotide (C-A-C-C-A). Neither 30S nor 50S subunits alone are sufficient for binding of the phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide; the presence of both subunits is necessary. The data suggest that phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to ribosomes represents the binding of the aminoacyl-terminus of phenylalanyl-tRNA and that the presence of an amino acid with an unsubstituted amino group attached to the oligonucleotide (C-A-C-C-A) is required for binding to this potassium-dependent site. Furthermore, the ribosome itself has the capability of distinguishing between aminoacyl-oligonucleotides with N-substituted and unsubstituted amino acids-
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrell B. G., Sanger F. The sequence of phenylalanine tRNA from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(4):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Chemical and physical characterization of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2906–2915. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerman H. W., Steers E., Jr, Redfield B. G., Weissbach H. Methionyl soluble ribonucleic acid transformylase. I. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1522–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A., Clark B. F., Cory S. Nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):232–233. doi: 10.1038/218232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Blew D., Warrington R. C., von Tigerstrom M., Tener G. M. A general procedure for the isolation of specific transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3459–3468. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Millward S., Blew D., von Tigerstrom M., Wimmer E., Tener G. M. The separation of soluble ribonucleic acids on benzoylated diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3043–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P., Stewart M. L. Inhibition of the attachment of messenger ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):719–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Chapeville F. The behaviour of acetylphenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid in polyphenylalanine synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. A., Doctor B. P., Loebel J. E., Nirenberg M. W. RNA codons and protein synthesis. IX. Synonym codon recognition by multiple species of valine-, alanine-, and methionine-sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. Action of sparsomycin on ribosome-catalysed peptidyl transfer. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):356–358. doi: 10.1038/222356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Nirenberg M. Regulatory mechanisms and protein synthesis. X. Codon recognition on 30 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):145–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 3. The formation of peptide bonds by ribosomes in the absence of supernatant enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2810–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 8. Survey of the effect of antibiotics of N-acetyl-phenylalanyl-puromycin formation: possible mechanism of chloramphenicol action. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. I. The effect of streptomycin and ribosomal dissociation on 14-C-aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. VII. The role of the 3'-hydroxyl-terminal end of transfer ribonucleic acid for interaction with ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. X. Phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to ribosomes and the mechanism of chloramphenicol action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 15;36(4):589–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XI. Antibiotic effects on phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):709–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Translocation, aminoacryl-oligonucleotides, and antibiotic action. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:395–410. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uziel M., Gassen H. G. Phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli B. Isolation and characterization of oligonucleotides from ribonuclease T-1 and ribonuclease A hydrolysates. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1643–1655. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Haba G. L. INHIBITION BY PUROMYCIN OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1721–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Elson D. Interconversions between inactive and active forms of ribosomal subunits. FEBS Lett. 1969 Apr;3(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



