Abstract
Electrophoretic patterns of enzymes in single vertebrate erythrocytes may be visualized with the use of capillary tube polyacrylamide columns and stains which amplify the enzymatic activity. The following points have thereby been demonstrated:
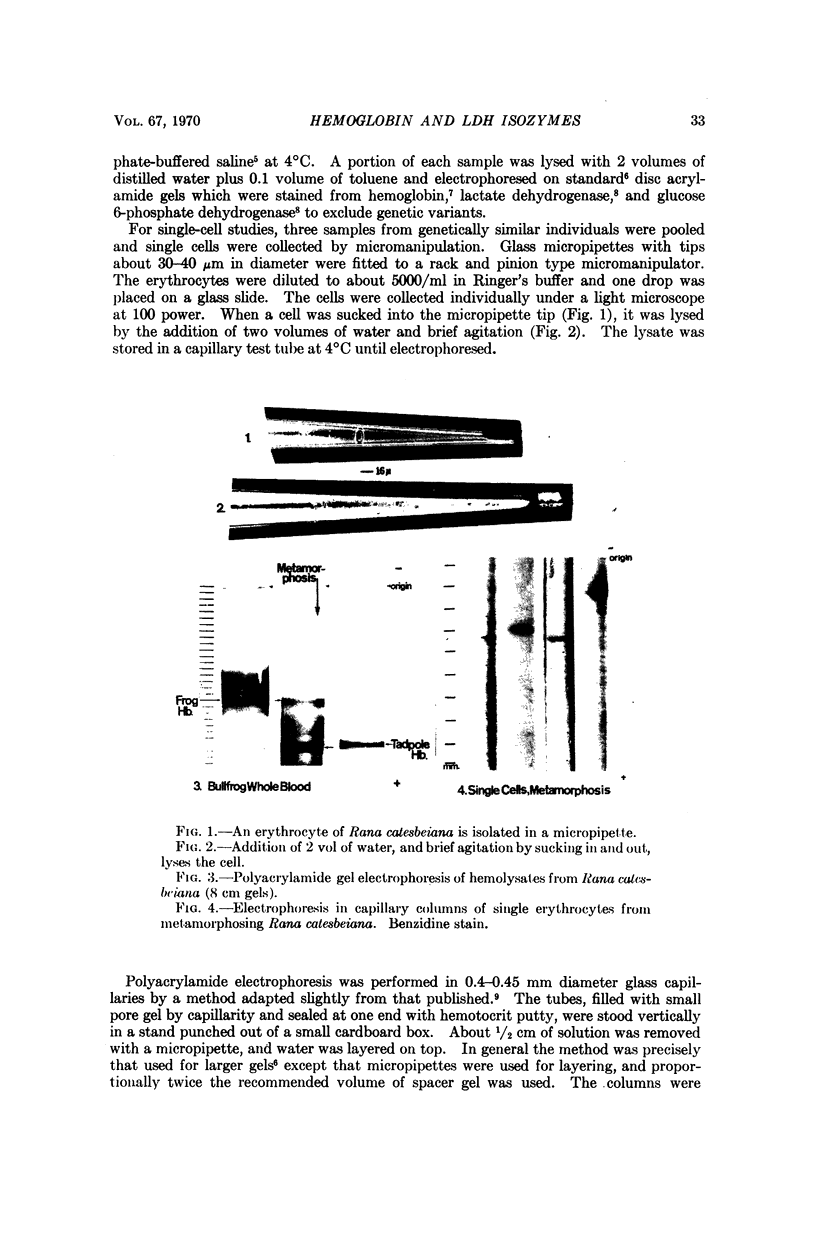
1. Peripheral blood of metamorphosing bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) contains two molecular forms of hemoglobin: embryonic (tadpole) and adult (frog). Only one of these forms is found in each erythrocyte.
2. Human umbilical cord blood contains fetal and adult hemoglobins; both forms may be found in individual erythrocytes, in varying proportions.
3. Both lactate dehydrogenase isozymes found in whole blood of bullfrogs and humans are found in individual erythrocytes, but the proportions differ from cell to cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cahn R. D., Zwilling E., Kaplan N. O., Levine L. Nature and Development of Lactic Dehydrogenases: The two major types of this enzyme form molecular hybrids which change in makeup during development. Science. 1962 Jun 15;136(3520):962–969. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3520.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni A., De la Chapelle A., Chui D., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Control mechanisms of the conversion from synthesis of embryonic to adult hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 20;165(1):194–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb27789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRATZER W. B., ALLISON A. C. Multiple haemoglobins. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1960 Nov;35:459–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1960.tb01523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbach U. Acrylamide gel electrophoresis in capillary columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;107(1):180–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90417-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Ingram V. M. Hemoglobin synthesis during amphibian metamorphosis. I. Chemical studies on the hemoglobins from the larval and adult stages of Rana catesbeiana. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 28;32(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Rottländer E., Peltre G., Müller B. The immune response to a hybrid protein molecule; specificity of secondary stimulation and of tolerance induction. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):581–606. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. R. In vivo and in vitro interactions of human haemoglobins A,S and C with a variant haemoglobin E. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1042–1044. doi: 10.1038/2191042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. R., Prasad R. Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes--a compilation of recipes. Biochem Genet. 1970 Apr;4(2):297–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00485780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]