Abstract
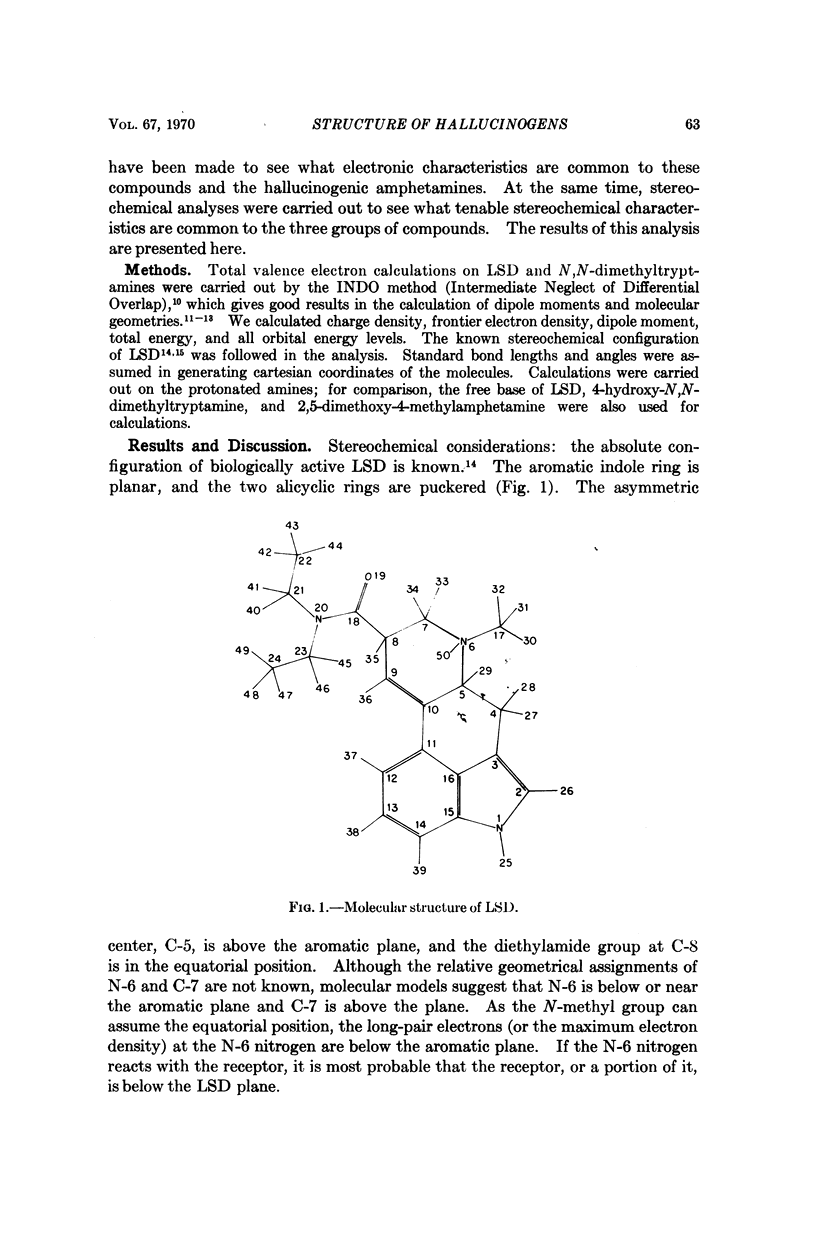
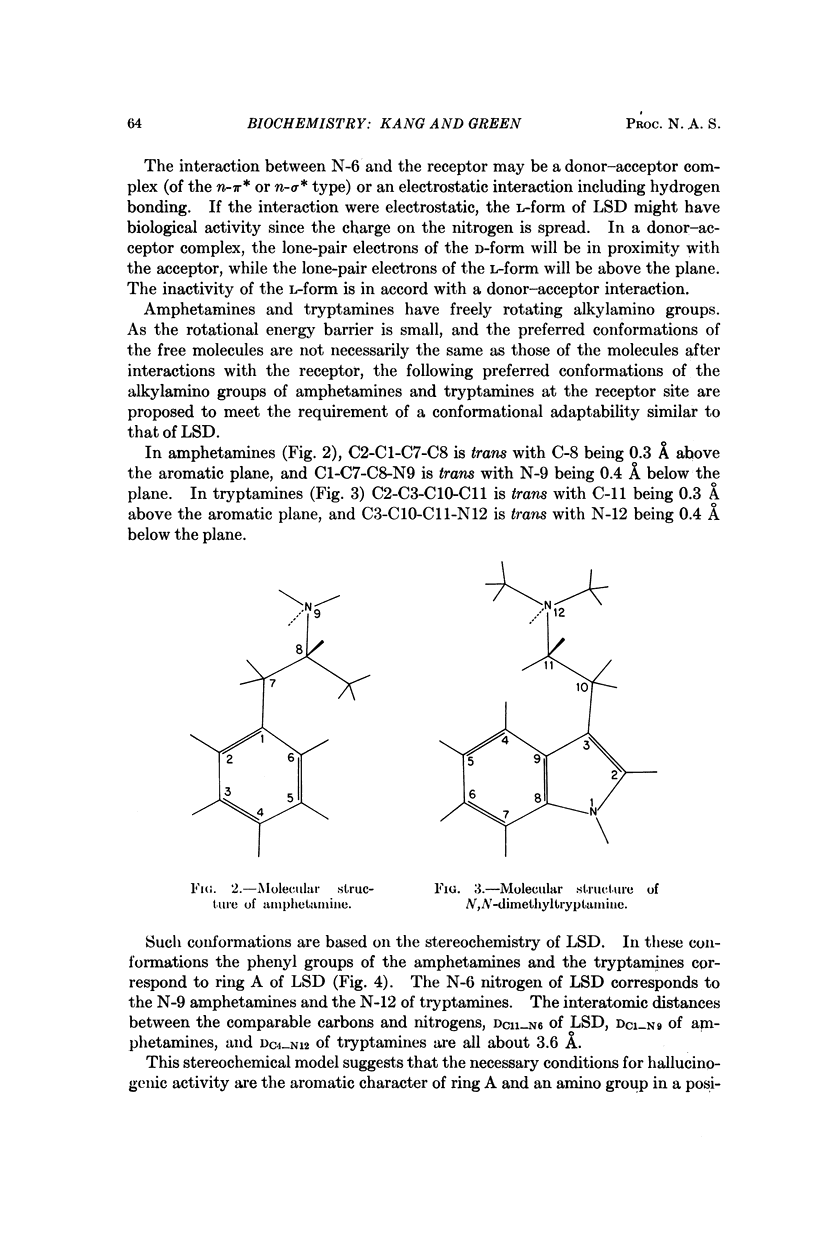
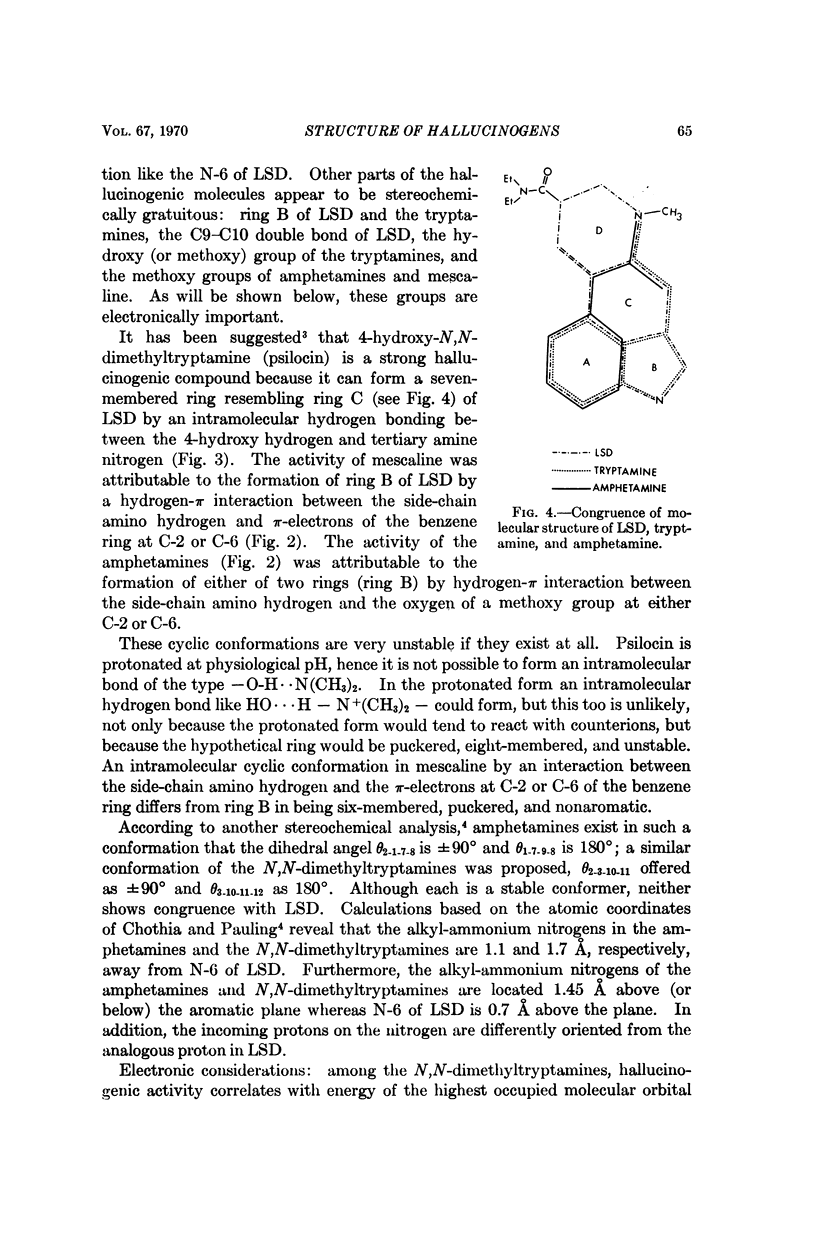
Stereochemical considerations and total valence electron calculations suggest congruities among the ostensibly dissimilar hallucinogenic compounds, D-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), indolcalkylamines, and methoxylated amphetamines. In LSD the aromatic benzene ring A and the N-6 nitrogen are essential for hallucinogenic activity; these sites may react with the receptor. The conformations of amphetamines and indolealkylamines at the receptor are such that the aromatic benzene ring lies like ring A of LSD and the alkylamino nitrogen lies like the N-6 of LSD. Ring A may interact with the receptor by forming a π-molecular complex, as suggested by the correlation between hallucinogenic activity and energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital (EH) of congeneric series. The N-6 nitrogen of LSD and the sterically congruent nitrogen of the other hallucinogenic compounds may react with the receptor by forming a donor acceptor complex of the n-π* or n-σ* type. Other portions of the hallucinogenic molecules confer a favorable EH: these include the methoxy and hydroxyl groups of the amphetamines (and mescaline), and the indolealkylamines; and the pyrrole ring of LSD and the indolealkylamines.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chothia C., Pauling P. On the conformations of hallucinogenic molecules and their correlation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1063–1070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISBELL H., WOLBACH A. B., WIKLER A., MINER E. J. Cross tolerance between LSD and psilocybin. Psychopharmacologia. 1961;2:147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00407974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARREMAN G., ISENBERG I., SZENT-GYORGYI A. On the mechanism of action of chlorpromazine. Science. 1959 Oct 30;130(3383):1191–1192. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3383.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S., Green J. P. Correlation between activity and electronic state of hallucinogenic amphetamines. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):645–645. doi: 10.1038/226645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulgin A. T., Sargent T., Naranjo C. Structure--activity relationships of one-ring psychotomimetics. Nature. 1969 Feb 8;221(5180):537–541. doi: 10.1038/221537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Merril C. R. A relationship between the hallucinogenic activity of drugs and their electronic configuration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):258–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Richelson E. Psychedelic drugs: steric factors that predict psychotropic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):206–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLBACH A. B., Jr, ISBELL H., MINER E. J. Cross tolerance between mescaline and LSD-25, with a comparison of the mescaline and LSD reactions. Psychopharmacologia. 1962 Mar 12;3:1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00413101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLBACH A. B., Jr, MINER E. J., ISBELL H. Comparison of psilocin with psilocybin, mescaline and LSD-25. Psychopharmacologia. 1962;3:219–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00412109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


