Abstract
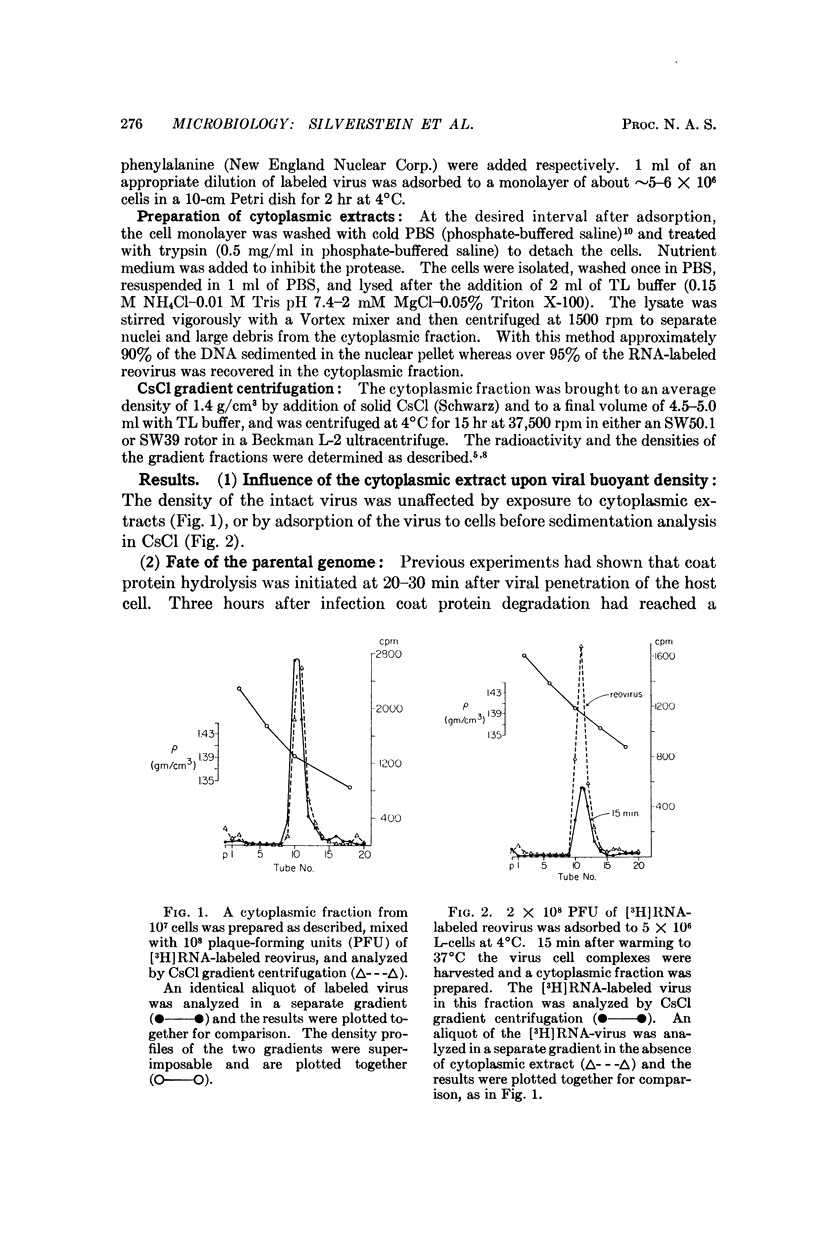
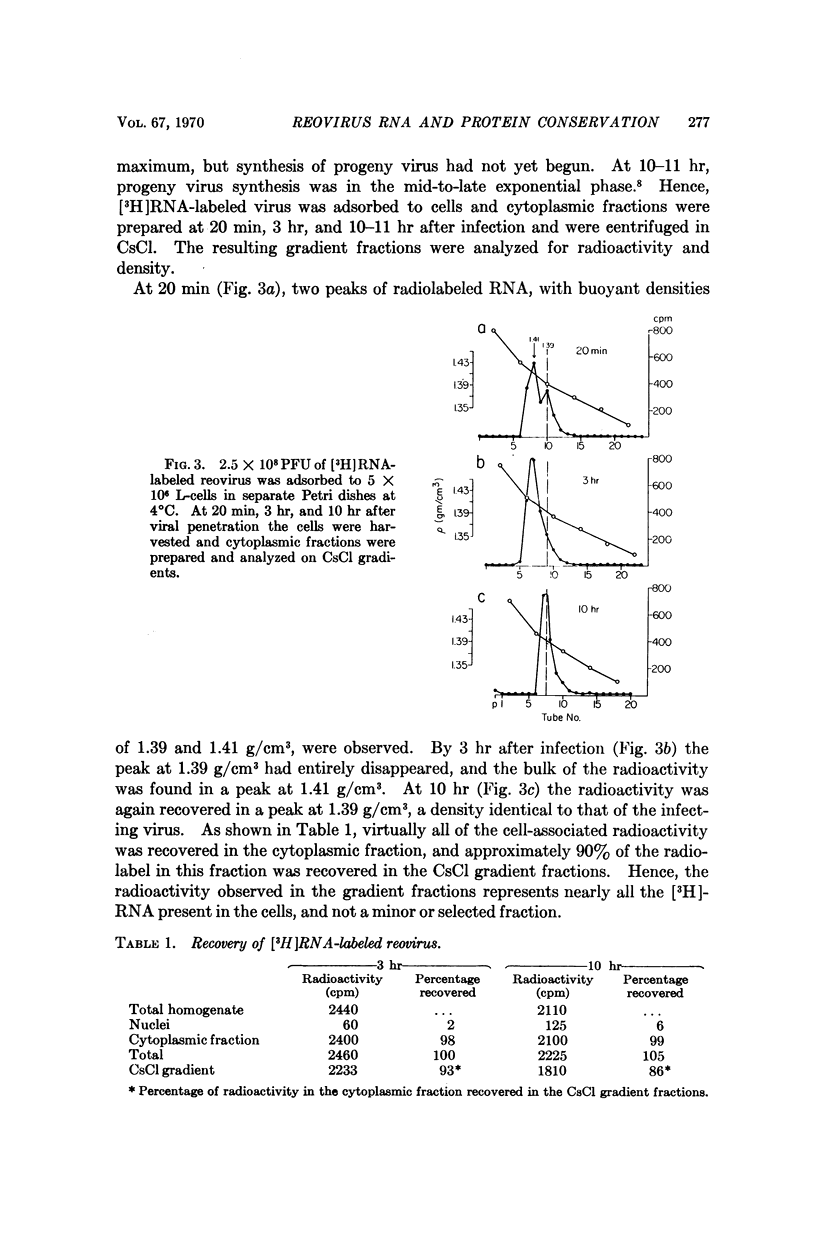
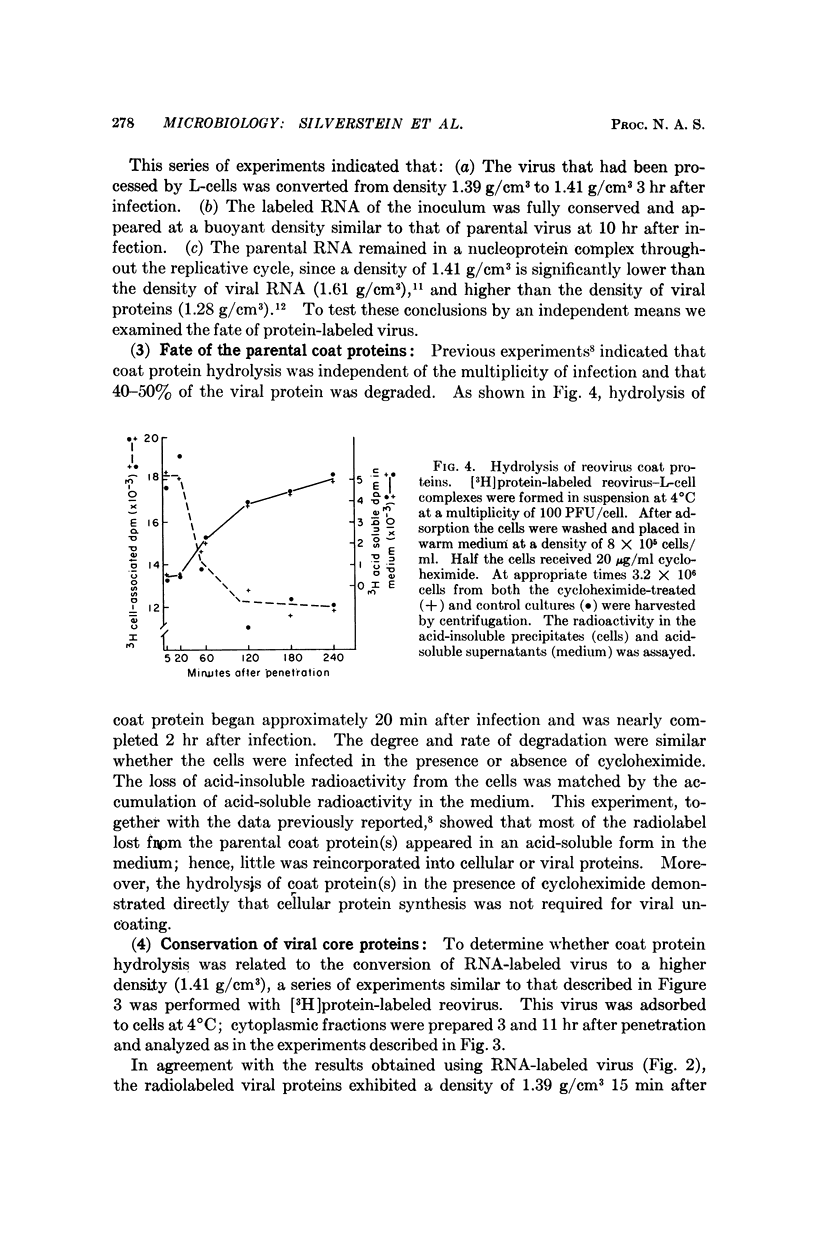
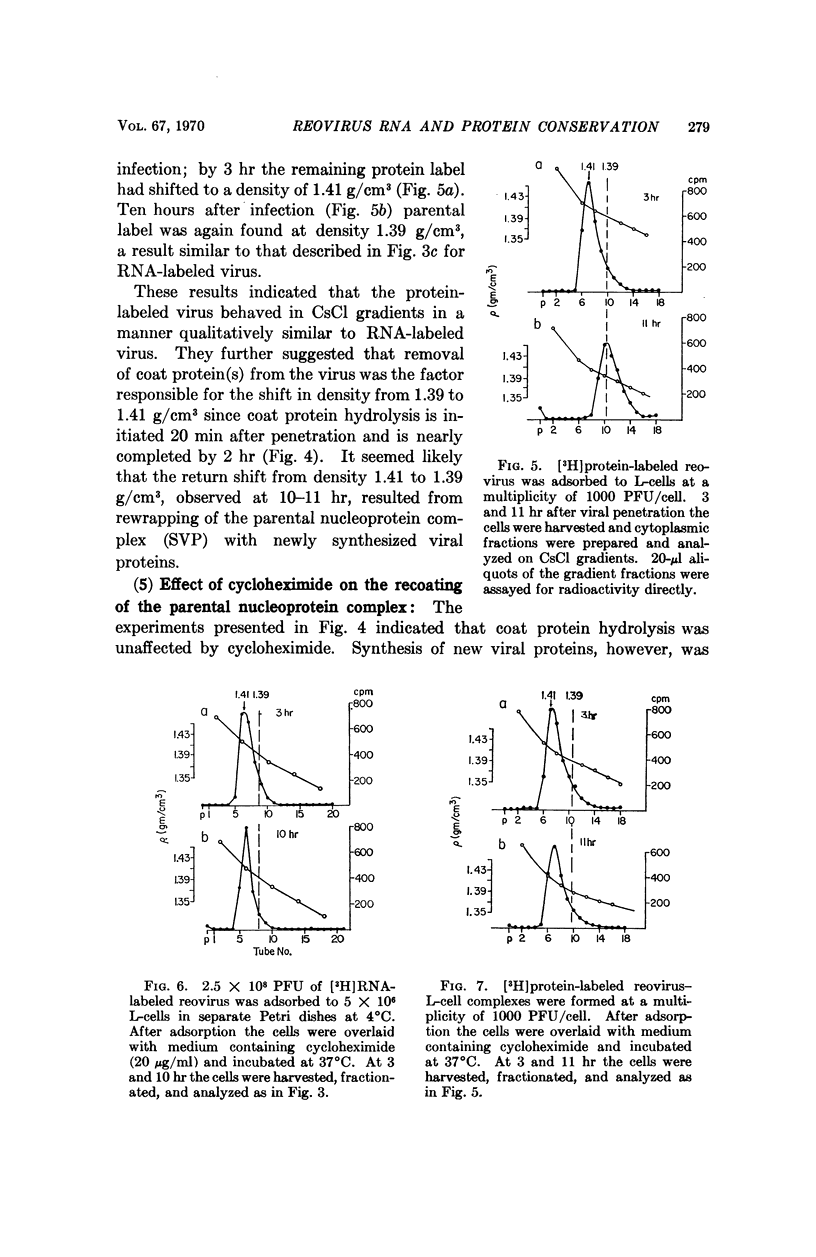
The fate of parental reovirions in the viral replicative cycle has been analyzed using CsCl density centrifugation. After penetration of L-cells, reovirus is converted from a particle of density 1.39 g/cm3 to a subviral particle of density 1.41 g/cm3. This alteration in density is temporally correlated with the hydrolysis of viral coat proteins and is qualitatively similar when particles are labeled in their RNA or protein. Ten hours after infection, when synthesis of progeny virus is underway, the parental RNA and protein are again found at density 1.39 g/cm3. These data demonstrate conservation of the parental RNA and protein in the subviral particle throughout the replicative cycle.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHARD W., TOURNIER P. Ultrastructural cytochemistry applied to the study of virus infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:67–82. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Oie H. K. Role of lysine in the replication of reovirus: I. Synthesis of complete and empty virions. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):890–895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.890-895.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Shatkin A. J. Structural proteins of reoviruses. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1353-1359.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYOR H. D., JAMISON R. M., JORDAN L. E., VANMITCHELL M. REOVIRUSES. II. STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION OF THE VIRION. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1548–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1548-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Inactivity of purified reovirus RNA as a template for E. coli polymerases in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Millward S., Graham A. F. Regulation of transcription of the Reovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



