Abstract
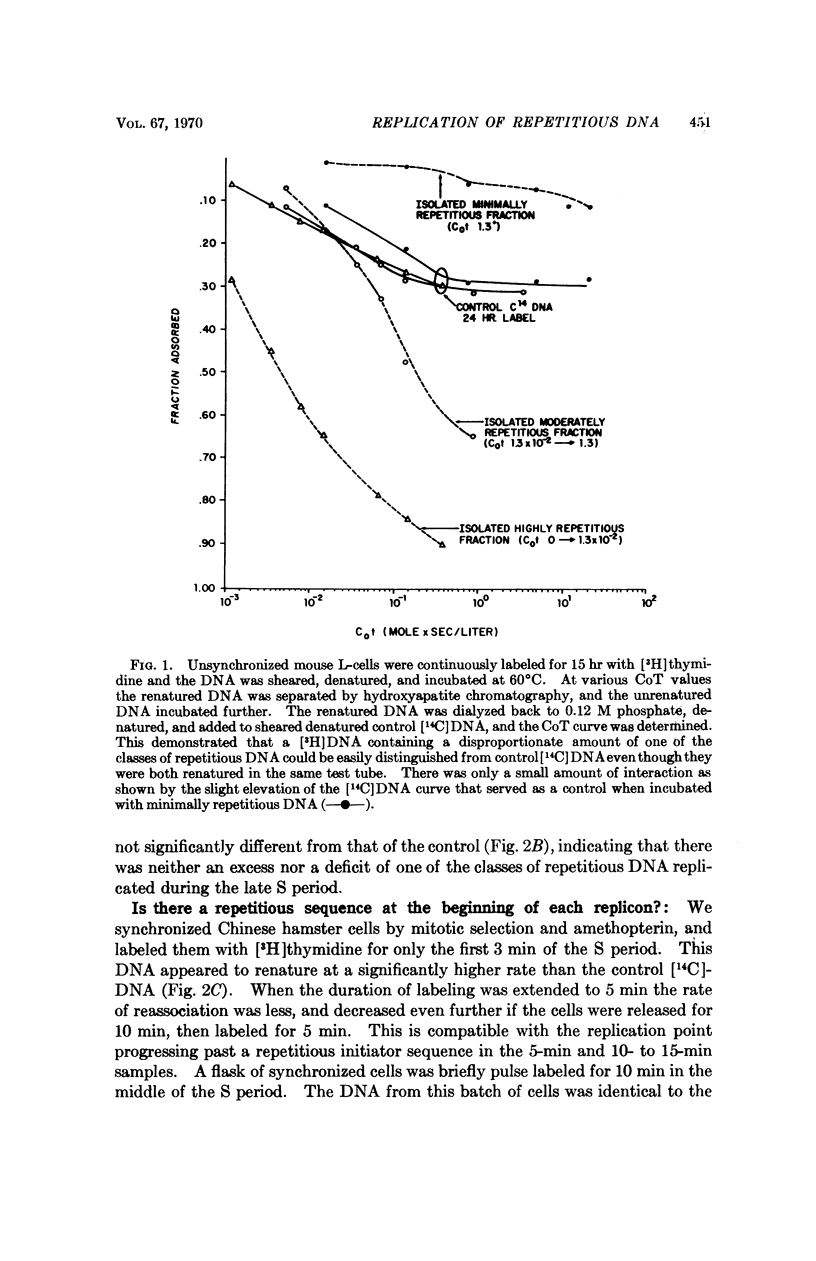
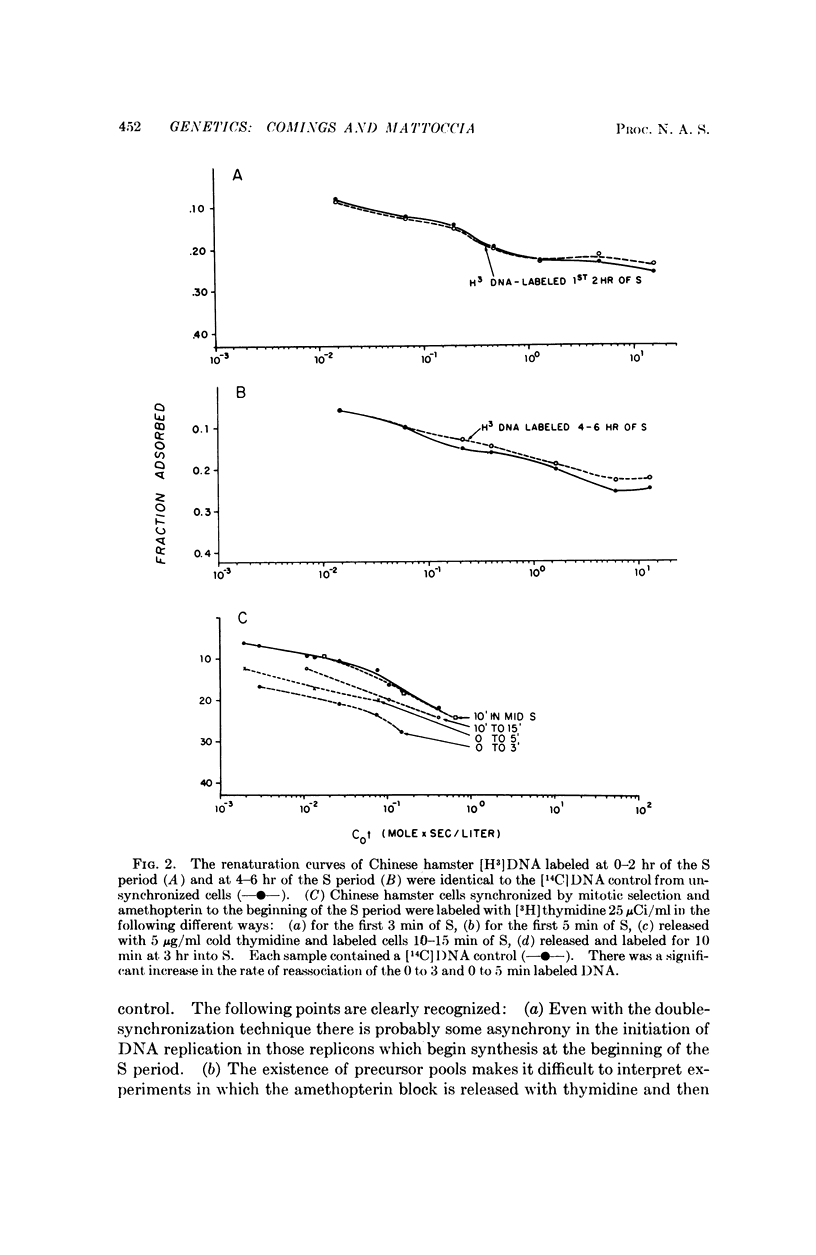
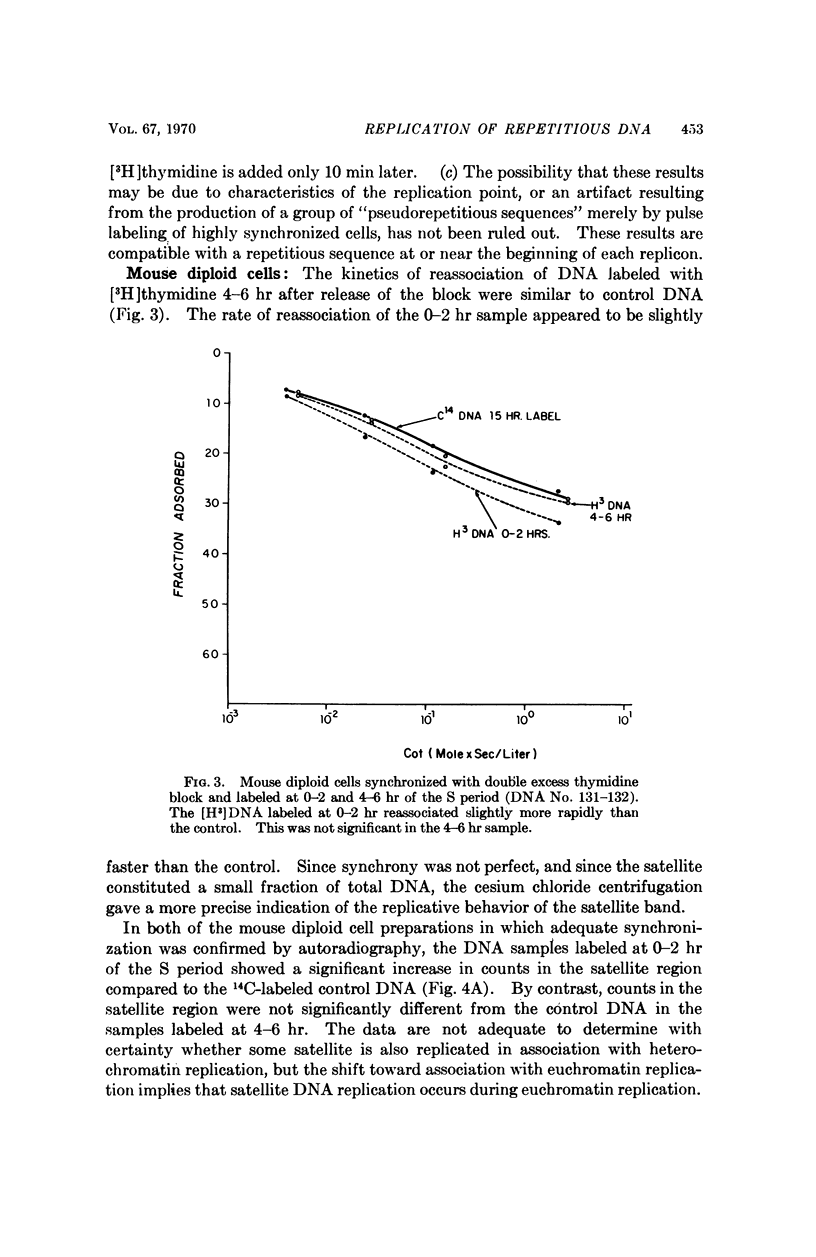
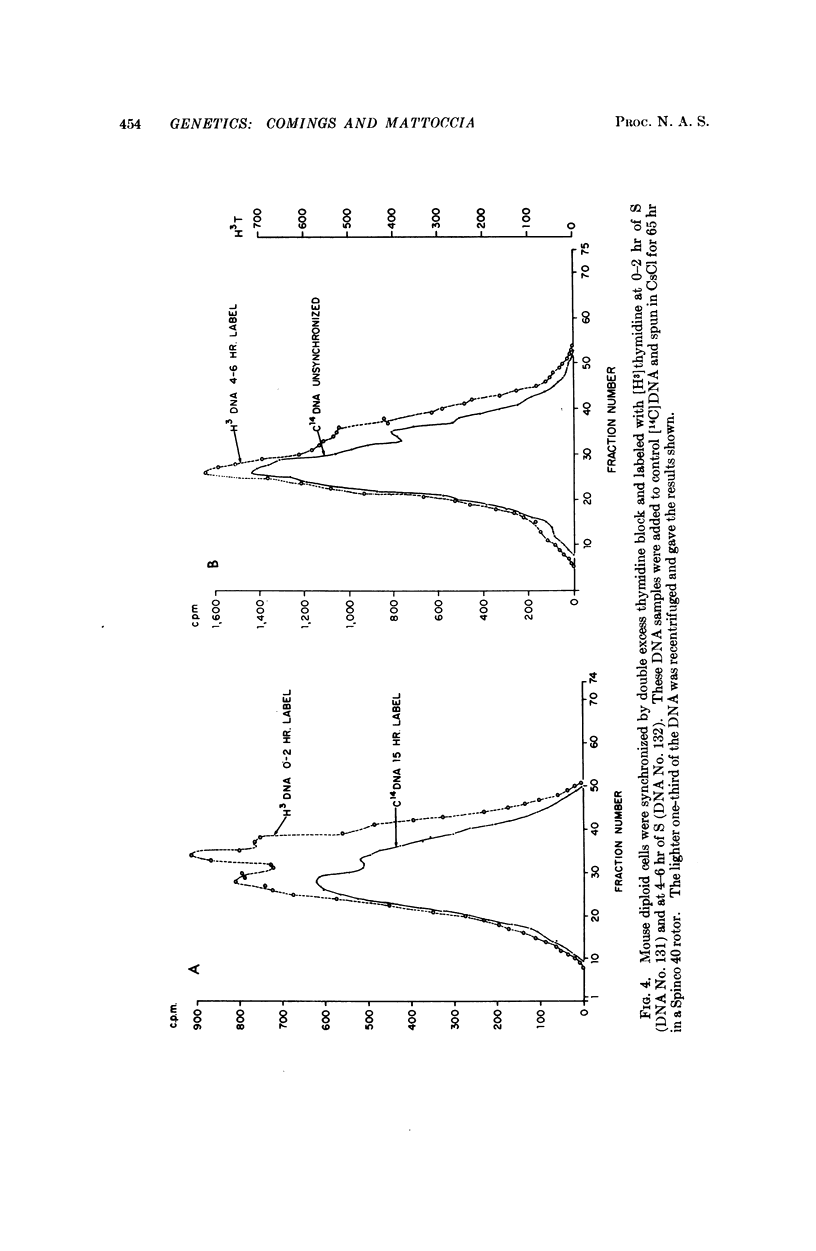
The renaturation kinetics of labeled DNA derived from synchronized Chinese hamster cells indicate that the three classes of repetitious DNA replicate uniformly throughout the S period, and that a piece of repetitious DNA may occur at or near the beginning of each replicon. Studies with mouse-cell DNA suggest that mouse satellite DNA replicates when euchromatin replicates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaldi F., Giacomoni D., Zito-Bignami R. On the duplication of ribosomal RNA cistrons in Chinese hamster cells. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(3):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTSMA D., BUDKE L., VOS O. STUDIES ON SYNCHRONOUS DIVISION OF TISSUE CULTURE CELLS INITIATED BY EXCESS THYMIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:301–309. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond H. E., Flamm W. G., Burr H. E., Bond S. B. Mouse satellite DNA. Further studies on its biological and physical characteristics and its intracellular localization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):289–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel J., Hanania N., Tapiero H., Harel L. RNA replication by nuclear satellite DNA in different mouse cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Nov 25;33(4):696–701. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John H. A., Birnstiel M. L., Jones K. W. RNA-DNA hybrids at the cytological level. Nature. 1969 Aug 9;223(5206):582–587. doi: 10.1038/223582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAZAWA Y., THOMAS C. A., Jr NUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITION OF SHORT SEGMENTS OF DNA MOLECULES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:223–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Schildkraut C. L. Isolated mammalian metaphase chromosomes. II. Fractionated chromosomes of mouse and Chinese hamster cells. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 14;40(2):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUECKERT R. R., MUELLER G. C. Studies on unbalanced growth in tissue culture. I. Induction and consequences of thymidine deficiency. Cancer Res. 1960 Dec;20:1584–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. L., Maio J. J. Studies on the intranuclear distribution and properties of mouse satellite DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):76–93. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Klevecz R. Synchronization of Chinese hamster cells by reversal of colcemid inhibition. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Dec;40(3):660–664. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasmineh W. G., Yunis J. J. Localization of mouse satellite DNA in constitutive heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jan;59(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



