Abstract
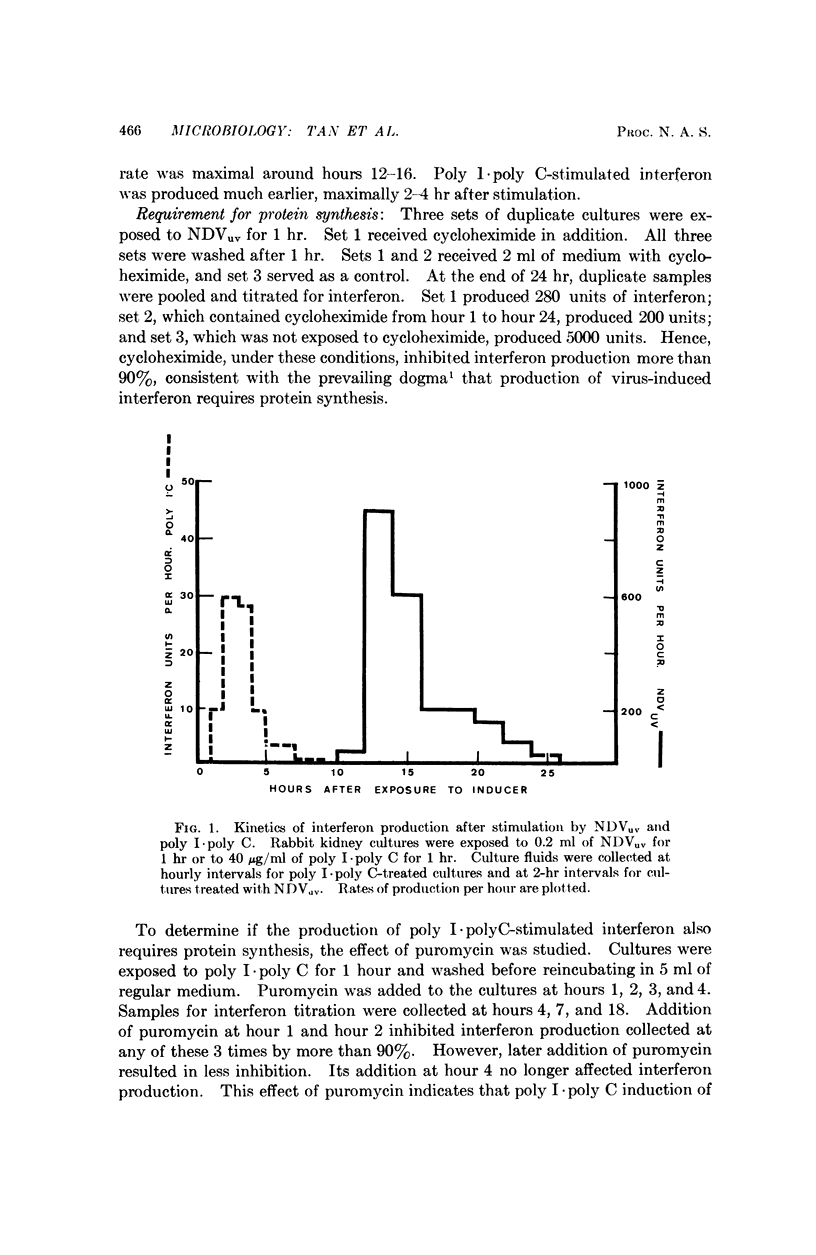
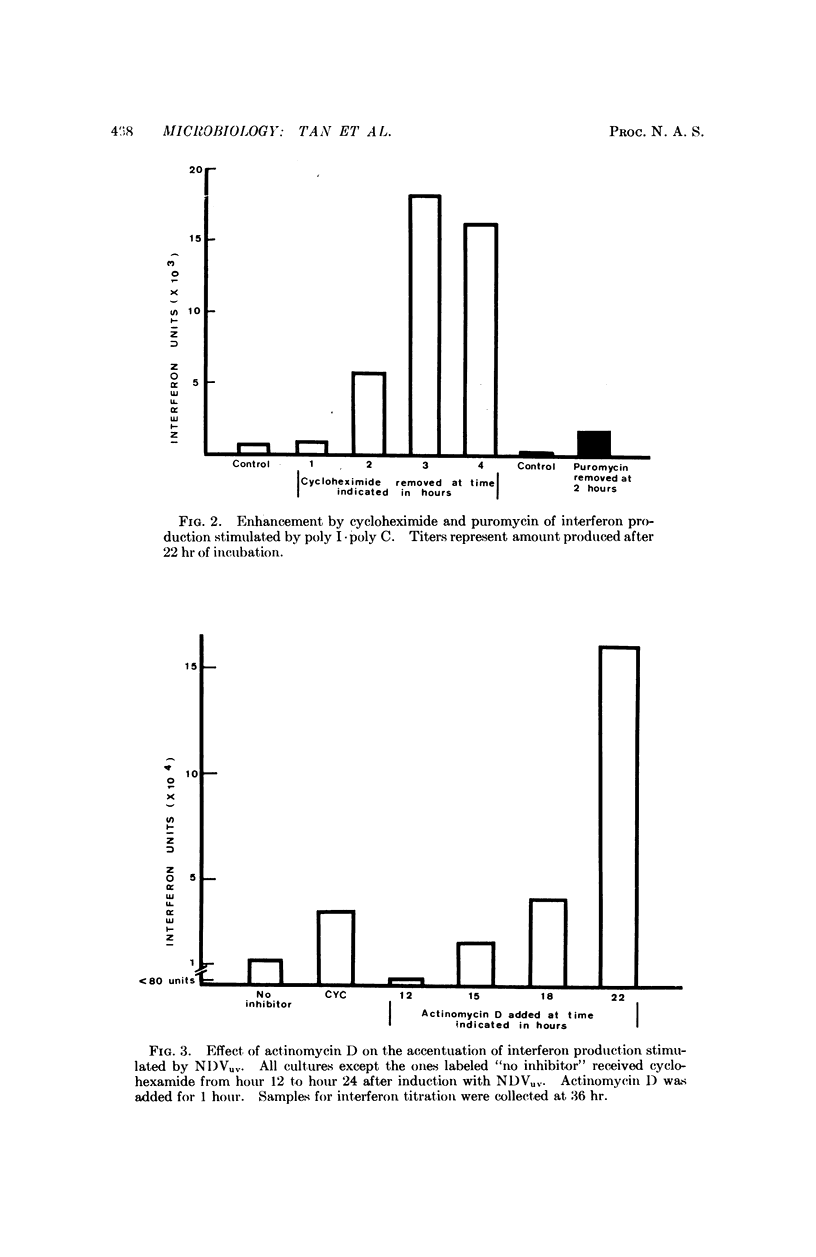
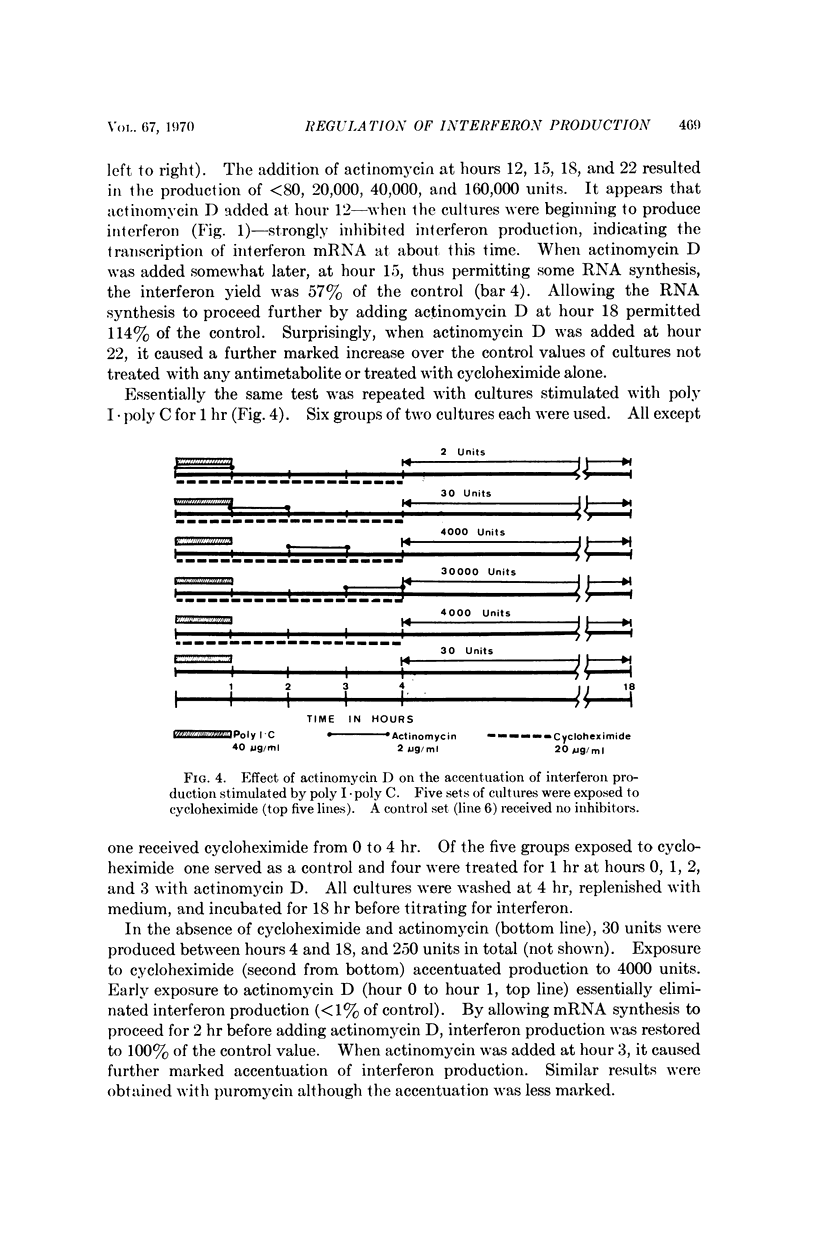
Cycloheximide, at a protein-inhibitory concentration, when given to rabbit kidney cell cultures that had been exposed either to UV-irradiated Newcastle Disease virus or to a complex of polyinosinic and polycytidylic acids (poly I·poly C), enhanced the production of interferon. The enhancement was greater if, in addition to cycloheximide, the cells were also treated with actinomycin D. On the basis of these findings, a mechanism, consisting primarily of the production of a control protein which normally checks interferon production, is postulated for interferons stimulated by these two substances.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance, V. In vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):340–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M. S., Bausek G. H., Merigan T. C. Interferon inducers in vitro: difference in sensitivity to inhbitiros of RNA and protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Aug 2;161(3840):465–468. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3840.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Effect of interferon treatment on interferon production. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):872–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. IDENTIFICATION AND "INDUCTION" OF INTERFERON. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Dec;28:367–381. doi: 10.1128/br.28.4.367-381.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M., KONO Y. EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D ON VIRUS AND ENDOTOXIN-INDUCED INTERFERONLIKE INHIBITORS IN RABBITS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Ke Y. H. The mechanism of stimution of interferon production by a complexed polyribonucleotide. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90214-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke Y. H., Ho M. Studies on the physico-chemical inactivation of rabbit inerferons. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):433–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Hallum J. V. Inhibition of induction of interferon synthesis in L-cells pretreated with interferon. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):473–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Hallum J. V. Interferon production in mice by double-stranded synthetic polynucleotides: induction or release? Virology. 1968 May;35(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R., Taube S. E. Influence of inhibitors of protein synthesis on interferon formation in mice. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



