Abstract
The ubiquitous bacterial RNA-binding protein Hfq is involved in stress resistance and pathogenicity. In Sinorhizobium meliloti, Hfq is essential for the establishment of symbiosis with Medicago sativa and for nitrogen fixation. A proteomic analysis identifies 55 proteins with significantly affected expression in the hfq mutant; most of them are involved in cell metabolism or stress resistance. Important determinants of oxidative stress resistance, such as CysK, Gsh, Bfr, SodC, KatB, KatC, and a putative peroxiredoxine (SMc00072), are downregulated in the hfq mutant. The hfq mutant is affected for H2O2, menadione, and heat stress resistance. Part of these defects could result from the reductions of rpoE1, rpoE2, rpoE3, and rpoE4 expression levels in the hfq mutant. Some proteins required for efficient symbiosis are reduced in the hfq mutant, contributing to the drastic defect in nodulation observed in this mutant.
Gene expression in bacteria is regulated by a wide diversity of mechanisms, including alternative sigma factors, transcriptional regulatory proteins, attenuation mechanisms (including riboswitches) (15), and translational and posttranslational regulations (37). The interplay of central regulatory proteins and alternative sigma factors allows the creation of complex regulatory networks modulating transcription (4).
Compared to transcription regulation, the mechanisms affecting the regulation of translation are less understood. Studies dedicated to translation regulation have increased over the past few years (55, 76, 77). An important development has been the recognition of small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) that have emerged as crucial actors of translation regulation. In enterobacteria, most sRNAs require Hfq to complex with their targets. Hfq is an RNA chaperone necessary for the pairing of sRNAs with mRNAs (40). Furthermore, Hfq affects translation efficiency by allowing the polyadenylation of specific mRNAs (44). Thus, Hfq is a central actor in translation regulation (72). Hfq is also able to affect transcription, directly by coupling with RNA polymerase (67) or indirectly via its action on sRNAs modulating translation of sigma factors (19, 32, 69).
Due to its central role, hfq inactivation results in a pleiotropic phenotype in enterobacteria and Brucella abortus, including growth defects, stress susceptibility, and altered pathogenicity (56, 65, 76). Our accompanying study shows that loss of hfq impairs the ability of Sinorhizobium meliloti to establish a nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with its legume host, Medicago sativa. S. meliloti faces numerous stresses during the course of invading the developing root nodules and colonizing the plant cells (21, 22, 35, 46, 62). Bacterial abilities to resist and adapt to these stresses are of crucial importance for the symbiosis. Oxidative stress has been the most intensively investigated stress that S. meliloti must withstand and appears as a key factor for bacterium-plant cell interaction. To cope with oxidative stress, S. meliloti cells posses a detoxification system involving various proteins, which includes 3 catalases (KatA, KatB, and KatC) (62) and 2 superoxide dismutases (SodB and SodC) (29, 58). katA and katB expression is controlled by the repressor OxyR (34). No specific regulatory protein has been identified for sodB and sodC expression. katC and sodC are also expressed during the stationary phase of growth under the control of the alternative sigma factor RpoE2 (26). In other bacteria, the production of catalases and superoxide dismutases is also controlled at the translational level by sRNAs (40, 42, 56, 66, 74). Such regulatory mechanism has never been identified in S. meliloti.
Our accompanying study shows that an hfq mutant of S. meliloti is drastically affected in its ability to colonize and establish symbiosis with its host and in the free-living state displays a pleiotropic phenotype that includes growth defects. To identify proteins involved in these defects, we chose a proteomic approach and identified a set of 55 proteins differentially expressed in the hfq mutant and correlated the nature of these proteins with the stress and nodulation phenotypes of the hfq mutant.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and culture conditions.
The bacterial strains used in this study are detailed in Table 1. S. meliloti strains were grown aerobically at 30°C in the complex medium LB (43) to an optical density at 570 nm (OD570) of 1.5 to 1.8; they were then inoculated in minimal galactose aspartate salts (GAS) medium (31) or LB medium at an OD570 of 0.1. Escherichia coli strains were grown aerobically in LB medium at 37°C. For the selection of E. coli strains, ampicillin was added at 50 or 100 μg/ml, tetracycline at 10 μg/ml, chloramphenicol at 25 μg/ml, and neomycin or kanamycin at 50 μg/ml. For the selection of S. meliloti strains, streptomycin was used at 100 μg/ml, tetracycline at 5 μg/ml, and neomycin at 25 μg/ml.
TABLE 1.
S. meliloti strains used in this work
| Strain | Description or genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| RM1021 | WT strain, Su 47 derivative; Smr | |
| R874 | Sm1021 katC::Neor | 26 |
| R326 | Sm1021 sodB::Tetr | 26 |
| R815 | SM1021 sodC::Gmr | 26 |
| R641 | SM1021 rpoE2::Gmr | 26 |
| R356 | SM1021 hfq-lacZ-Gmr | 8a |
| R602 | 1021 rpoE1::′uidA-KanrrpoE1+ | This study |
| R635 | 1021 rpoE2::′uidA-NeorrpoE2+ | This study |
| R605 | 1021 rpoE3::′uidA-KanrrpoE3+ | This study |
| R562 | 1021 rpoE4::′uidA-KanrrpoE4+ | This study |
| R603 | R356 rpoE1::′uidA-KanrrpoE1+ | This study |
| R671 | R356 rpoE2::′uidA-KanrrpoE2+ | This study |
| R672 | R356 rpoE3::′uidA-KanrrpoE3+ | This study |
| R673 | R356 rpoE4::′uidA-KanrrpoE4+ | This study |
Pulse-labeling and extraction of proteins.
At each labeling time point, 1 ml of culture grown as described above was fed 925 kBq of [35S]methionine-cysteine protein labeling mixture (43.475 × 103 GBq mmol−1) for 15 min. The radioactivity incorporation was stopped by adding 5 μl of a nonradioactive methionine-cysteine solution (2 and 0.4%, respectively [wt/vol]). Protein extraction was done as previously described (36).
2-D gel electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF MS analysis.
After being harvested by centrifugation, bacterial cells were washed in TE (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA [pH 6.8]). The cell pellet was resuspended in the same buffer with 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Cells were disrupted by three passages through a French press (1,200 lb/in2), and cell debris were removed by centrifugation at 4°C and 12,000 × g for 30 min. The protein concentration in the supernatant fraction was determined according to the method of Lowry (39a). For analytical and preparative two-dimensional (2-D) gels, 200- and 500-μg quantities of crude protein extract were solubilized in the rehydration solution and submitted to 2-D gel electrophoresis as previously described (36). The preparative gels were stained with Coomassie blue R, while the gels containing radiolabeled proteins were dried under a vacuum and exposed to Kodak Hyperfilm-MP. Digitized images were quantified using MELANIE image software. The optical density of each spot over its area (volume) was calculated as a percentage of the relative OD of the gel image. The results are the means from two to four individual experiments, with standard deviations that did not exceed 20%. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) analysis was performed as described previously (36).
Protein carbonylation.
Cells were grown in GAS medium to stationary growth phase and collected by centrifugation (13,000g, 5 min). The pellet was washed and resuspended in phosphate buffer (50 mM phosphate, pH 7, 0.1 mM EDTA). Protein carbonylation content was determined according to reference 49. Protein extracts were submitted to 2-D gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and carbonylated proteins revealed using an OxyBlot protein oxidation detection kit (Chemicom International).
DNA manipulations and mutant constructions.
Standard protocols were used for DNA manipulations (57).
β-Glucuronidase and β-galactosidase assay and catalase and SOD detection.
The β-glucuronidase and β-galactosidase assays were carried out as described previously (7, 43), with clarified cell lysates obtained by disrupting bacteria with glass beads. Specific activities are expressed as nanomoles of ortho-nitrophenol liberated per minute per milligram of protein. Protein concentration was determined by the method of Bradford (13a), with bovine serum albumin as a standard. The results are the means from at least three independent experiments, and the standard deviation was less than 10%. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity on 10% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels was visualized by nitroblue tetrazolium-negative staining as described previously (9). Catalase activity was revealed on nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels as previously described (62).
Survival following challenge test.
Wild-type (WT) and hfq strains were grown in LB or GAS medium. Cells were collected during exponential or stationary growth phase and challenged by incubating them at 50°C or by adding 100 mM H2O2. Survival was determined by plating on LB agar medium serial dilutions of challenged suspension. The results are the means from four independent experiments.
Resistance to exogenous O2−.
Strains were grown in GAS medium to stationary growth phase; harvested by centrifugation; washed twice in 1 mM EDTA, 50 mM pH 7.8 potassium phosphate buffer (PBS); and adjusted to a density of 108 cells ml−1. The same buffer containing 1 mM xanthine (corresponding to the maximum solubility of xanthine) was added to cells along with 1,000 U ml−1 of bovine liver catalase to detoxify any H2O2 generated by spontaneous dismutation of the O2− produced during the xanthine oxidase reaction. Superoxide generation was initiated by the addition of 0.5 U ml−1 of xanthine oxidase. Periodically, aliquots were collected and supplemented with 20 μM cytochrome c to follow superoxide production. The rate of cytochrome c reduction was monitored at 550 nm. To stop the reaction, cells were collected by centrifugation (15,000 × g, 3 min) and resuspended in the same volume of PBS. Cell survival was analyzed over time by 10-fold serial dilution and plating on LB plates.
Challenges with pyrogallol were performed by adding 2 mM pyrogallol and 1,000 U ml−1 of bovine liver catalase to cell suspension in PBS. Cells were incubated with shaking at 30°C, and aliquots were collected at different time intervals, centrifuged to remove pyrogallol, and resuspended in the same volume of PBS. Survival was determined as described above. The generation of superoxides was estimated by the auto-oxidation rate of pyrogallol at 420 nm and reduction of cytochrome c at 550 nm.
Construction of rpoE::uidA transcriptional fusions.
A chromosomal fragment containing the N-terminal coding end of the rpoE1, rpoE2, rpoE3, or rpoE4 open reading frame (ORF) and extending 2 kb upstream was amplified using the primers listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material for the S. meliloti 1021 strain. The amplicon was cloned into the pGEMT vector (Promega, La Jolla, CA). The uidA-Kanr cassette from pUIDK3 (7) was inserted downstream of the rpoE fragment by using restriction sites located within rpoE or in the vector polylinker (see Table S1 in the supplemental material), yielding a rpoE::uidA transcriptional fusion The fusion was then recovered using restriction sites flanking the fusion and inserted into pSUP102 (a mobilizable vector nonreplicative in S. meliloti) (63). Recombinant pSUP102 was transferred into S. meliloti by triparental mating. Single-crossover recombinants were selected as Neor colonies, and recombination was confirmed by PCR. The mutation was transduced to RM1021 and its hfq derivative using ΦM12, yielding stains bearing rpoE-uidA fusions in the wild-type and hfq backgrounds (Table 1).
RESULTS
Analysis of the hfq proteome.
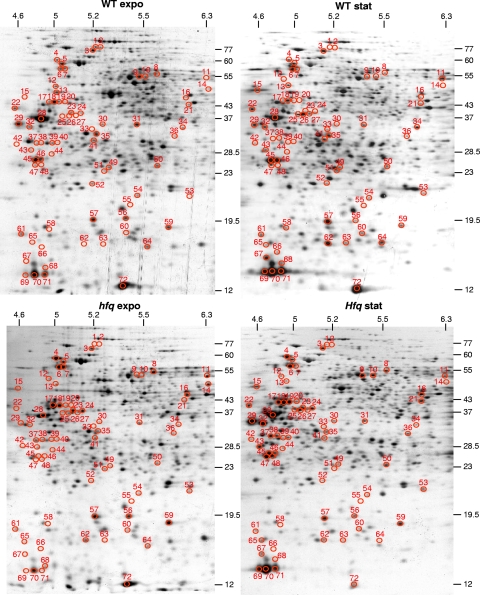
Proteins produced by S. meliloti WT and hfq mutant strains were analyzed by 2-D gel electrophoresis. Cells grown in GAS minimal medium were collected in exponential or stationary growth phases. Two strategies were adopted, (i) analysis of newly synthesized proteins after a pulse-labeling of 15 min with [35S]methionine and (ii) analysis of total proteins stained by Coomassie blue. Gel patterns showed that hfq mutation drastically altered protein expression (Fig. 1). We did not observe significant differences between the two strategies, suggesting that Hfq mainly affects protein synthesis rather than protein stability.
FIG. 1.
Detection of proteins affected in the hfq mutant. WT and hfq strains were grown in GAS medium and collected during exponential growth phase (expo) or in late stationary growth phase (stat). Protein extracts were resolved by 2-D gel electrophoresis.
35S-labeled protein spots were quantified on 2-D gels. From four independent experiments, only spots exhibiting at least a 2-fold variation in the hfq mutant compared to the level for the WT strain were kept for further investigations. In order to assess the number of differentially regulated proteins, only the spots that perfectly overlapped on the 2-D gels obtained from these experiments were considered (1,000 in exponential and 903 in stationary growth phase). Four hundred forty-two proteins were downregulated and 75 upregulated in the hfq mutant during exponential growth phase, compared to the WT levels. In contrast, during the stationary phase of growth, 100 proteins were upregulated and 66 downregulated in the hfq mutant background compared to the levels for its parental strain.
Identification of the proteins whose levels of expression were affected in the hfq mutant was performed by excising well-separated spots from the Coomassie blue-stained gels, digesting them with trypsin, and subjecting them to MALDI-TOF analysis. Among the spots analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS, only the 72 spots that matched with a single protein in S. meliloti were retained. Thirteen of them showed 2 to 4 isoforms (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). The abundance of isoforms is consistent with a previous study of S. meliloti (45). With isoforms taken into account, only 55 distinct proteins were identified as being up- or downregulated in the hfq mutant during exponential or stationary growth phase (Table 2). Ten of these proteins have an unknown function; 29 are involved in cell metabolism, among which 17 are periplasmic binding proteins of ABC-type uptake systems; 6 are related to ribosomes and translation (ribosomal proteins, elongation factors, and ribosome recycling factor); and 7 are related to stress response and 3 to more-global functions (energy supply, secretion, and cell division).
TABLE 2.
Proteins differentially expressed during exponential and stationary growth phases in the hfq mutant in comparison to the WT levels
| ORF | Gene | Phase (ratio)a corresponding to: |
Putative function | Reference(s) identifying protein(s) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overexpression | Repression | Detected in nodulesb | Affected by hfq mutation in other organismsc | |||
| SMa0312 | Stat (0.5) | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| SMb20025 | Expo (0.5); Stat (0.35) | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| SMb20091 | Expo (0.48); Stat (0.32) | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| SMb20428 | ehuB | Stat (2.0) | Expo (0.5) | Ectoine binding protein | 20, 21 | |
| SMb21176 | phoD | Expo (0.22) | Phosphate binding protein | 20, 21, 45 | ||
| SMb21181 | Expo (5.7); Stat (4.4) | Putative glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase | ||||
| SMb21441 | Expo (2.6) | Stat (0.34) | Putative inosine-5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase | |||
| SMb21549 | thtR | Stat (3.4) | Putative sulfotransferase | |||
| SMb21647 | agpA | Expo (0.19) | α-Galactoside binding protein | |||
| SMc00072 | Expo (0.5); Stat (0.1) | Hypothetical peroxiredoxin | ||||
| SMc00140 | Expo (2.0); Stat (2.4) | Amino acid binding protein | 20, 21 | |||
| SMc00153 | Stat (2.0) | Hypothetical protein | 20 | |||
| SMc00242 | Expo (2.6); Stat (2.0) | Sugar binding protein | ||||
| SMc00357 | efp | Expo (0.5) | Elongation factor EF-P | 32 (EC, −) | ||
| SMc00419 | gshB1 | Expo (0.45); Stat (0.35) | Glutathione synthetase | 20 | ||
| SMc00421 | cysK1 | Expo (0.38); Stat (0.45) | Cysteine synthase A | 8, 45 | 32 (EC, +); 64 (ST, +) | |
| SMc00595 | Stat (2.1) | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| SMc00770 | potF | Expo (0.28) | Putrescine-binding protein | 64 (ST, +) | ||
| SMc00784 | Stat (0.35) | Putative iron binding ABC transport system | 10, 20, 21 | |||
| SMc00786 | dppA1 | Expo (2.5); Stat (3.7) | Dipeptide-binding protein | 64, 78 (ST, +); 32 (EC, +) | ||
| SMc00883 | Expo (0.42) | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| SMc00912 | groES1 | Stat (0.23) | 10-KDa chaperonin A protein; chaperonin GroES | 3 (repression); 20 | 32 (EC, −) | |
| SMc00948 | glnA | Stat (2.9) | Glutamine synthetase I | 10 (absence and repression); 20, 23, 45 (absence) | 32 (EC, −) | |
| SMc01028 | eno | Expo (0.50); Stat (0.37) | Enolase | 10 (repression) | ||
| SMc01033 | Stat (0.43) | Probable arylesterase | ||||
| SMc01169 | ald | Expo (2.6); Stat (2.1) | Probable alanine dehydrogenase | 20 | 32 (EC, −) | |
| SMc01208 | ppiB | Stat (0.5) | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B protein | 32, 74 (EC, −); 78 (ST, −); 19 (VC, +) | ||
| SMc01273 | Expo (0.5) | S-Formylglutathione hydrolase | ||||
| SMc01318 | rplL | Expo (2.1) | Stat (0.21) | 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 | 21 | 65 (ST, −) |
| SMc01326 | tufB | Stat (0.37) | Elongation factor EF-Tu | 10 (repression); 11, 45 | 65 (ST, −) | |
| SMc01418 | Expo (0.33) | Hypothetical signal peptide protein | 20 | |||
| SMc01525 | dppA2 | Expo (4.1); Stat (3.2) | Putative dipeptide binding periplasmic protein | 32 (EC, −); 64, 78 (ST, +), | ||
| SMc01700 | ppiA | Expo (0.50); Stat (0.40) | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 64 (ST, +); 19 (VC, +) | ||
| SMc01834 | Stat (2.0) | Hypothetical protein | 20 | |||
| SMc01852 | pfk | Stat (3.5) | Pyrophosphate-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase | 64 (ST, −) | ||
| SMc01861 | murE | Expo (3.7) | Probable UDP-N-acetylmuramoylalanyl-d-Glutamate-2,6-diaminopimelate ligase | |||
| SMc01874 | ftsZ1 | Stat (0.48) | Cell division protein FtsZ | 3 (repression); 20 (absence) | 68 (EC, +) | |
| SMc01946 | livK | Expo (2.6); Stat (4.7) | Leucine-specific binding protein | 20, 21 | 64 (ST, +) | |
| SMc02098 | frr | Expo (2.6) | Ribosome recycling factor | |||
| SMc02100 | tsf | Expo (4.5) | Elongation factor EF-Ts | 32 (EC, −); 64, 78 (ST, +) | ||
| SMc02118 | Stat (6.4) | Expo (0.29) | Periplasmic binding ABC transporter | 20, 21 | ||
| SMc02156 | Expo (0.07) | Hypothetical protein | 3, 17, 21 | |||
| SMc02344 | Stat (2.2) | Periplasmic binding protein | ||||
| SMc02495 | Stat (0.5) | Putative translaldolase | 20 | |||
| SMc02501 | atpD | Expo (0.43); Stat (0.5) | F0F1 ATP synthase subunit beta | 20, 38 | 32 (EC, −) | |
| SMc02509 | sitA | Stat (2.2) | Iron-manganese binding protein | 3, 21 | ||
| SMc02514 | Expo (0.5) | Putative periplasmic binding protein | ||||
| SMc02692 | rplY | Expo (0.5) | 50S ribosomal protein L25 | 20 | 32 (EC, −); 78 (ST, −) | |
| SMc02720 | clpP2 | Expo (0.5) | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit | 20 | ||
| SMc02737 | Expo (3.4) | Putative GB binding protein | ||||
| SMc02788 | secB | Stat (0.25) | Protein-export protein SecB; | 20, 21 | ||
| SMc02884 | Expo (0.5) | Putative lipoprotein precursor | 20 | |||
| SMc03124 | Expo (3.2); Stat (4.1) | Peptide/nickel transport system substrate binding | ||||
| SMc03157 | Stat (9.9) | Expo (0.31) | d-Methionine transport system substrate binding | |||
| SMc03786 | bfr | Expo (0.35); Stat (0.29) | Probable bacterioferritin (BFR) (cytochrome b1) (cytochrome b557) protein | 3, 10 (repression) | 64, 78 (ST, −) | |
The number in parentheses represents the ratio of protein abundance in the mutant strain to that in the wild-type strain. Stat, stationary phase; Expo, exponential phase.
Listed are references identifying the corresponding protein in nodules in proteomic or transcriptomic studies of nodulation. The absence of the protein in nodules or the repression of transcription is indicated in parentheses.
+ and − denote up- and downregulation, respectively, of the corresponding protein. EC, ST, and VC correspond to Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, and Vibrio cholerae, respectively.
Transport systems.
Periplasmic solute binding proteins (PBP) of ABC-type transport systems represent a dominant class of proteins affected by hfq mutation (17/55). Some periplasmic binding proteins are also regulated by Hfq in E. coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, as was shown by the identification of sRNA gcvB's targets in S. Typhimurium (61) and E. coli (51-53). All the identified periplasmic binding proteins controlled by gcvB in E. coli and S. Typhimurium relate to the uptake of amino acids and peptides.
Compared to the levels for the S. meliloti RM1021 WT strain, in the hfq mutant, 11 of these PBP are upregulated and 6 downregulated. These transporters are involved in the uptake of peptides (DppA1, DppA2, and SMc03124), amino acids (LivK, SMc03124, SMc03157, AapJ, and SMc00140), carbon supply (SMc02737, SMc02344, SMc0024, Ehu, and AgpA), and minerals (PhoD, SitA, SMc00784) (41). All the proteins involved in the uptake of peptides or amino acids are upregulated in the hfq mutant. The iron (SMc00784) and phosphate (PhoD) binding proteins are downregulated while SitA (mainly involved in manganese uptake) (16) is upregulated. The involvement of Hfq in regulating iron uptake proteins is also documented for other organisms (40, 76).
Oxidative stress.
Five proteins affected by hfq mutation are related to oxidative stress defenses. SitA participates in Mn2+ uptake and contributes to resistance to H2O2 and superoxide (16). During stationary growth phase, SitA is more abundant in the hfq mutant than in the WT strain. Cysteine synthase (CysK), bacterioferritin (Bfr), glutathione synthetase (GshB1), and the peroxiredoxin (SMc00072) are important proteins involved in oxidative stress defenses (1, 14, 39, 46, 75). Compared to the WT strain, they are less abundant in the hfq mutant during exponential and stationary growth phases (Table 2).
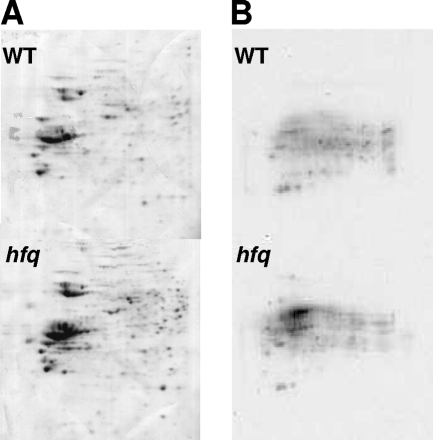
Oxidative stress resistance involves numerous proteins. Insufficient synthesis of CysK, Bfr, and GshB may be partly responsible for the reduced ability of S. meliloti to repair oxidative damage during aerobic growth. To analyze whether oxidative defenses are altered during aerobic growth, we looked for a characteristic consequence of increased oxidative damage by examining the carbonylation of proteins (49). During stationary growth phase, 107 ± 10 nM carbonyl/mg of protein was detected in the WT strain and 152 ± 14 nM carbonyl/mg of protein was observed in the hfq mutant. Carbonylation was confirmed by examining proteins separated by SDS-PAGE and 2-D gel electrophoresis (Fig. 2). Notably, carbonylated proteins were colocalized with the predominant proteins possessing various isoforms (LivK with SMc01946 and SMc00242, AapJ with SMc02118 and SMc02156, and PhoD with SMb21176) (Fig. 2), suggesting that these isoforms could result from protein carbonylation.
FIG. 2.
Visualization of protein carbonylation. WT and hfq strains were grown on GAS medium and collected during late stationary growth phase. Proteins were separated by 2-D gel electrophoresis. Gels were stained with Coomassie blue (A) or transferred on a nitrocellulose sheet for carbonyl detection (B) using the OxyBlot protein oxidation detection system.
These data are in accordance with the key role of Hfq in oxidative stress adaptation in other bacteria. Indeed, in E. coli (40, 74), S. Typhimurium (78), Brucella abortus (56), and Neisseria meningitidis (42), mutation in hfq has been shown to alter the synthesis of superoxide dismutases and other detoxification enzymes. An hfq mutation also affects catalase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa (66). Therefore, we compared the production levels of SODs and catalases in the hfq mutant of S. meliloti and its parental strain.
Resistance to superoxide.
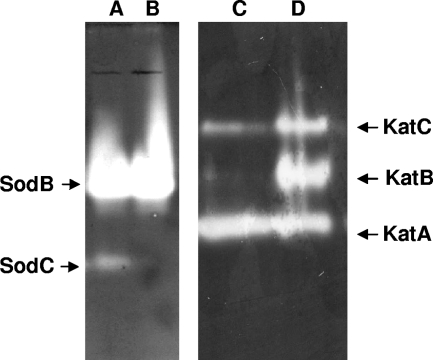
The pattern of superoxide dismutases was determined by resolving cell lysate on native polyacrylamide gels and then staining to reveal SOD activity. When harvested during exponential growth, the SOD patterns were identical for both strains, as both the parent and the hfq mutant expressed only SodB activity (data not shown). The WT strain produced SodB and SodC during stationary growth phase, while the hfq mutant did not exhibit any SodC activity (Fig. 3). In other bacteria, Hfq controls SodB synthesis (40, 76). Our proteomic study revealed hfq/WT SodB ratios of 1 and 0.6 during exponential and stationary growth phases, respectively, suggesting that SodB is slightly less produced in the hfq mutant during stationary growth phase. We analyzed the survival of the WT and sodB, sodC, and hfq mutants challenged with the intracellular superoxide generator methyl viologen (MV) and extracellular superoxide generators.
FIG. 3.
Gel assays of SOD and catalase activities. WT (A, D) and hfq (B, C) strains were grown on GAS medium and collected during stationary growth phase, and SOD (A, B) or catalase (C, D) activities were revealed on nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels as described in Materials and Methods.
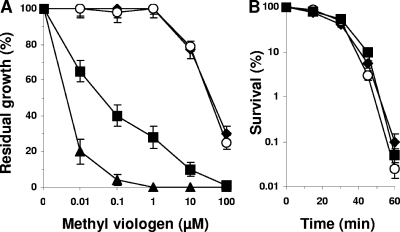
S. meliloti 1021 (WT) and its derivatives were grown in GAS medium supplemented with 0 to 100 μM MV (Fig. 4A). The growth of the WT strain was not affected by 1 μM MV but is affected at 10 μM MV. The sodC strain behaved as the WT strain did. In contrast, the growth of the hfq mutant was reduced by 60% in the presence of 0.1 μM MV. In comparison, the growth of the sodB mutant was abolished at 0.1 μM MV (Fig. 4A). These data clearly show that despite the presence of relatively similar amounts of SodB in the cell, the hfq mutant is much more sensitive than its parental strain to the redox cycling agent MV. Thus, the hfq mutation must affect other components of the cellular defenses against intracellular superoxides. Since SodC activity was not detected in the hfq mutant, the rates of survival against external superoxides produced by xanthine-xanthine oxidase and pyrogallol in the WT, hfq, and sodC strains were analyzed. Superoxides produced by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase assay did not affect the survival of any strain (data not shown). No difference of survival was observed between the three strains when challenged with 2 mM pyrogallol (Fig. 4B). Two distinct extracellular generators were used in this experiment. The production of superoxides was verified using cytochrome c oxidation; thus, it appears that the lack of Hfq or SodC does not affect resistance against external superoxides in S. meliloti.
FIG. 4.
Resistance to superoxide. (A) Influence of methyl viologen on the growth of WT (closed diamonds), hfq (closed squares), sodB (closed triangles), and sodC (open circles) strains. Cells were grown in GAS medium containing 0 to 100 μM methyl viologen to late stationary growth phase. Residual growth corresponds to the ratio of maximal growth yield in GAS medium supplemented with methyl viologen to maximal growth yield in GAS medium for each strain. The results are the averages from three independent experiments, and the bars represent the standard deviations. (B) Influence of pyrogallol on bacterial survival. Cells of WT (closed diamonds), hfq (closed squares), and sodC (open circles) strains were grown in GAS medium, collected by centrifugation, and incubated in PBS buffer containing 2 mM pyrogallol and 1,000 U ml−1 of bovine liver catalase. Aliquots were removed periodically, and survival was estimated by serial dilution and plating on LB plates. The results are the means from five independent experiments, and the standard deviations are indicated.
The hfq mutant strain is affected for H2O2 resistance.
Protection from hydrogen peroxide stress involves CysK (1, 14), Bfr (75), peroxiredoxin SMc00072 (22, 39), and GshB (46). The levels of these four proteins are reduced in the S. meliloti hfq mutant in both exponential and stationary growth phases. Thus, any change in the H2O2 resistance caused by the hfq mutation would be expected to be equivalent in the exponential and stationary growth phases.
Cellular survival upon exposure to 100 mM H2O2 was measured by using cells grown in GAS medium and collected during the exponential or stationary growth phase. Similar patterns of lethality were observed for the WT and the katC and hfq mutant strains challenged during exponential growth (2- to 3-log reduction of viable cells after 30 min of challenge) (Fig. 5). The WT strain was not severely affected by H2O2 challenge during stationary growth phase. In contrast, the hfq mutant was drastically affected, and a 3-log reduction of viable cells was observed after 30 min of exposure (Fig. 5). The similar behavior patterns of the WT and hfq strains during exponential growth phase suggest that CysK, Bfr, and SMc00072 reduction does not significantly affect the H2O2 resistance of the hfq mutant. Therefore, the vulnerability of the hfq mutant to H2O2 stress during stationary growth phase involves at least one other oxidative defense mechanism. Catalases are important for H2O2 resistance in S. meliloti (62). Moreover, catalase production is affected by Hfq in other organisms (66). Thus, we analyzed the activity of catalases in the WT and hfq mutant strains.
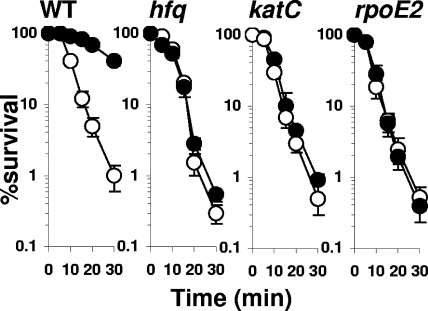
FIG. 5.
Sensitivity of S. meliloti WT, hfq, katC, and rpoE2 strains to H2O2. All the strains were grown in GAS medium. Cells were collected in exponential (open symbols) or stationary (closed symbols) phases of growth and challenged with 100 mM H2O2. The data are represented as percent survival relative to the level for unstressed cells (t = 0 min). The results are the means from five independent experiments.
Analyzing the catalase content by a gel activity assay (62) allowed the detection of KatA, KatB, and KatC activities in both the WT and the hfq mutant strains. The amounts of KatA were similar in hfq and WT strains (Fig. 3). Instead, KatB was barely detectable and KatC was highly reduced in the hfq mutant, compared with the levels for the parental strain (Fig. 3). KatC has been shown to be the main determinant of H2O2 resistance during stationary growth (26). katC and hfq mutants exhibited similar H2O2 survival responses (Fig. 5), suggesting that KatC reduction participates in the H2O2 sensitivity of an hfq mutant in stationary growth phase.
Resistance to heat stress.
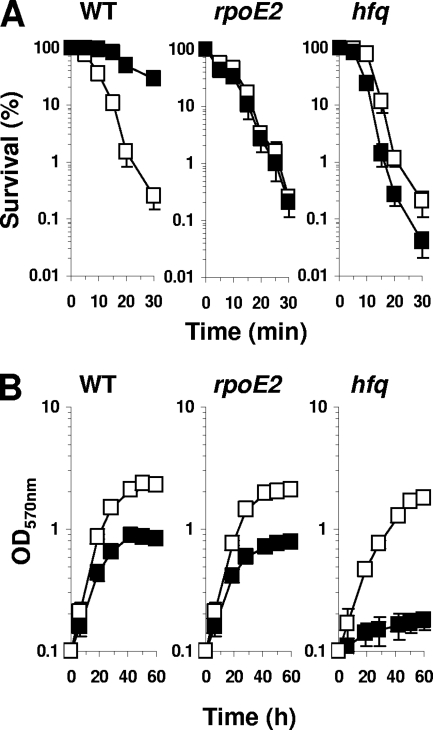
The lack of Hfq led to a drastic reduction of GroES1 and ClpP2 synthesis. E. coli GroES and ClpP were reported to be involved in protein folding and degradation (70) and are required to overcome high temperatures. Thus, we tested the hfq mutant for its sensitivity to a heat shock at 50°C for increasing periods of time. During the exponential phase of growth, the WT strain showed a 3-log loss of viability after 30 min of challenge at 50°C. The WT strain became resistant to heat stress during stationary phase, and its viability decreased only by 50% after 30 min of challenge (Fig. 6). The hfq mutant exhibited 3- and 4-log reductions of viability during the exponential and stationary phases of growth, respectively (Fig. 6). Our results here revealed that Hfq is crucial for heat stress survival only during the stationary phase of growth.
FIG. 6.
Resistance to heat stress of WT, hfq, and rpoE2 strains. (A) Cells were grown in GAS medium and collected during exponential (open symbols) or stationary (closed symbols) growth phase. Cells were challenged at 50°C for 0 to 30 min. The results are the means from five independent experiments. (B) Cells were grown in GAS medium at 30°C (open symbols) or at 40°C (closed symbols).
Hfq modulates rpoE expression.
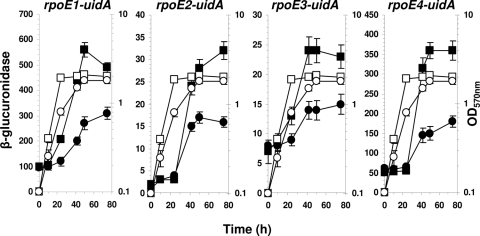
Many points of evidence indicate that multiple phenotypic alterations of the hfq mutant result from defects in transcriptional control. For example, Hfq-dependent sRNAs affect the translation of various alternative sigma factors, such as rpoS or rpoE in enterobacteria (24, 32). S. meliloti does not encode an RpoS sigma factor, although numerous rpoE genes are annotated in its genome (29). Two observations suggested that Hfq might play a role in RpoE regulation. The expression of SMc01418, the most abundant protein in the stationary phase of wild-type cells (10% of the total protein), was greatly reduced in the hfq mutant (1.7% of the total protein). SMc01418, which encodes an RpoE antisigma factor (54), is the first gene in an operon containing rpoE1, the usual structure of rpoE operons. The second indication of the involvement of Hfq in regulating the levels of rpoE expression in S. meliloti was suggested by the fact that various proteins, such as SMb21441 (60), SodC, and KatC (26), previously described as encoded by genes transcribed by RpoE2-containing RNA polymerase, are affected by the hfq mutation. In order to investigate the influence of Hfq on rpoE gene expression, transcriptional fusions between uidA and rpoE1, rpoE2, rpoE3, and rpoE4 were constructed and recombined in the chromosome by a single crossover, thereby yielding strains carrying in tandem an rpoE-uidA fusion and the WT rpoE gene. The expression levels of these fusions in the WT strain and the hfq mutant were analyzed (Fig. 7). The expression of the rpoE1 and rpoE3 genes was induced at the end of exponential growth in the WT strain, while rpoE2 and rpoE4 were induced during stationary growth phase. The same induction patterns were conserved in the hfq mutant, but the level of induction was reduced (Fig. 7).
FIG. 7.
Hfq affects rpoE expression. Strains bearing an uidA transcriptional fusion with rpoE1, rpoE2, rpoE3, and rpoE4 in a WT genetic background (squares) or in an hfq genetic background (circles) were grown in GAS medium. Growth, represented by the OD570 of the culture (open symbols) and β-glucuronidase specific activity (closed symbols), was determined periodically. β-Glucuronidase is expressed as nanomoles of substrate hydrolyzed per min and mg of protein. The results are the averages from at least three independent experiments, and the standard deviations are indicated.
Our results indicate that Hfq is required for optimal synthesis of RpoE1, RpoE2, RpoE3, and RpoE4. The observed effect of Hfq on RpoE synthesis is opposite to that described for E. coli (32, 69), S. Typhimurium (24), and Vibrio cholerae (19). In E. coli and S. Typhimurium, rpoE expression increases after envelope stress. The loss of Hfq function mimics envelope stress by allowing an increase of outer membrane protein (OMP) production (24). RpoE activates the transcription of the sRNAs RybB and MicA, which participate in the decay of the omp mRNA, allowing a regulatory loop to maintain envelope homeostasis (48).
In order to quantify the phenotypic consequences of Hfq control of RpoE, we compared the survival abilities of the hfq and rpoE2 mutants and their parental strain under H2O2 and heat shock stresses. The mutant lacking RpoE2 lost its H2O2 resistance in stationary growth phase because of the absence of KatC. The hfq mutant exhibited the same degree of sensitivity to H2O2 as the katC and rpoE2 mutant strains (Fig. 5). These results highly suggest that the increased sensitivity to H2O2 of the hfq mutant during stationary growth could result from the reduction of RpoE2 production in the cell and the consequent reduction in KatC expression.
In S. meliloti, groESL5 and rpoH2 belong to the RpoE2 regulon (60). During the exponential phase of growth, the resistance of a mutant lacking RpoE2 to heat stress is similar to that of the WT and the hfq mutant strains (Fig. 6). When stationary phase was reached, the WT strain displayed more resistance to heat stress. This heat resistance was not observed in the rpoE2 mutant (Fig. 6). The hfq mutant was more affected by heat stress in stationary growth phase than the rpoE2 mutant. The hfq mutant was not affected for heat shock survival during exponential growth phase. Nevertheless, we observed that the hfq mutant grew poorly at 40°C in GAS medium while the WT and rpoE2 mutant strains still grew (Fig. 6). Therefore, the hfq mutant's heat stress sensitivity involves more genes than those of the RpoE2 regulon.
GroELS chaperones are crucially important in heat shock resistance (12). Among the various gro genes of S. meliloti, groEL1 and groEL5 are particularly important for heat shock; their expression is induced by heat shock, and the growth of the double mutant groEL1-groEL5 is dramatically affected at 40°C (12). Of the two operons, groELS5 and groELS1, only groELS5 is RpoE2 dependent. We have shown that optimal synthesis of GroES1 and RpoE2 is Hfq dependent. Thus, the high heat shock sensitivity of the hfq mutant strain can be explained by the simultaneous defect of groELS1 and groELS5 expression as previously reported (12), the reduced expression of groELS5 being a consequence of the control of rpoE2 by Hfq.
Proteins present in nodules whose expression is altered in an hfq mutant.
Among the 55 Hfq-regulated proteins identified in this paper, 22 have previously been shown to be expressed in nodules by proteomic (20, 21, 45) or transcriptomic (3, 10) analysis. Only 5 of the 22 proteins were produced at a higher level in the hfq mutant than in the WT strain (SMc00140, LivK, SMc00153, SitA, and SMc01834). Two proteins exhibit a more complex pattern of expression. RplL is overproduced during exponential growth and repressed during stationary growth, while EhuB presents the opposite behavior. The other proteins (15/22) are produced at lower levels in the hfq mutant than in its parental strain. PhoD, SMc01418, SMc02156, SMc02692, ClpP2, RplY, and SMc02884 exhibited a reduced synthesis during exponential growth. SMc00784, GroES1, SMc01033, TufB, SMc02495, and SecB are repressed during the stationary phase of growth. Only 3 proteins, GshB1, CysK1, and AtpD, are repressed in both exponential and stationary phases of growth. It is difficult to speculate about the impact of these variations of the proteome of the hfq mutant on symbiosis since some proteins, like enolase, are downregulated during symbiosis (10) and are nevertheless essential for nodulation (25). Others, like SMc00242 and SitA, are essential for an efficient symbiosis establishment (16) and are overproduced during exponential growth in the hfq mutant. Nevertheless, among the proteins present at lower levels in the hfq mutant, PhoD, groES1, GshB1, CysK, and KatB-KatC have previously been shown to be essential for efficient nodulation.
DISCUSSION
Carbon and nitrogen metabolism plays a central role during symbiosis (50). Rhizobia are heterotrophic and can assimilate a wide range of rhizosphere carbon and nitrogen sources. Their metabolic diversity is reflected in their large genome sizes, with many genes devoted to transport and catabolic pathways (29). The striking importance of Hfq in regulating the levels of various periplasmic binding proteins devoted to carbon supply could be important for the competitiveness of S. meliloti in the rhizosphere (27). These transport systems would be expected to be less important in the nodules since dicarboxylic acids are the main carbon and energy source for bacteroids (50). This expectation is consistent with the observation that an agpA mutant is not affected for symbiosis (28). Nevertheless, the reduction of various carbon uptake systems could have a cumulative effect.
Mineral assimilation is also affected in the hfq strain. For example, the synthesis of PhoD binding protein is reduced. phoD mutants are affected for growth in low-P-concentration media (5) and form nodules which fail to fix nitrogen (6). The reduction of PhoD synthesis could contribute to the symbiotic defect of the hfq strain.
Our data suggest that the additive effects of the alterations of several pathways in the hfq mutant result in the symbiotic deficiency. Certain factors involved in adaptation to various stresses may be particularly important. The hfq mutant strain is less resistant to heat shock, and GroES1 is downregulated. S. meliloti possesses four groESL operons and one groEL gene, but the only groEL gene required for symbiosis is groEL1 (12); groEL1 mutants are delayed in nodulation and are unable to fix nitrogen (47). The alteration of groES1 observed in this study must contribute to the symbiotic defect of the hfq mutant. Oxidative defenses are also dramatically affected in the hfq mutant. We observed that scavenging and detoxification enzymes are affected. Several of these alterations have been shown individually to affect symbiosis and nitrogen fixation. This is particularly true for peroxide defenses. GshB is downregulated in the hfq mutant. A gshB mutant showed a delayed-nodulation phenotype coupled to reduced nitrogen fixation capacity. This phenotype was linked to abnormal nodule development (33). KatB and KatC are both downregulated in the hfq strain. A katB katC double mutant nodulates poorly and displays abnormal infection (35).
The significance of Hfq effects on superoxide defenses is less clear. Alfalfa was shown to produce O2− in infection threads and infected cells (59). The gene sodC is specifically induced during Medicago infection (3). Therefore, SodC is expected to detoxify plant reactive oxygen species (ROS) and thus to be important for nodulation. This hypothesis was supported by the role of SodC in other bacteria. Hfq is required for the optimal production of SodC during stationary phase in B. abortus (30), and SodC-defective strains of B. abortus (30) or S. enterica (2) are affected in virulence. Nevertheless, this is not true in all bacteria, since the lack of SodC in Haemophilus ducreyi has no consequence on the virulence (13). We showed that the sodC mutant did not lose resistance against external superoxides. Moreover, in S. meliloti, SodC is not produced in an rpoE2 mutant but symbiotic behavior is not affected (60). Thus, it seems that downregulation of SodC does not contribute to the symbiotic deficiency of the hfq mutant. SodB was only slightly affected in the hfq strain. Although SodB was described as essential for nodulation in S. meliloti RM5000 (58), its inactivation in S. meliloti RM1021 did not affect symbiotic behavior (16).
Many of the phenotypic defects of the S. meliloti hfq strain are similar to those previously described to occur in hfq mutants of E. coli and S. Typhimurium. Conservation of Hfq and similarities in loss-of-function phenotypes suggest that similarities in downstream targets should also exist across different bacteria. We analyzed the extent of this conservation in differential regulation of putative targets by comparing the proteins affected in the S. meliloti hfq mutant to those affected in hfq mutants of other bacteria in proteomic or transcriptomic studies (19, 32, 65, 78). Of the 55 proteins identified in this study, 16 (29%) were previously described as affected by hfq mutation in other bacteria, mainly in E. coli (Table 2). Some proteins are affected similarly (up- or downregulated) in S. meliloti and E. coli (Efp, DppA1, GroES, PpiB, AtpD, and RplY) and in S. meliloti and S. Typhimurium (DppA1, DppA2, RplL, RplY, TufB, Tsf, Bfr, and LivK). The other proteins (CysK1, PotF, GlnA, Ald, PpiA, Pfk, and FtsZ) are regulated in opposite directions. This reversal in direction of differential expression has also previously been observed in phylogenetically closely related bacteria. For example, in E. coli and S. Typhimurium, Ppi, Dpp, and Tsf show opposite directions for hfq-dependent regulation in the two bacteria (32, 65). These differences may be due to the differences in ecological roles and niches that different bacteria adapt to. Other S. meliloti targets of Hfq, such as periplasmic binding proteins, were not identified in proteomic and transcriptomic studies of E. coli and S. Typhimurium hfq strains. Nevertheless, other studies concerning specific sRNAs have shown that periplasmic binding proteins of ABC transporters are affected in E. coli and S. Typhimurium hfq mutants (51-53, 61).
The conservation of Hfq targets is not obligatorily shared with an identical regulation mechanism. For instance, we observed that rpoE gene expression is affected in the S. meliloti hfq mutant as previously observed for E. coli and S. Typhimurium; nevertheless, the loss of Hfq reduced rpoE expression in S. meliloti and increased it in enterobacteria, suggesting different regulatory mechanisms and probably distinct sRNAs participating in this regulation.
Taken together, these data show that the close phenotype of hfq in distantly related bacteria results from a high level of conservation of Hfq targets in these bacteria. In all these bacterial groups, Hfq is implicated in the regulation of various metabolic and stress responses. This diversity must be associated with the involvement of numerous sRNAs in the regulation of metabolism. In E. coli and S. Typhimurium, most of the defects associated with the hfq mutation were explained by the involvement of specific sRNAs (76). sRNAs were also predicted in S. meliloti by using bioinformatics tools (18, 71, 73); their role and targets remain to be identified. Our work has emphasized the key role of Hfq in S. meliloti proteome homeostasis. This study has broadened the number of Hfq targets in S. meliloti and enabled the identification of putative sRNA targets.
Acknowledgments
We thank S. Georgeault, C. Monnier, M. Uguet, and M. C. Savary for technical assistance.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant GM31030 (to G.C.W.), MIT Center for Environmental Health Sciences grant NIEHS P30 ES002109, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, and the Ministère de la Recherche et de l'Education Nationale. L.B.-B. was supported by Region Bretagne (and NIH grant GM31030). G.C.W. is an American Cancer Society Research Professor.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 14 January 2010.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jb.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ackerley, D. F., Y. Barak, S. V. Lynch, J. Curtin, and A. Matin. 2006. Effect of chromate stress on Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 188:3371-3381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ammendola, S., P. Pasquali, F. Pacello, G. Rotilio, M. Castor, S. J. Libby, N. Figueroa-Bossi, L. Bossi, F. C. Fang, and A. Battistoni. 2008. Regulatory and structural differences in the Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutases of Salmonella enterica and their significance for virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 283:13688-13699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ampe, F., E. Kiss, F. Sabourdy, and J. Batut. 2003. Transcriptome analysis of Sinorhizobium meliloti during symbiosis. Genome Biol. 4:R15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Balleza, E., L. N. Lopez-Bojorquez, A. Martinez-Antonio, O. Resendis-Antonio, I. Lozada-Chavez, Y. I. Balderas-Martinez, S. Encarnacion, and J. Collado-Vides. 2009. Regulation by transcription factors in bacteria: beyond description. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 33:133-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bardin, S., S. Dan, M. Osteras, and T. M. Finan. 1996. A phosphate transport system is required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation by Rhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 178:4540-4547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bardin, S. D., and T. M. Finan. 1998. Regulation of phosphate assimilation in Rhizobium (Sinorhizobium) meliloti. Genetics 148:1689-1700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bardonnet, N., and C. Blanco. 1992. uidA antibiotic resistance cassettes for insertion mutagenesis, gene fusion and genetic constructions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 93:243-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barnett, M. J., C. J. Toman, R. F. Fisher, and S. R. Long. 2004. A dual-genome Symbiosis Chip for coordinate study of signal exchange and development in a prokaryote-host interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:16636-16641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8a.Barra-Bily, L., S. P. Pandey, A. Trautwetter, C. Blanco, and G. C. Walker. 2010. The Sinorhizobium meliloti RNA chaperone Hfq mediates symbiosis of S. meliloti and alfalfa. J. Bacteriol. 192:1710-1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beauchamp, C., and I. Fridovich. 1971. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 44:276-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Becker, A., H. Berges, E. Krol, C. Bruand, S. Ruberg, D. Capela, E. Lauber, E. Meilhoc, F. Ampe, F. J. de Bruijn, J. Fourment, A. Francez-Charlot, D. Kahn, H. Kuster, C. Liebe, A. Puhler, S. Weidner, and J. Batut. 2004. Global changes in gene expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 under microoxic and symbiotic conditions. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 17:292-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bestel-Corre, G., E. Dumas-Gaudot, V. Poinsot, M. Dieu, J. F. Dierick, D. van Tuinen, J. Remacle, V. Gianinazzi-Pearson, and S. Gianinazzi. 2002. Proteome analysis and identification of symbiosis-related proteins from Medicago truncatula Gaertn. by two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 23:122-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bittner, A. N., A. Foltz, and V. Oke. 2007. Only one of five groEL genes is required for viability and successful symbiosis in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 189:1884-1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bong, C. T., K. R. Fortney, B. P. Katz, A. F. Hood, L. R. San Mateo, T. H. Kawula, and S. M. Spinola. 2002. A superoxide dismutase C mutant of Haemophilus ducreyi is virulent in human volunteers. Infect. Immun. 70:1367-1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13a.Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carmel-Harel, O., and G. Storz. 2000. Roles of the glutathione- and thioredoxin-dependent reduction systems in the Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae responses to oxidative stress. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54:439-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Coppins, R. L., K. B. Hall, and E. A. Groisman. 2007. The intricate world of riboswitches. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10:176-181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Davies, B. W., and G. C. Walker. 2007. Disruption of sitA compromises Sinorhizobium meliloti for manganese uptake required for protection against oxidative stress. J. Bacteriol. 189:2101-2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.De-la-Pena, C., Z. Lei, B. S. Watson, L. W. Sumner, and J. M. Vivanco. 2008. Root-microbe communication through protein secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 283:25247-25255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.del Val, C., E. Rivas, O. Torres-Quesada, N. Toro, and J. I. Jimenez-Zurdo. 2007. Identification of differentially expressed small non-coding RNAs in the legume endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti by comparative genomics. Mol. Microbiol. 66:1080-1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ding, Y., B. M. Davis, and M. K. Waldor. 2004. Hfq is essential for Vibrio cholerae virulence and downregulates sigma expression. Mol. Microbiol. 53:345-354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Djordjevic, M. A. 2004. Sinorhizobium meliloti metabolism in the root nodule: a proteomic perspective. Proteomics 4:1859-1872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Djordjevic, M. A., H. C. Chen, S. Natera, G. Van Noorden, C. Menzel, S. Taylor, C. Renard, O. Geiger, and G. F. Weiller. 2003. A global analysis of protein expression profiles in Sinorhizobium meliloti: discovery of new genes for nodule occupancy and stress adaptation. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 16:508-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dombrecht, B., C. Heusdens, S. Beullens, C. Verreth, E. Mulkers, P. Proost, J. Vanderleyden, and J. Michiels. 2005. Defence of Rhizobium etli bacteroids against oxidative stress involves a complexly regulated atypical 2-Cys peroxiredoxin. Mol. Microbiol. 55:1207-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Encarnacion, S., Y. Guzman, M. F. Dunn, M. Hernandez, M. del Carmen Vargas, and J. Mora. 2003. Proteome analysis of aerobic and fermentative metabolism in Rhizobium etli CE3. Proteomics 3:1077-1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Figueroa-Bossi, N., S. Lemire, D. Maloriol, R. Balbontin, J. Casadesus, and L. Bossi. 2006. Loss of Hfq activates the sigmaE-dependent envelope stress response in Salmonella enterica. Mol. Microbiol. 62:838-852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Finan, T. M., I. Oresnik, and A. Bottacin. 1988. Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti defective in succinate metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 170:3396-3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Flechard, M., C. Fontenelle, A. Trautwetter, G. Ermel, and C. Blanco. 2009. Sinorhizobium meliloti rpoE2 is necessary for H2O2 stress resistance during the stationary growth phase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 290:25-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fry, J., M. Wood, and P. S. Poole. 2001. Investigation of myo-inositol catabolism in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae and its effect on nodulation competitiveness. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 14:1016-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gage, D. J., and S. R. Long. 1998. alpha-Galactoside uptake in Rhizobium meliloti: isolation and characterization of agpA, a gene encoding a periplasmic binding protein required for melibiose and raffinose utilization. J. Bacteriol. 180:5739-5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Galibert, F., T. M. Finan, S. R. Long, A. Puhler, P. Abola, F. Ampe, F. Barloy-Hubler, M. J. Barnett, A. Becker, P. Boistard, G. Bothe, M. Boutry, L. Bowser, J. Buhrmester, E. Cadieu, D. Capela, P. Chain, A. Cowie, R. W. Davis, S. Dreano, N. A. Federspiel, R. F. Fisher, S. Gloux, T. Godrie, A. Goffeau, B. Golding, J. Gouzy, M. Gurjal, I. Hernandez-Lucas, A. Hong, L. Huizar, R. W. Hyman, T. Jones, D. Kahn, M. L. Kahn, S. Kalman, D. H. Keating, E. Kiss, C. Komp, V. Lelaure, D. Masuy, C. Palm, M. C. Peck, T. M. Pohl, D. Portetelle, B. Purnelle, U. Ramsperger, R. Surzycki, P. Thebault, M. Vandenbol, F. J. Vorholter, S. Weidner, D. H. Wells, K. Wong, K. C. Yeh, and J. Batut. 2001. The composite genome of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Science 293:668-672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gee, J. M., M. W. Valderas, M. E. Kovach, V. K. Grippe, G. T. Robertson, W. L. Ng, J. M. Richardson, M. E. Winkler, and R. M. Roop II. 2005. The Brucella abortus Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase is required for optimal resistance to oxidative killing by murine macrophages and wild-type virulence in experimentally infected mice. Infect. Immun. 73:2873-2880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gouffi, K., V. Pichereau, J. P. Rolland, D. Thomas, T. Bernard, and C. Blanco. 1998. Sucrose is a nonaccumulated osmoprotectant in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 180:5044-5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guisbert, E., V. A. Rhodius, N. Ahuja, E. Witkin, and C. A. Gross. 2007. Hfq modulates the sigmaE-mediated envelope stress response and the sigma32-mediated cytoplasmic stress response in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 189:1963-1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Harrison, J., A. Jamet, C. I. Muglia, G. Van de Sype, O. M. Aguilar, A. Puppo, and P. Frendo. 2005. Glutathione plays a fundamental role in growth and symbiotic capacity of Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 187:168-174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jamet, A., E. Kiss, J. Batut, A. Puppo, and D. Herouart. 2005. The katA catalase gene is regulated by OxyR in both free-living and symbiotic Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 187:376-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jamet, A., S. Sigaud, G. Van de Sype, A. Puppo, and D. Herouart. 2003. Expression of the bacterial catalase genes during Sinorhizobium meliloti-Medicago sativa symbiosis and their crucial role during the infection process. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 16:217-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jebbar, M., L. Sohn-Bosser, E. Bremer, T. Bernard, and C. Blanco. 2005. Ectoine-induced proteins in Sinorhizobium meliloti include an ectoine ABC-type transporter involved in osmoprotection and ectoine catabolism. J. Bacteriol. 187:1293-1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kaberdin, V. R., and U. Blasi. 2006. Translation initiation and the fate of bacterial mRNAs. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30:967-979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Larrainzar, E., S. Wienkoop, W. Weckwerth, R. Ladrera, C. Arrese-Igor, and E. M. Gonzalez. 2007. Medicago truncatula root nodule proteome analysis reveals differential plant and bacteroid responses to drought stress. Plant Physiol. 144:1495-1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Limauro, D., E. Pedone, I. Galdi, and S. Bartolucci. 2008. Peroxiredoxins as cellular guardians in Sulfolobus solfataricus: characterization of Bcp1, Bcp3 and Bcp4. FEBS J. 275:2067-2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39a.Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265-275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Masse, E., and S. Gottesman. 2002. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99:4620-4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mauchline, T. H., J. E. Fowler, A. K. East, A. L. Sartor, R. Zaheer, A. H. Hosie, P. S. Poole, and T. M. Finan. 2006. Mapping the Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 solute-binding protein-dependent transportome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:17933-17938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Metruccio, M. M., L. Fantappie, D. Serruto, A. Muzzi, D. Roncarati, C. Donati, V. Scarlato, and I. Delany. 2009. The Hfq-dependent small noncoding RNA NrrF directly mediates Fur-dependent positive regulation of succinate dehydrogenase in Neisseria meningitidis. J. Bacteriol. 191:1330-1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Miller, J. H. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 44.Mohanty, B. K., V. F. Maples, and S. R. Kushner. 2004. The Sm-like protein Hfq regulates polyadenylation dependent mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 54:905-920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Natera, S. H., N. Guerreiro, and M. A. Djordjevic. 2000. Proteome analysis of differentially displayed proteins as a tool for the investigation of symbiosis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 13:995-1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Naya, L., R. Ladrera, J. Ramos, E. M. Gonzalez, C. Arrese-Igor, F. R. Minchin, and M. Becana. 2007. The response of carbon metabolism and antioxidant defenses of alfalfa nodules to drought stress and to the subsequent recovery of plants. Plant Physiol. 144:1104-1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ogawa, J., and S. R. Long. 1995. The Rhizobium meliloti groELc locus is required for regulation of early nod genes by the transcription activator NodD. Genes Dev. 9:714-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Papenfort, K., V. Pfeiffer, F. Mika, S. Lucchini, J. C. Hinton, and J. Vogel. 2006. SigmaE-dependent small RNAs of Salmonella respond to membrane stress by accelerating global omp mRNA decay. Mol. Microbiol. 62:1674-1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Perez, J. M., F. A. Arenas, G. A. Pradenas, J. M. Sandoval, and C. C. Vasquez. 2008. Escherichia coli YqhD exhibits aldehyde reductase activity and protects from the harmful effect of lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes. J. Biol. Chem. 283:7346-7353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Prell, J., and P. Poole. 2006. Metabolic changes of rhizobia in legume nodules. Trends Microbiol. 14:161-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pulvermacher, S. C., L. T. Stauffer, and G. V. Stauffer. 2009. Role of the Escherichia coli Hfq protein in GcvB regulation of oppA and dppA mRNAs. Microbiology 155:115-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pulvermacher, S. C., L. T. Stauffer, and G. V. Stauffer. 2009. Role of the sRNA GcvB in regulation of cycA in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 155:106-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pulvermacher, S. C., L. T. Stauffer, and G. V. Stauffer. 2009. The small RNA GcvB regulates sstT mRNA expression in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 191:238-248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Raivio, T. L., and T. J. Silhavy. 2001. Periplasmic stress and ECF sigma factors. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55:591-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Repoila, F., and F. Darfeuille. 2009. Small regulatory non-coding RNAs in bacteria: physiology and mechanistic aspects. Biol. Cell 101:117-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Roop, R. M., II, G. T. Robertson, G. P. Ferguson, L. E. Milford, M. E. Winkler, and G. C. Walker. 2002. Seeking a niche: putative contributions of the hfq and bacA gene products to the successful adaptation of the brucellae to their intracellular home. Vet. Microbiol. 90:349-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 58.Santos, R., S. Bocquet, A. Puppo, and D. Touati. 1999. Characterization of an atypical superoxide dismutase from Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 181:4509-4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Santos, R., D. Herouart, S. Sigaud, D. Touati, and A. Puppo. 2001. Oxidative burst in alfalfa-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiotic interaction. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 14:86-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sauviac, L., H. Philippe, K. Phok, and C. Bruand. 2007. An extracytoplasmic function sigma factor acts as a general stress response regulator in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 189:4204-4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sharma, C. M., F. Darfeuille, T. H. Plantinga, and J. Vogel. 2007. A small RNA regulates multiple ABC transporter mRNAs by targeting C/A-rich elements inside and upstream of ribosome-binding sites. Genes Dev. 21:2804-2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sigaud, S., V. Becquet, P. Frendo, A. Puppo, and D. Herouart. 1999. Differential regulation of two divergent Sinorhizobium meliloti genes for HPII-like catalases during free-living growth and protective role of both catalases during symbiosis. J. Bacteriol. 181:2634-2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Simon, R., M. O'Connell, M. Labes, and A. Puhler. 1986. Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 118:640-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sittka, A., S. Lucchini, K. Papenfort, C. M. Sharma, K. Rolle, T. T. Binnewies, J. C. Hinton, and J. Vogel. 2008. Deep sequencing analysis of small noncoding RNA and mRNA targets of the global post-transcriptional regulator, Hfq. PLoS Genet. 4:e1000163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sittka, A., V. Pfeiffer, K. Tedin, and J. Vogel. 2007. The RNA chaperone Hfq is essential for the virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 63:193-217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sonnleitner, E., S. Hagens, F. Rosenau, S. Wilhelm, A. Habel, K. E. Jager, and U. Blasi. 2003. Reduced virulence of a hfq mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa O1. Microb. Pathog. 35:217-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sukhodolets, M. V., and S. Garges. 2003. Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with the ribosomal protein S1 and the Sm-like ATPase Hfq. Biochemistry 42:8022-8034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Takada, A., M. Wachi, and K. Nagai. 1999. Negative regulatory role of the Escherichia coli hfq gene in cell division. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266:579-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Thompson, K. M., V. A. Rhodius, and S. Gottesman. 2007. SigmaE regulates and is regulated by a small RNA in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 189:4243-4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Tomoyasu, T., A. Mogk, H. Langen, P. Goloubinoff, and B. Bukau. 2001. Genetic dissection of the roles of chaperones and proteases in protein folding and degradation in the Escherichia coli cytosol. Mol. Microbiol. 40:397-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ulve, V. M., E. W. Sevin, A. Cheron, and F. Barloy-Hubler. 2007. Identification of chromosomal alpha-proteobacterial small RNAs by comparative genome analysis and detection in Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021. BMC Genomics 8:467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Valentin-Hansen, P., M. Eriksen, and C. Udesen. 2004. The bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: a key player in RNA transactions. Mol. Microbiol. 51:1525-1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Valverde, C., J. Livny, J. P. Schluter, J. Reinkensmeier, A. Becker, and G. Parisi. 2008. Prediction of Sinorhizobium meliloti sRNA genes and experimental detection in strain 2011. BMC Genomics 9:416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Vecerek, B., I. Moll, T. Afonyushkin, V. Kaberdin, and U. Blasi. 2003. Interaction of the RNA chaperone Hfq with mRNAs: direct and indirect roles of Hfq in iron metabolism of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 50:897-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Velayudhan, J., M. Castor, A. Richardson, K. L. Main-Hester, and F. C. Fang. 2007. The role of ferritins in the physiology of Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium: a unique role for ferritin B in iron-sulphur cluster repair and virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 63:1495-1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Vogel, J. 2009. A rough guide to the non-coding RNA world of Salmonella. Mol. Microbiol. 71:1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Waters, L. S., and G. Storz. 2009. Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 136:615-628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Wilson, J. W., C. M. Ott, K. Honer zu Bentrup, R. Ramamurthy, L. Quick, S. Porwollik, P. Cheng, M. McClelland, G. Tsaprailis, T. Radabaugh, A. Hunt, D. Fernandez, E. Richter, M. Shah, M. Kilcoyne, L. Joshi, M. Nelman-Gonzalez, S. Hing, M. Parra, P. Dumars, K. Norwood, R. Bober, J. Devich, A. Ruggles, C. Goulart, M. Rupert, L. Stodieck, P. Stafford, L. Catella, M. J. Schurr, K. Buchanan, L. Morici, J. McCracken, P. Allen, C. Baker-Coleman, T. Hammond, J. Vogel, R. Nelson, D. L. Pierson, H. M. Stefanyshyn-Piper, and C. A. Nickerson. 2007. Space flight alters bacterial gene expression and virulence and reveals a role for global regulator Hfq. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104:16299-16304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]