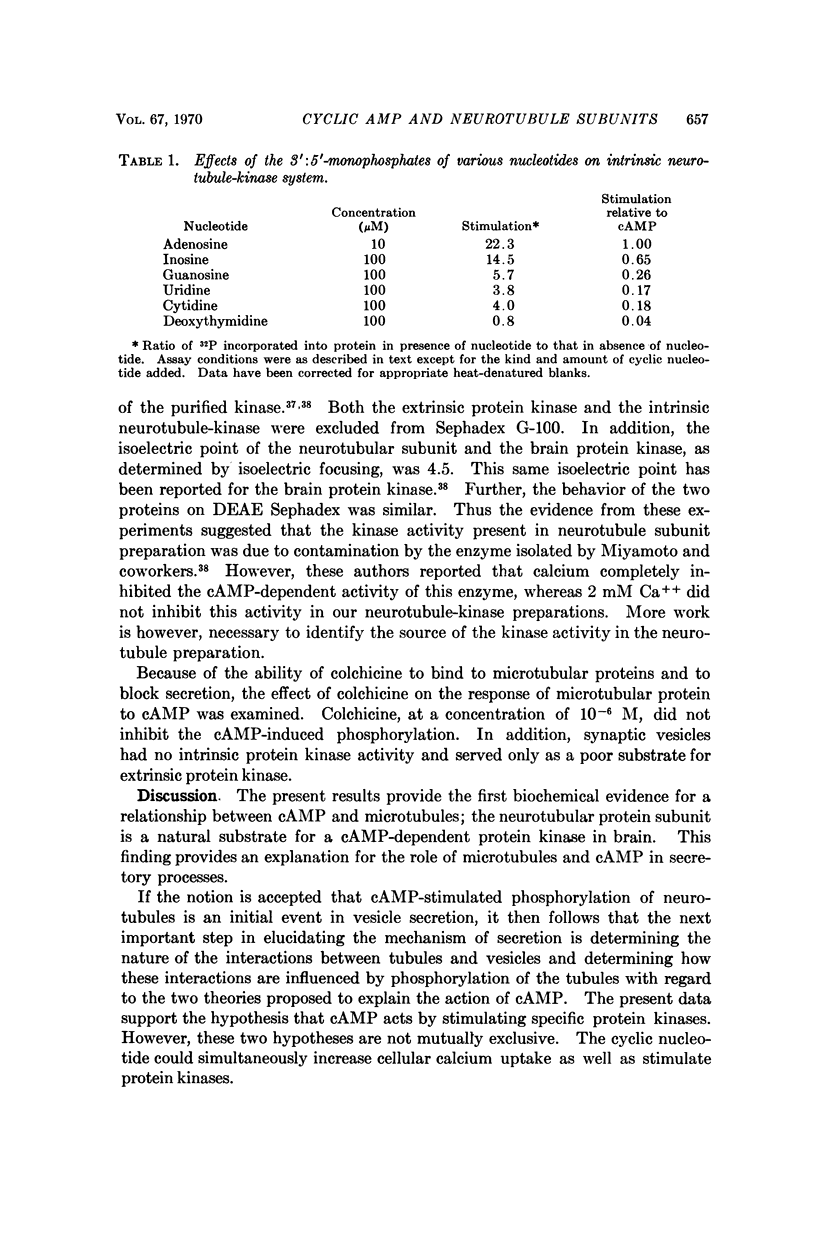
Abstract
The possible relationship between cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate (cAMP) and neurotubules in synaptic transmission has been explored. The neurotubular subunit protein from bovine cerebral cortex has been prepared. The addition of cAMP to this preparation in the presence of ATP stimulates the phosphorylation of serine residue(s) in the principal component of the preparation. The neurotubule subunit thus serves as a substrate for an intrinsic, cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinase closely associated with the neurotubule subunit. The significance of this finding is discussed in terms of a general model for cellular secretion involving microtubules, cyclic AMP, protein kinase, and calcium ion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Frigyesi T. L. Comparison of cerebral regional metabolism of [14C]leucine following third ventricle and intravenous administration in the cat. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):405–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge B. M., Burn J. H., Matschinsky F. M. Theophylline, epinephrine, and neostigmine facilitation of neuromuscular transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1893–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Krebs E. G. A cyclic AMP--stimulated protein kinase in adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falxa M. L., Gill T. J., 3rd Preparation and properties of an alkylated brain protein related to the structural subunit of microtubules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90530-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Long J. A., Jones A. L. The ultrastructure of endocrine glands. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:315–380. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. B. Mechanism for Plant Cellular Morphogenesis. Science. 1962 Dec 28;138(3548):1404–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3548.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):577–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. Studies on adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in rabbit cerebral cortex. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. The influence of chemical agents on the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-Phosphate in slices of rabbit cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3417–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Action of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent histone kinase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5763–5765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Phosphorylation of liver histone following the administration of glucagon and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1276–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAWISTA S. E. ON THE ACTION OF COLCHICINE, THE MELANOCYTE MODEL. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:361–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShan W. H., Hartley M. W. Production, storage and release of anterior pituitary hormones. Ergeb Physiol. 1965;56:264–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. 3. Purification and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6395–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. The role of the lac promotor locus in the regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1336–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Tenenhouse A. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, CA++, and membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1364–1370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., RALL T. W., MENON T. Adenyl cylase. I. Distribution, preparation, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H. Studies on sulfhydryl groups during cell division of sea-urchin eggs. 8. Some properties of mitotic apparatus proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 4;112(1):132–145. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6585(96)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Taylor E. W. Isolation of a protein subunit from microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):549–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Creveling C. R., Daly J. Stimulated formation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in cerebral cortex: synergism between electrical activity and biogenic amines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoor R. P., Ferguson F. C., Jr Colchicine. IV. Neuromuscular transmission in isolated frog and rat tissues. J Pharm Sci. 1965 May;54(5):779–780. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600540524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Hiramoto Y., Marsland D. Studies on the microtubules in heliozoa. 3. A pressure analysis of the role of these structures in the formation and maintenance of the axopodia of Actinosphaerium nucleofilum (Barrett). J Cell Biol. 1966 Apr;29(1):77–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.29.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtle J. R., Littleton G. K., Kipnis D. M. Stimulation of insulin secretion by theophylline. Nature. 1967 Feb 18;213(5077):727–728. doi: 10.1038/213727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P., SHERIDAN M. N. THE MORPHOLOGY AND ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF ISOLATED CEREBRAL CORTICAL SYNAPTIC VESICLES. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C., Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The colchicine-binding protein of mammalian brain and its relation to microtubules. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4466–4479. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
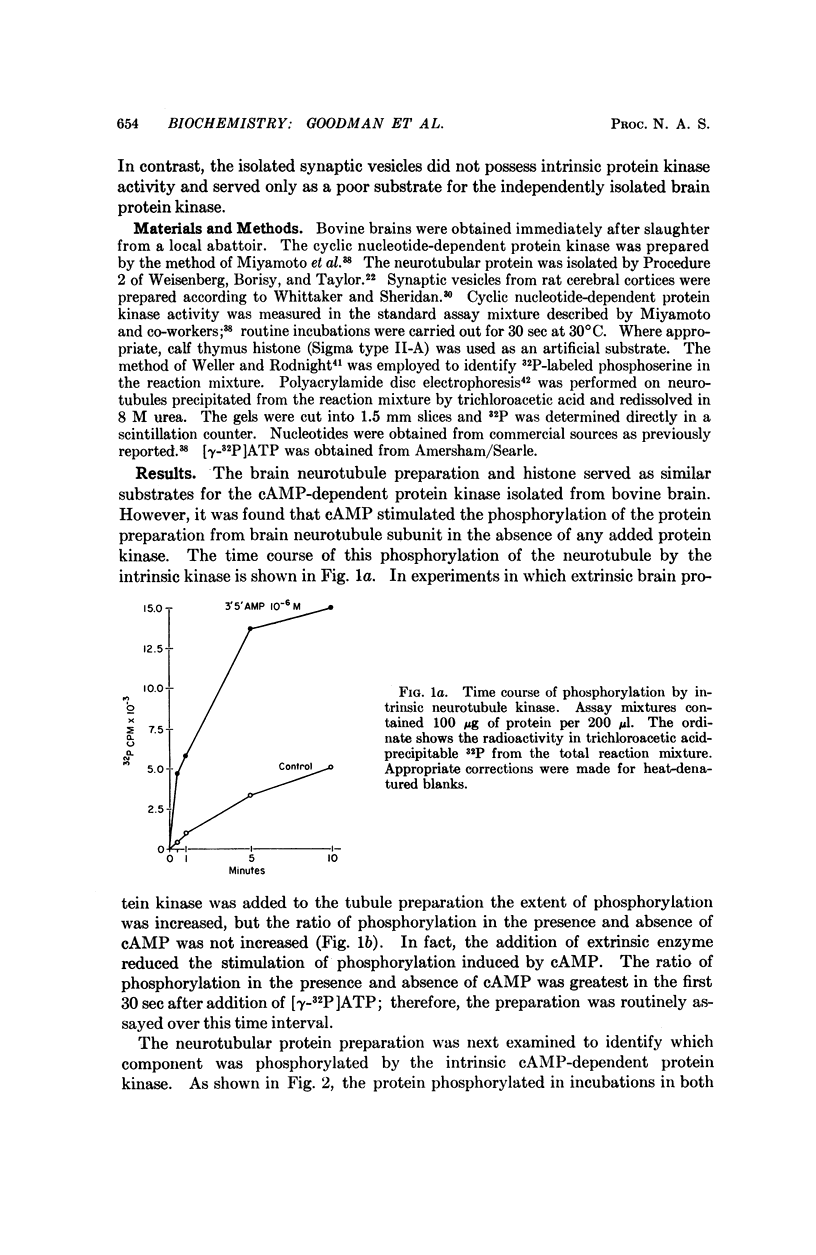
- Weller M., Rodnight R. Stimulation by cyclic AMP of intrinsic protein kinase activity in ox brain membrane preparations. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):187–188. doi: 10.1038/225187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]