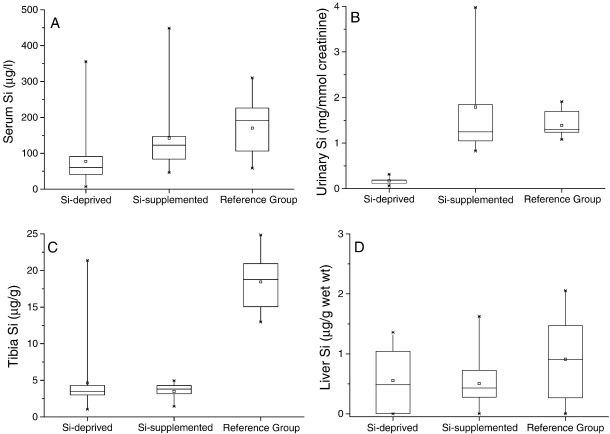
Fig. 1.
Fasting serum Si (A) and urinary Si excretion (B), and Si contents of the left tibia (C) and liver (D) of the rats in the Si-deprived group (n = 20 rats), Si-supplemented group (n = 10) and reference group (n = 10 rats on the standard rodent stock feed). [Urine samples were only available for eight rats in the Si-deprived group, five rats in the Si-supplemented group and seven rats in the reference group.] Fasting serum Si and urinary Si excretion were significantly lower in the Si-deprived group compared to the Si-supplemented group (P = 0.03 and P = 0.004, respectively; unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test). However, there were no significant differences in Si contents of the left tibia and the liver between the two groups.