Abstract
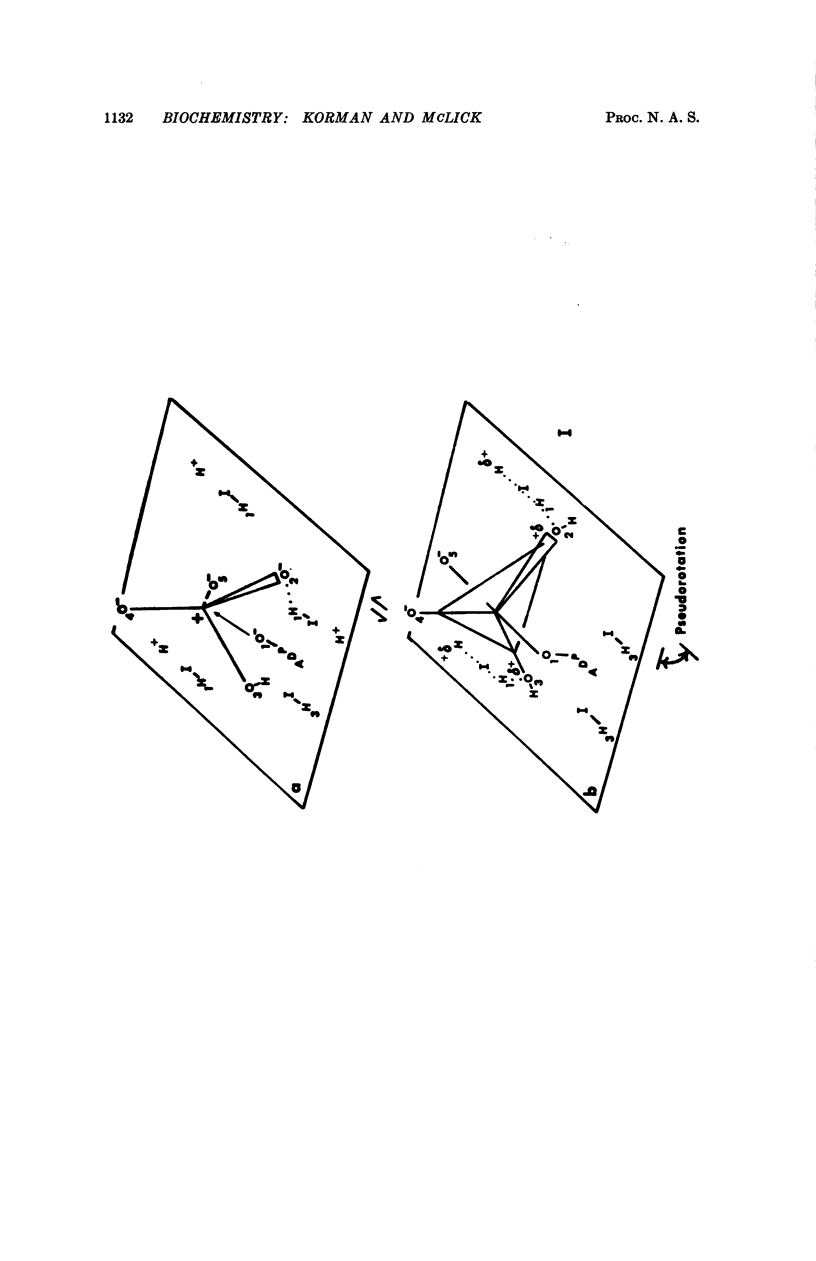
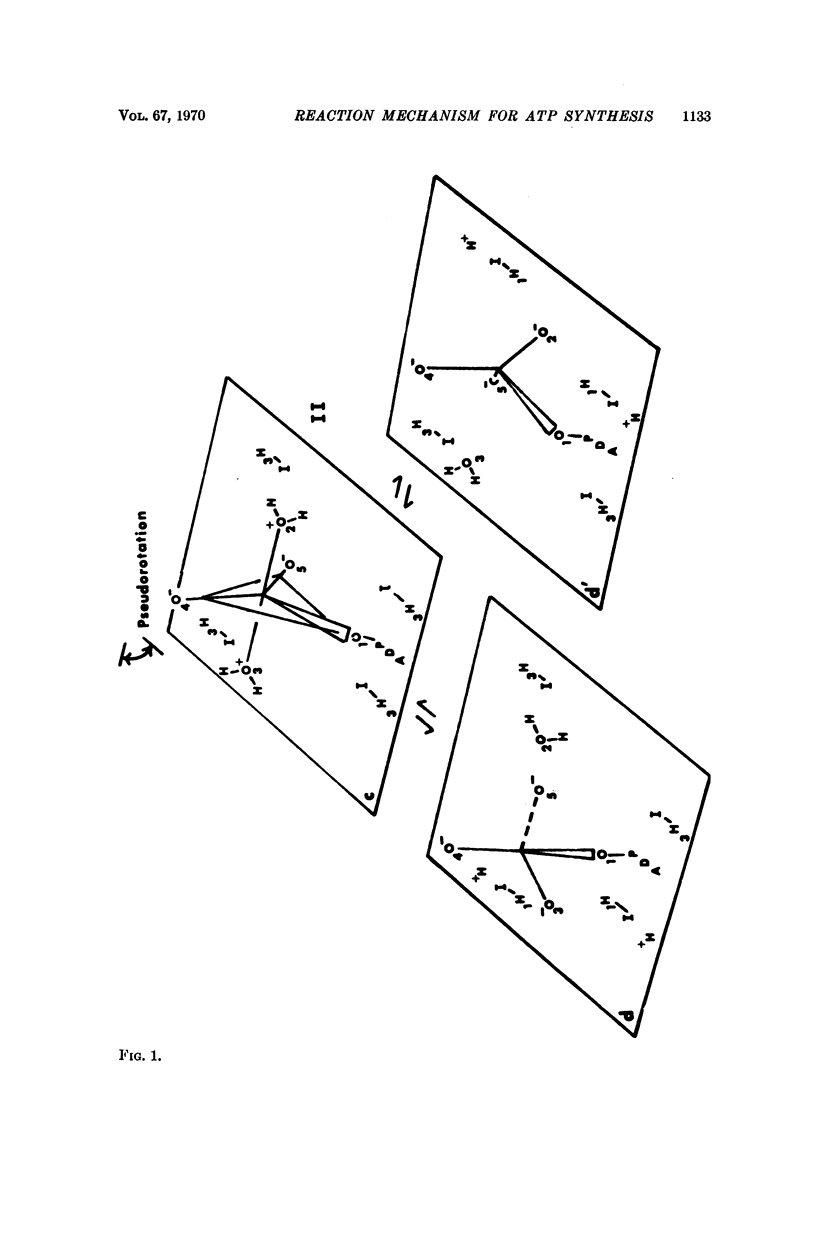
A mechanism is presented for the ATP synthesis reaction of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. This mechanism is a dynamic, stereospecific, microscopically reversible mechanism in which enzyme-bound substrates, ADP, and inorganic phosphate directly combine in a SN2 type of process which proceeds with retention of configuration at the phosphate phosphorus center. The mechanism involves unstable, pentacovalent trigonal bipyramidal reaction intermediates which are pseudorotationally related. The mechanism accounts for all of the observed net and equilibrium exchange reactions and their relative rates. All of the exchange reactions are directly referrable to the ATP synthesis mechanism, and are circumstantial traits of that mechanism.
Full text
PDF