Abstract
α-Bungarotoxin, a polypeptide of mol wt 8000 purified from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus, blocks irreversibly and specifically the excitation by cholinergic agonists on the isolated electroplax and on purified membrane fragments in vitro. The toxin also blocks the in vitro binding of decamethonium to a protein recently isolated from electric tissue. This observation strengthens our earlier conclusion that this protein is the cholinergic receptor macromolecule.
Full text
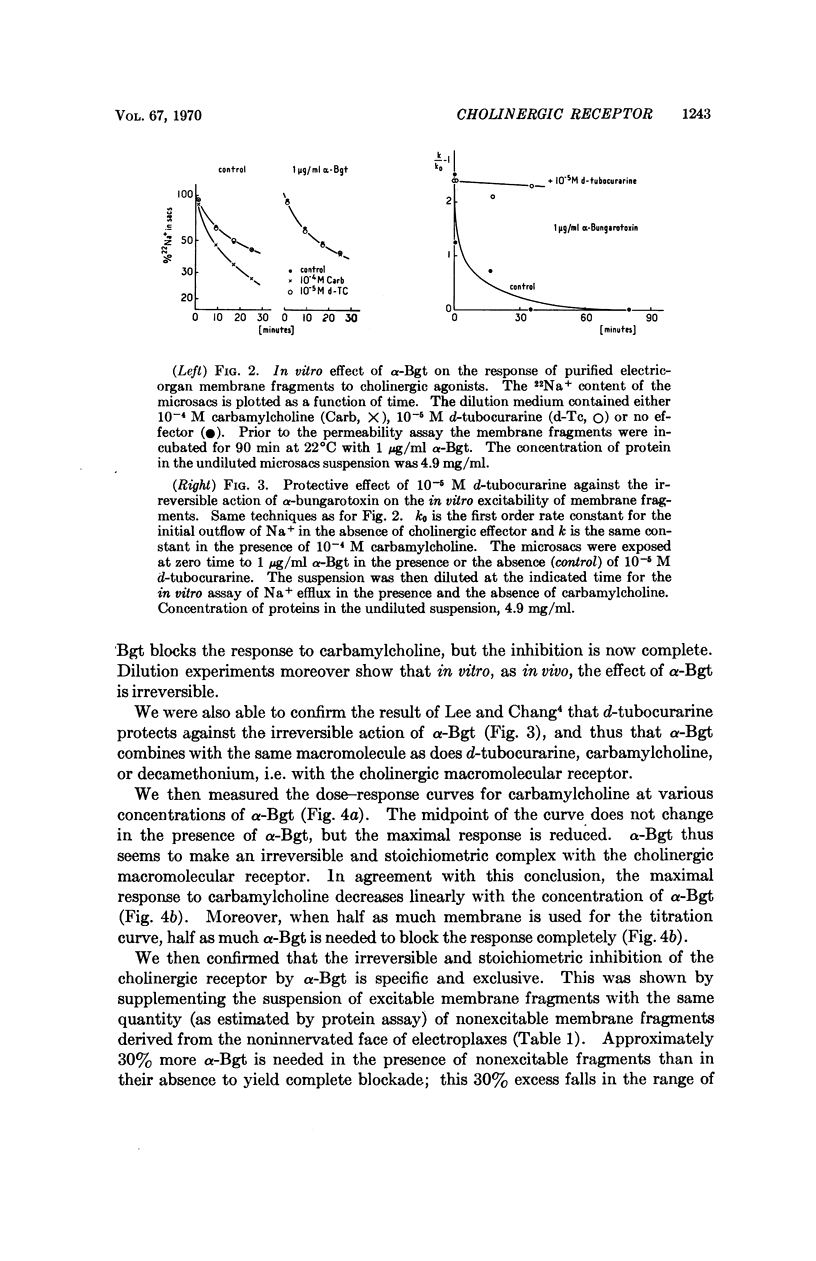
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAGAS C., PENNA-FRANCA E., NISHIE K., GARCIA E. J. A study of the specificity of the complex formed by gallamine triethiodide with a macromolecular constituent of the electric organ. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 May;75(1):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90414-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C., LEE C. Y. ISOLATION OF NEUROTOXINS FROM THE VENOM OF BUNGARUS MULTICINCTUS AND THEIR MODES OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING ACTION. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Jul 1;144:241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Gautron J., Israël M., Podleski T. Séparation de membranes excitables à partir de l'organe électrique d'Electrophorus electricus. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Nov 3;269(18):1788–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Huchet M., Meunier J. C. Extraction à partir du tissu électrique de gymnote d'une protéine présentant plusieurs propriétés caractéristiques du récepteur physiologique de l'acétylcholine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jun 8;270(23):2864–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRENPREIS S. Isolation and identification of the acetylcholine receptor protein of electric tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 18;44:561–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGMAN H. B., PODLESKI T. R., BARTELS E. CORRELATION OF MEMBRANE POTENTIAL AND POTASSIUM FLUX IN THE ELECTROPLAX OF ELECTROPHORUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:138–150. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREMZNER L. T., WILSON I. B. A PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1902–1905. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Changeux J. P. Démonstration de l'excitation par des agonistes cholinergiques à partir des fractions de membranes purifiées, in vitro. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Mar 9;270(10):1400–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., LASKOWSKI M., Jr Naturally occurring trypsin inhibitors. Adv Protein Chem. 1954;9:203–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Torre J. L., Lunt G. S., De Robertis E. Isolation of a cholinergic proteolipid receptor from electric tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C., Chiu T. H., Chiu P. J., Tseng T. C., Lee S. Y. Pharmacological properties of cardiotoxin isolated from Formosan cobra venom. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;259(4):360–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00536909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C. Modes of actions of purified toxins from elapid venoms on neuromuscular transmission. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(2):555–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Tseng L. F., Chiu T. H. Influence of denervation on localization of neurotoxins from clapid venoms in rat diaphragm. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1177–1178. doi: 10.1038/2151177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesca P., Paoletti C. A protein inhibitor of acid deoxyribonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):913–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Gilmour L. P. A muscarone-binding material in electroplax and its relation to the acetylcholine receptor. I. Centrifugal assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):496–503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Gilmour L. P., Eldefrawi M. E. A muscarone-binding material in electroplax and its relation to the acetylcholine receptor. II. Dialysis assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):438–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski T., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Compared effects of dithiotreitol on the interaction of an affinity-labeling reagent with acetylcholinesterase and the excitable membrane of the electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1239–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. A new kind of drug antagonism: evidence that agonists cause a molecular change in acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):394–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



