Abstract
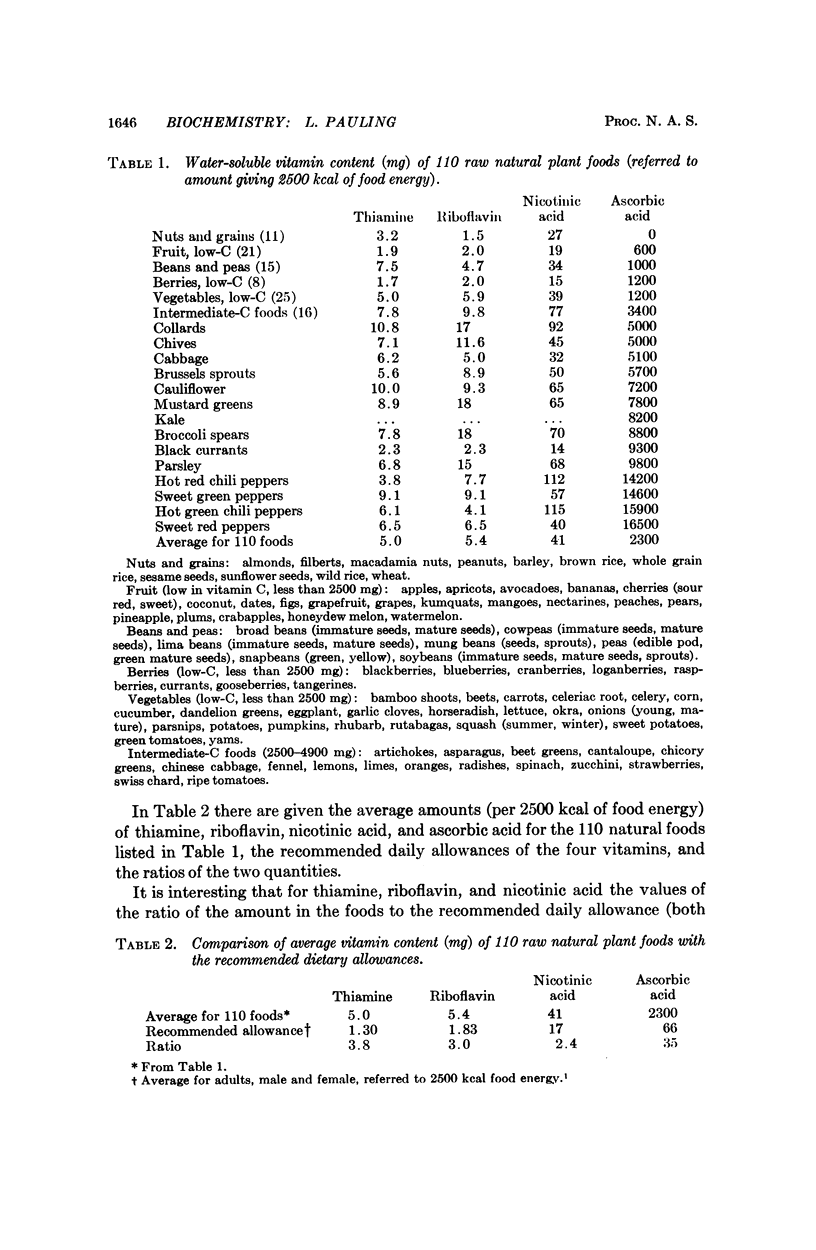
Ascorbic acid differs from other vitamins in that an exogenous source is required by only a few animal species. It is pointed out that this fact indicates that the amount contained in a diet of raw natural plant food is less than the optimum intake, corresponding to the best health. This argument leads to the conclusion that the optimum daily intake is about 2.3 g or more, for an adult with energy requirement 2500 kcal day-1.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNS J. J., MOSBACH E. H., SCHULENBERG S. Ascorbic acid synthesis in normal and drug-treated rats, studied with L-ascorbic-1-C14 acid. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri C. R., Chatterjee I. B. L-ascorbic acid synthesis in birds: phylogenetic trend. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):435–436. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz N. H. On the Evolution of Biochemical Syntheses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Jun;31(6):153–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.6.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L., Delbrück M. THE NATURE OF THE INTERMOLECULAR FORCES OPERATIVE IN BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES. Science. 1940 Jul 26;92(2378):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.92.2378.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L. Orthomolecular psychiatry. Varying the concentrations of substances normally present in the human body may control mental disease. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):265–271. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone I. Hypoascorbemia, the genetic disease causing the human requirement for exogenous ascorbic acid. Perspect Biol Med. 1966 Autumn;10(1):133–134. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1966.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Deason G. Individuality in vitamin C needs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1638–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



