Abstract
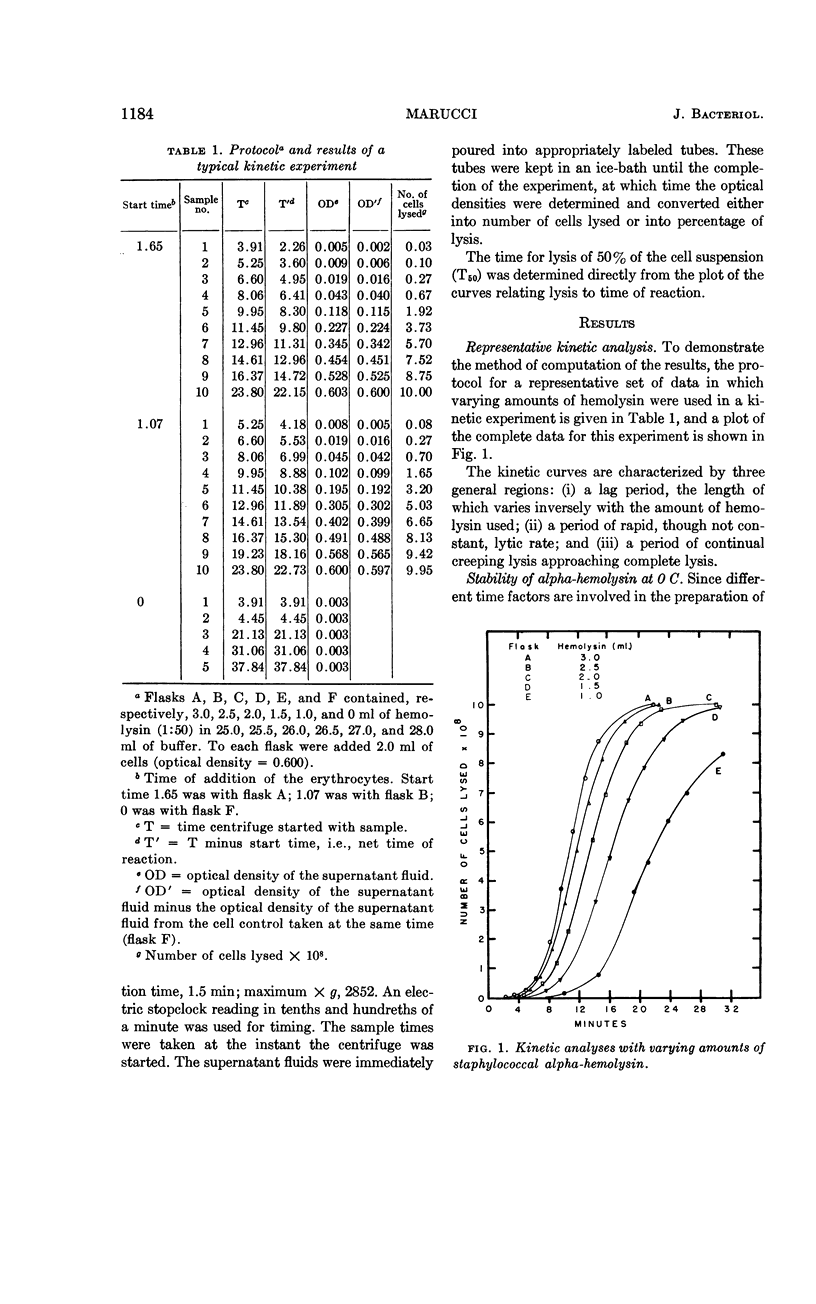
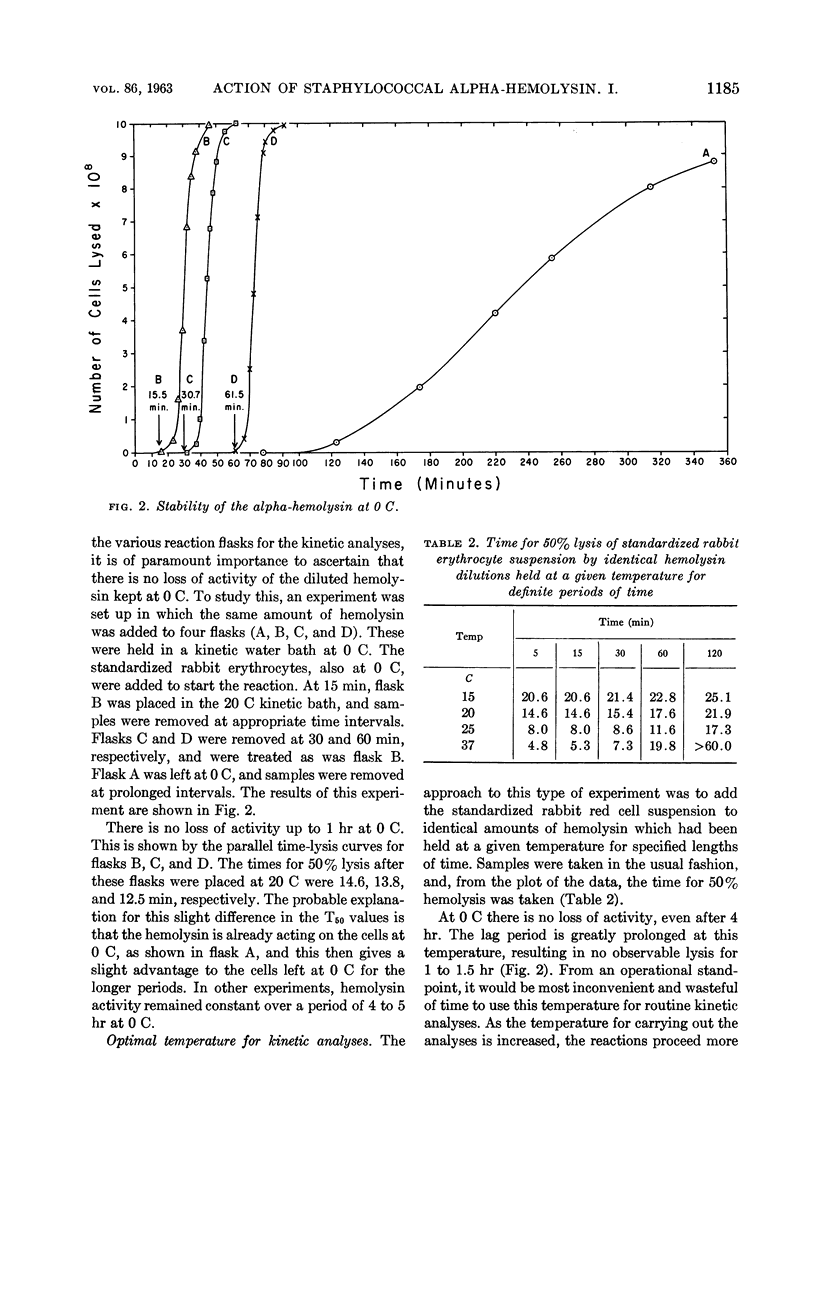
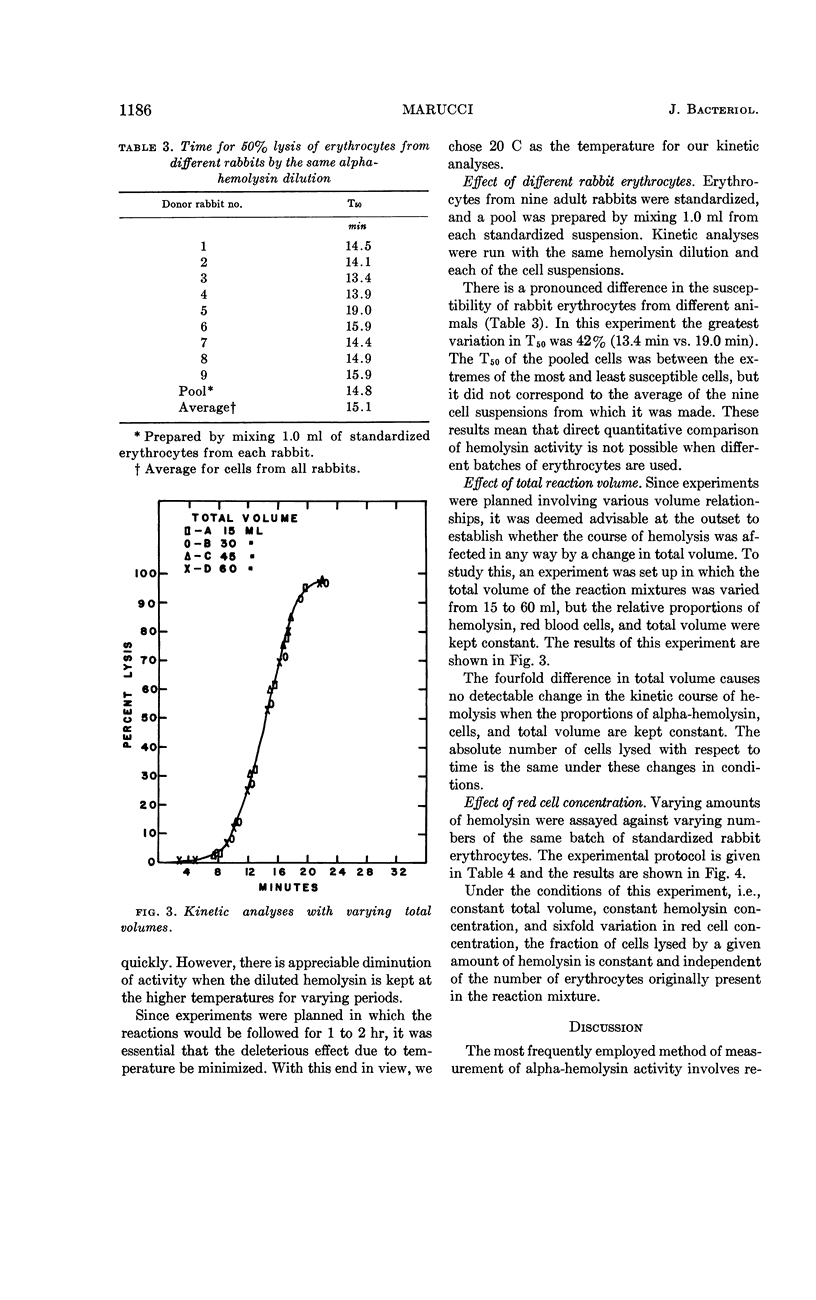
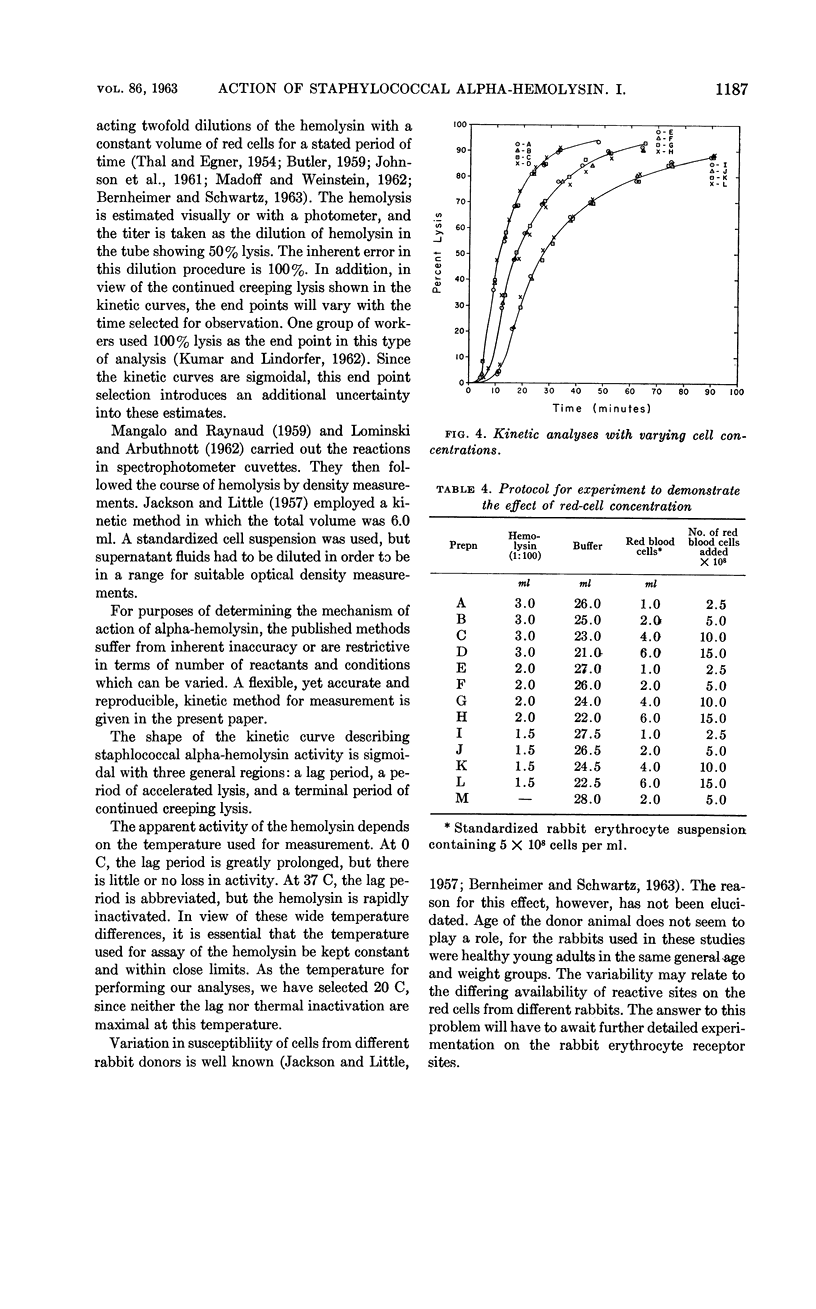
Marucci, Americo A. (Upstate Medical Center, Syracuse, N.Y.). Mechanism of action of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. I. Some factors influencing the measurement of alpha-hemolysin. J. Bacteriol. 86:1182–1188. 1963.—A kinetic method for the accurate and reproducible measurement of the action of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin on rabbit erythrocytes is described. The activity of the alpha-hemolysin depends upon the temperature used for measurement. At 37 C the hemolysin lyses cells faster, but it in turn is rather quickly inactivated. At 0 C there is no inactivation, but the rate of lysis is greatly decreased. There is no change in the activity with change in total reaction volume, providing that the concentrations of cells and hemolysin are kept constant. The fraction of rabbit red cells lysed by a given amount of hemolysin in a given time is constant and independent of the total number of cells in the reaction mixture.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER L. O. Studies on the preparation and isoelectric point of staphylococcal alpha-haemolysin. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):67–73. doi: 10.1042/bj0710067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., LITTLE R. M. Staphylococcal toxins. I. Factors affecting the hemolytic activity of alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Feb;3(1):47–54. doi: 10.1139/m57-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR S., LINDORFER R. K. The characterization of staphylococcal toxins. I. The electrophoretic migration of the alpha hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal, and leucocidal activities of crude toxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1095–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOMINSKI I., ARBUTHNOTT J. P. Some characteristics of Staphylococcus alpha haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:515–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAARUCCI A. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF STAPHYLOCCAL ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN. II. ANALYSIS OF THE KINETIC CURVE AND INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTIBODY. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1189–1195. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1189-1195.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF M. A., WEINSTEIN L. Purification of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:914–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.914-918.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J., THATCHER F. S., MONTFORD J. Studies with staphylococcal toxins. V. Possible identification of alpha hemolysin with a proteolytic enzyme. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:183–194. doi: 10.1139/m60-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A., EGNER W. Local effect of staphylococcal toxin; studies on blood vessels with particular reference to phenomenon dermonecrosis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 May;57(5):392–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


