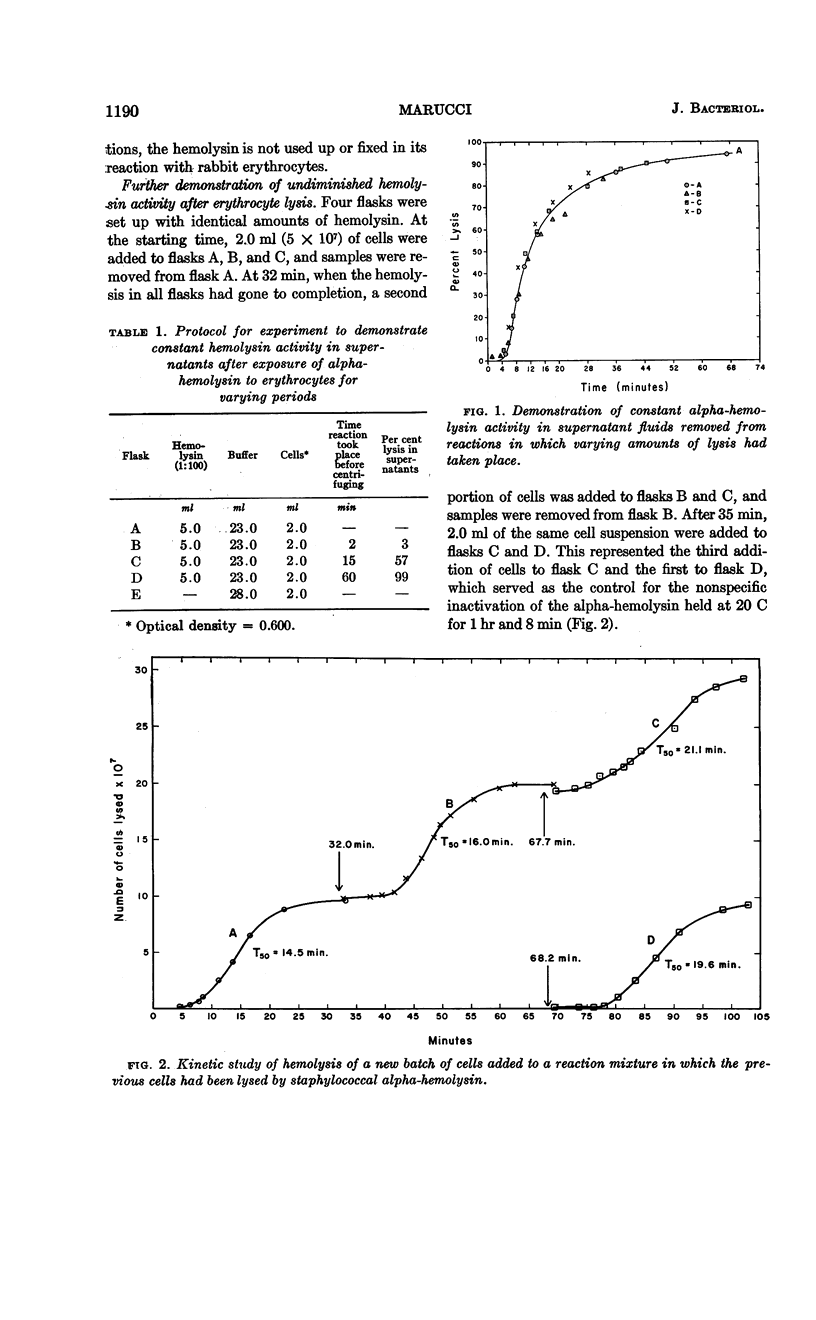
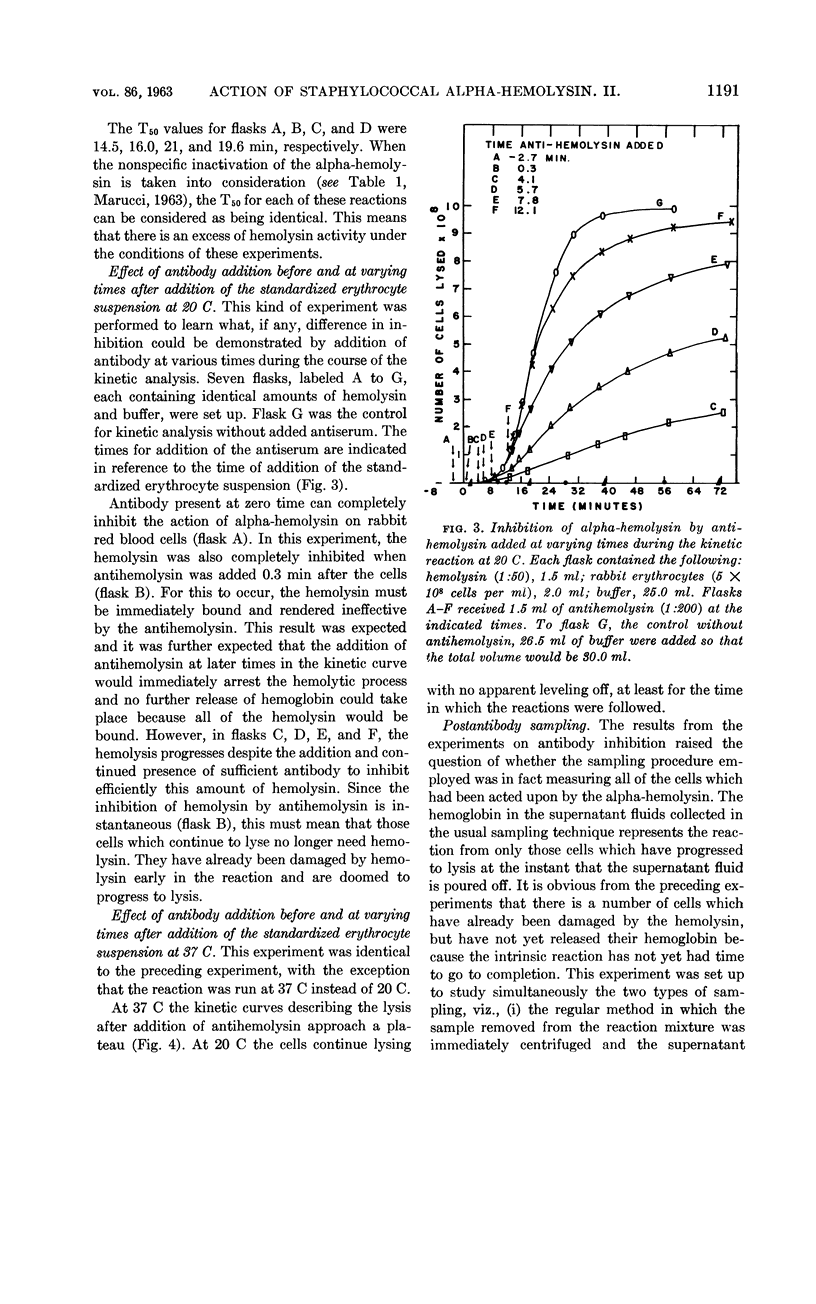
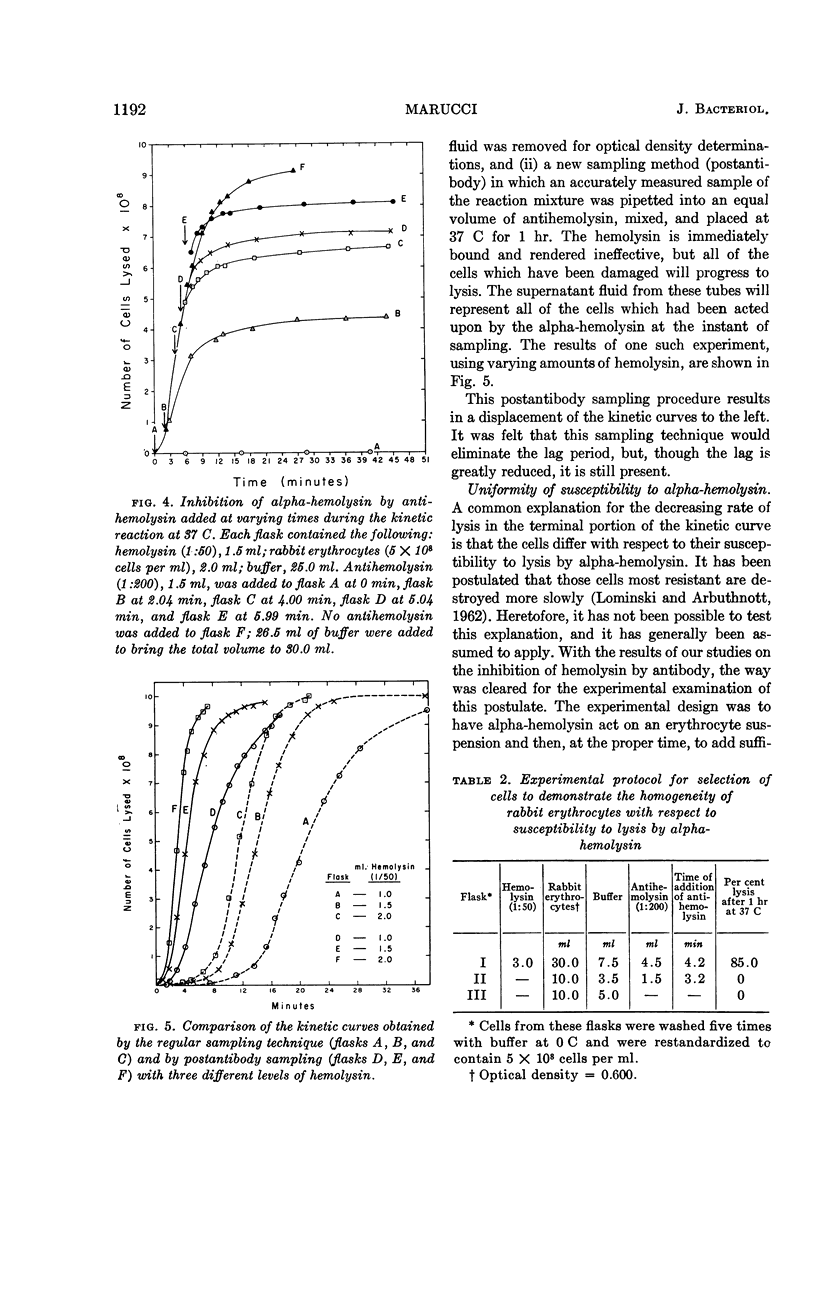
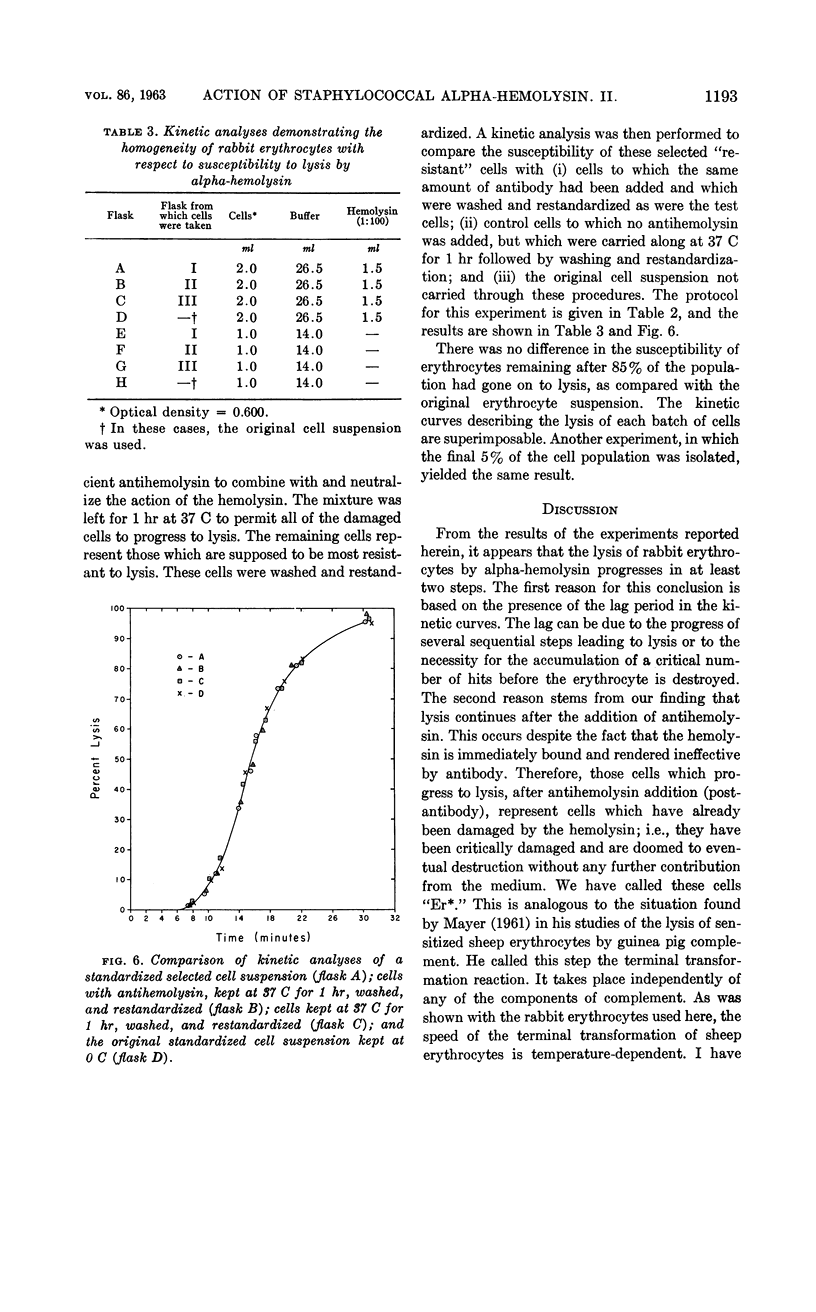
Abstract
Marucci, Americo A. (Upstate Medical Center, Syracuse, N.Y.). Mechanism of action of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. II. Analysis of the kinetic curve and inhibition by specific antibody. J. Bacteriol. 86:1189–1195. 1963.—At least two steps are necessary before the rabbit erythrocyte is lysed by staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. The first step involves the reaction of alpha-hemolysin with the red cell. The second step, leading to the release of hemoglobin, is an intrinsic reaction of the damaged red cell and takes place without further participation of hemolysin. The speed of this intrinsic reaction is temperature-dependent. Erythrocytes taken from the same rabbit do not vary in their susceptibility to the alpha-hemolysin. From the results of the experiments described herein, a preliminary hypothesis on the mechanism of action of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin is given.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CINADER B. Antibody to enzymes--a three-component system. Introduction: immunochemistry of enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 8;103:495–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR S., LINDORFER R. K. The characterization of staphylococcal toxins. I. The electrophoretic migration of the alpha hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal, and leucocidal activities of crude toxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1095–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOMINSKI I., ARBUTHNOTT J. P. Some characteristics of Staphylococcus alpha haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:515–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARUCCI A. A. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN. I. SOME FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MEASUREMENT OF ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1182–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1182-1188.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J., THATCHER F. S., MONTFORD J. Studies with staphylococcal toxins. V. Possible identification of alpha hemolysin with a proteolytic enzyme. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:183–194. doi: 10.1139/m60-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


