Abstract
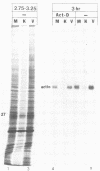
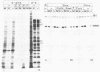
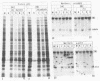
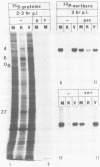
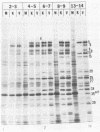
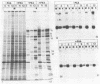
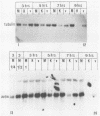
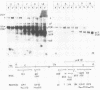
Herpes simplex virus virions contain one or more functions which mediate shutoff of host protein synthesis, disaggregation of host polyribosomes, and degradation of host mRNA. We studied aspects of the host shutoff mechanism by using herpes simplex virus type 1 mutants deficient in virion-induced shutoff of host protein synthesis (G. S. Read and N. Frenkel, J. Virol. 46:498-512, 1983). Shutoff of host protein synthesis by the wild-type virus was associated with degradation of host mRNAs, including beta-actin, alpha-tubulin, and heat shock protein 70. In contrast, the virion host shutoff (vhs) mutants were deficient to various degrees in their ability to induce host mRNA degradation; the extent of mRNA degradation correlated well with the extent of inhibition of host protein synthesis. This finding suggests that inhibition of host protein synthesis and degradation of host mRNA were mediated by the same virion-associated function. Virion-induced degradation of host mRNA was not prevented by inhibitors of ribosome translocation, nor could it be augmented, for mutant vhs-1, by drugs which disaggregate polyribosomes. This suggests that mRNA in polyribosomes, as well as nonpolyribosomal mRNA, is susceptible to virion-induced degradation. Finally, the half-life of viral transcripts was also prolonged in cells infected with the vhs-1 mutant virus, suggesting that the vhs function indiscriminately decreased the half-lives of both host and viral mRNAs. The vhs function may thus play a dual role in virus infection. (i) It inhibits host gene expression, and (ii) it enables rapid transitions in the expression of viral genes which are sequentially transcribed as infection progresses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastow K. F., Bouchard J., Ren X. J., Cheng Y. C. Synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase and metabolism of related RNA in a methotrexate resistant human cell line infected with herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Flynn C. Electrophoresis in the presence of Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 stains polyacrylamide gels during protein fractionation. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):84–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley P. J., Davies J. A., McCullagh K. G., Kerr I. M. Activation of the ppp(A2'p)nA system in interferon-treated, herpes simplex virus-infected cells and evidence for novel inhibitors of the ppp(A2'p)nA-dependent RNase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., Cannon M., Davies J. Mechanism of inhibition of eukaryotic protein synthesis by trichothecene fungal toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):30–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Rapid alterations in initiation rate and recruitment of inactive RNA are temporally correlated with S6 phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):539–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rushford C. L., Dorney D. J., Wilson G. N., Schmickel R. D. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: molecular analysis of cloned fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., McMenamin M. M. Early virion-associated suppression of cellular protein synthesis by herpes simplex virus is accompanied by inactivation of mRNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jul;65(Pt 7):1225–1228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-7-1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Suppression of the synthesis of cellular macromolecules by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):37–51. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M., Morse L. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XI. Apparent clustering of functions effecting rapid inhibition of host DNA and protein synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):825–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.825-827.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González R. G., Blackburn B. J., Schleich T. Fractionation and structural elucidation of the active components of aurintricarboxylic acid, a potent inhibitor of protein nucleic acid interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 24;562(3):534–545. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Tanese N., Fuchs E. Complementary DNA sequence of a human cytoplasmic actin. Interspecies divergence of 3' non-coding regions. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Sadler J. R., Betz J. L. Virion component of herpes simplex virus type 1 KOS interferes with early shutoff of host protein synthesis induced by herpes simplex virus type 2 186. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):312–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.312-316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R. Studies on the selectivity of DNA precipitation by spermine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5493–5504. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C. Inhibition of host protein synthesis and degradation of cellular mRNAs during infection by influenza and herpes simplex virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1644–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom H. C., Liao W. S., Taylor J. M., Willwerth G. E., Eadline T. S. Rapid and selective shutoff of plasma protein production in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected hepatoma cells. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):548–562. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Capasso O., Heintz N., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle control of the human HSP70 gene: implications for the role of a cellular E1A-like function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):628–633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H. Analysis of the two steps in polypeptide chain initiation inhibited by pactamycin. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):811–818. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Türler H. Simian virus 40 and polyoma virus induce synthesis of heat shock proteins in permissive cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus-infected cells contain a function(s) that destabilizes both host and viral mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1926–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Shriver K., Dawson C., Chan W. L. Herpes simplex virus infection causes the accumulation of a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Burka E. R., Conconi F. M., Perl W., Rifkind R. A. Polyribosome dissociation and formation in intact reticulocytes with conservation of messenger ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1437–1443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayman B. A., Nishioka Y. Differential stability of host mRNAs in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Nucleotide sequence and structural features of a novel US-a junction present in a defective herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.140-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Structure and role of the herpes simplex virus DNA termini in inversion, circularization and generation of virion DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai H., Maxwell I. H., Pizer L. I. Herpesvirus infection alters the steady-state levels of cellular polyadenylated RNA in polyoma virus-transformed BHK cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1131–1134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1131-1134.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Jones G., Silverstein S. Inhibition by vesicular stomatitis virus of herpes simplex virus-directed protein synthesis. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarianni E. L., Preston C. M. Activation of cellular stress protein genes by herpes simplex virus temperature-sensitive mutants which overproduce immediate early polypeptides. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L. Initiation and elongation of protein synthesis in growing cells: differential inhibition by cycloheximide and emetine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jul;182(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Beard P. The effect of herpes virus infection on mRNA in polyoma virus transformed cells. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):477–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Borman G. S., Rousta M. K. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1374–1375. doi: 10.1038/2061374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Weil S., Hunter A. R. Changes in RNA metabolism and accumulation of presumptive messenger RNA during transition from the growing to the quiescent state of cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):745–766. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schek N., Bachenheimer S. L. Degradation of cellular mRNAs induced by a virion-associated factor during herpes simplex virus infection of Vero cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):601–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.601-610.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D., Pizer L. I. Herpesvirus infection modifies adenovirus RNA metabolism in adenovirus type 5-transformed cells. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.1-12.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus-induced changes in cellular and adenovirus RNA metabolism in an adenovirus type 5-transformed human cell line. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):474–487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.474-487.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Quantitation of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA in infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):889–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.889-901.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. Polysomes and protein synthesis in cells infected with a DNA virus. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejedor F., Amils R., Ballesta J. P. Photoaffinity labeling of the pactamycin binding site on eubacterial ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3667–3672. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]