Abstract
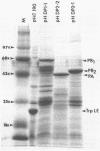
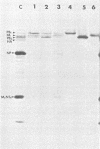
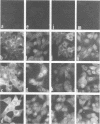
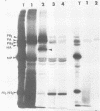
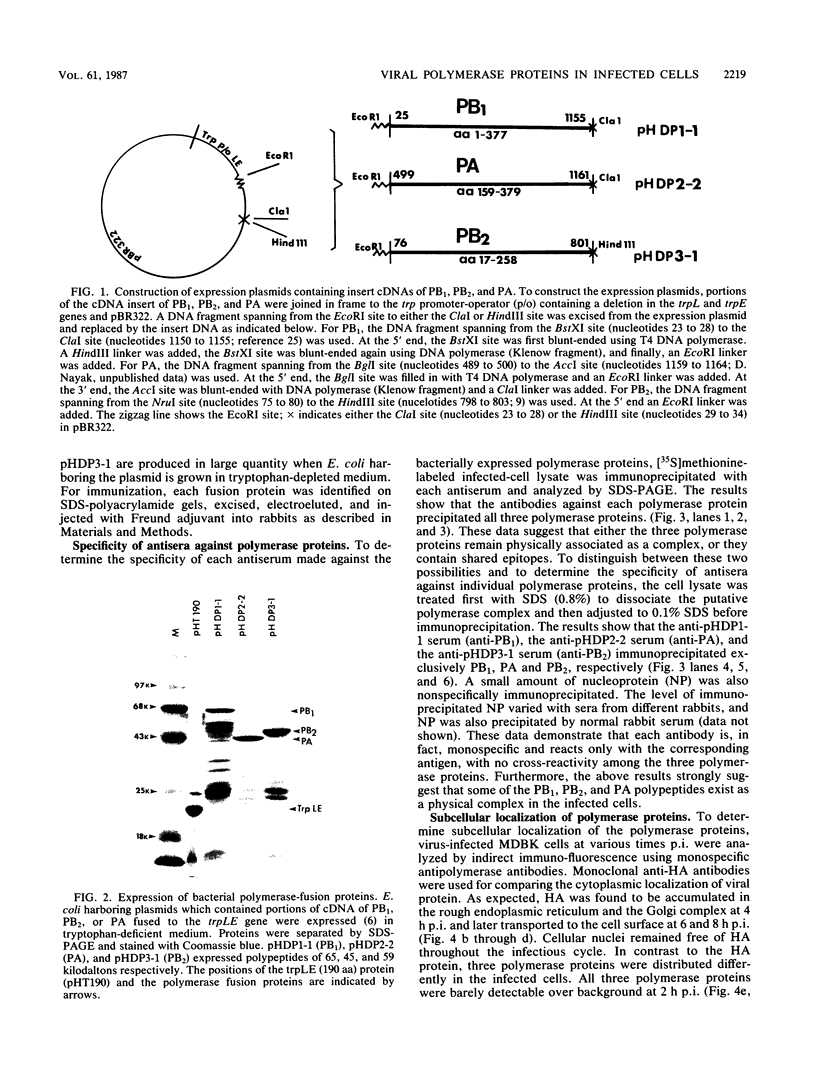
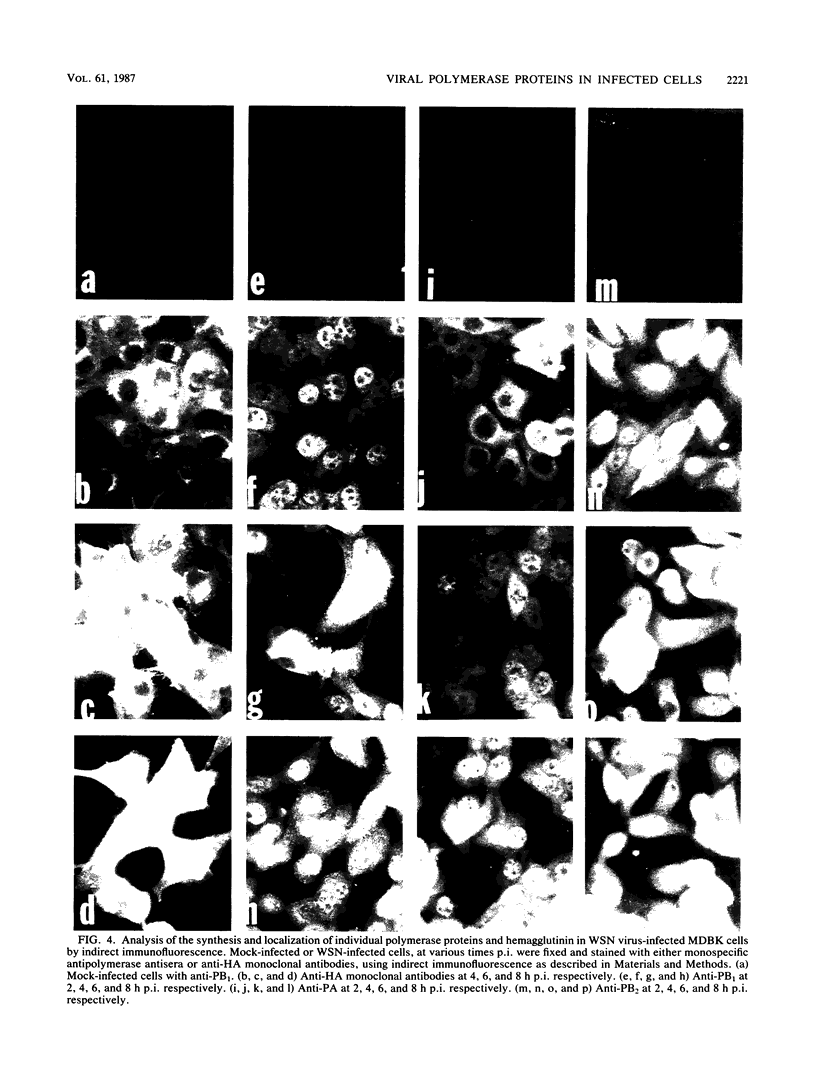
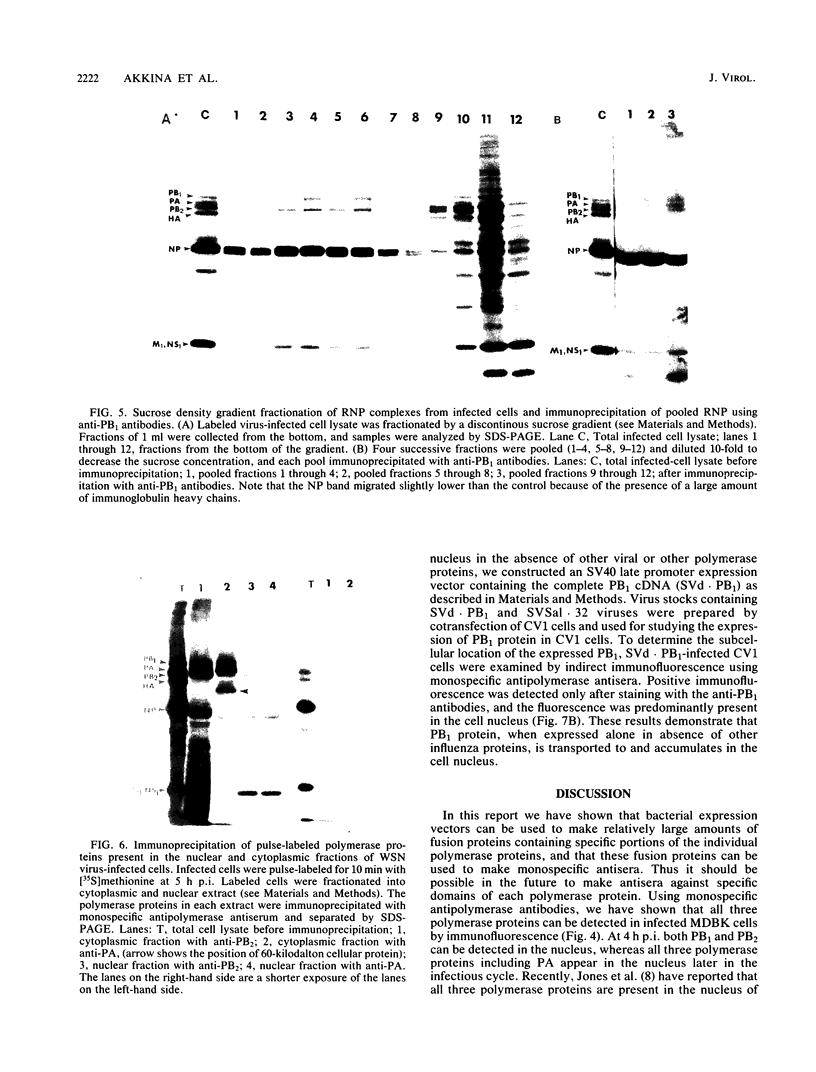
The biosynthesis, nuclear transport, and formation of a complex among the influenza polymerase proteins were studied in influenza virus-infected MDBK cells by using monospecific antisera. To obtain these monospecific antisera, portions of cloned cDNAs encoding the individual polymerase proteins (PB1, PB2, or PA) of A/WSN/33 influenza virus were expressed as fusion proteins in Escherichia coli, and the purified fusion proteins were injected into rabbits. Studies using indirect immunofluorescence showed that early in the infectious cycle (4 h postinfection) of influenza virus, PB1 and PB2 are present mainly in the nucleus, whereas PA is predominantly present in the cytoplasm of the virus-infected cells. Later, at 6 to 8 h postinfection, all three polymerase proteins are apparent both in the cytoplasm as well as the nucleus. Radiolabeling and immunoprecipitation analyses showed that the three polymerase proteins remain physically associated as a complex in either the presence or the absence of ribonucleoproteins. In the cytoplasm, the majority of the polymerase proteins remain unassociated, whereas in the nucleus they are present as a complex of three polymerase proteins. To determine whether a polymerase protein is transported into the nucleus individually, PB1 was expressed from the cloned cDNA by using the simian virus 40 late promoter expression vector. PB1 alone, in the absence of the other polymerase proteins or the nucleoprotein, accumulates in the nucleus. This suggests that the formation of a complex with other viral protein(s) is not required for either nuclear transport or nuclear accumulation of PB1 protein and that the PB1 protein may contain an intrinsic signal(s) for nuclear transport.
Full text
PDF


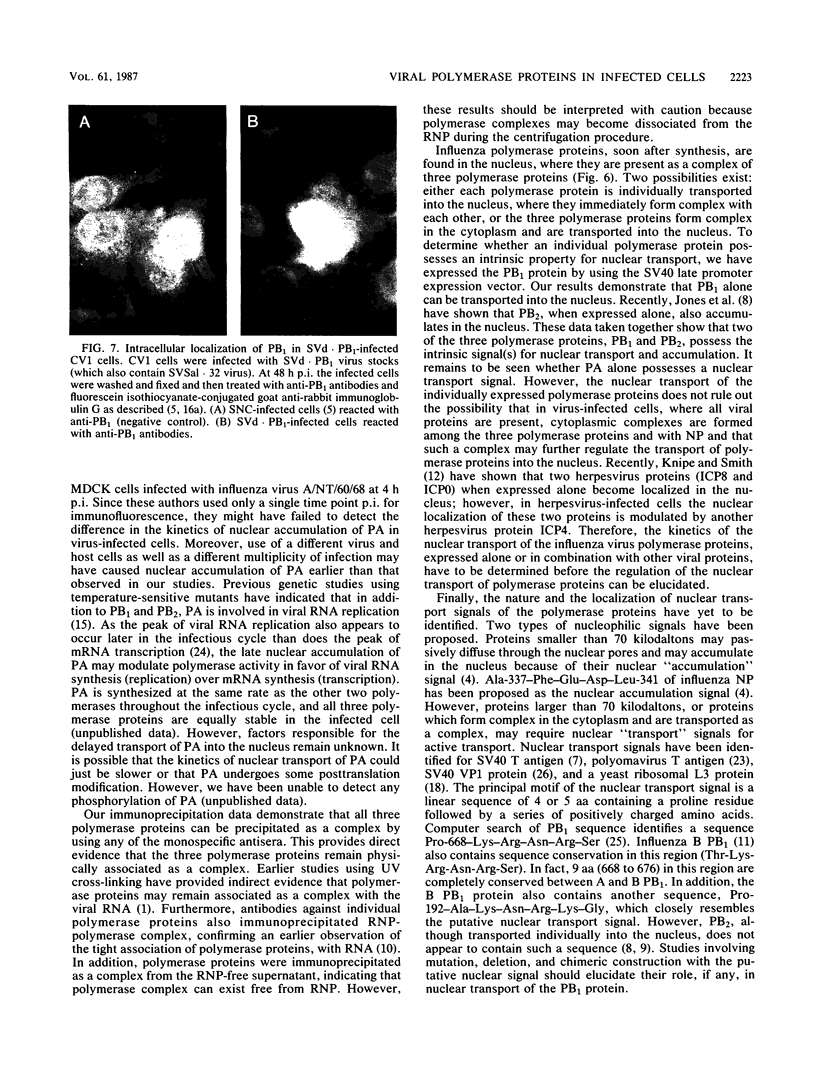

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braam J., Ulmanen I., Krug R. M. Molecular model of a eucaryotic transcription complex: functions and movements of influenza P proteins during capped RNA-primed transcription. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briedis D. J., Conti G., Munn E. A., Mahy B. W. Migration of influenza virus-specific polypeptides from cytoplasm to nucleus of infected cells. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow N. L., Simpson R. W. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity associated with virions and subviral particles of myxoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J., Dimmock N. J., Colman A. Identification of the sequence responsible for the nuclear accumulation of the influenza virus nucleoprotein in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Bos T. J., Nayak D. P. Active influenza virus neuraminidase is expressed in monkey cells from cDNA cloned in simian virus 40 vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3976–3980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Bos T., Ueda M., Nayak D. P., Dowbenko D., Compans R. W. Immune response to human influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Mar;21(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detjen B. M., St Angelo C., Katze M. G., Krug R. M. The three influenza virus polymerase (P) proteins not associated with viral nucleocapsids in the infected cell are in the form of a complex. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.16-22.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. M., Reay P. A., Philpott K. L. Nuclear location of all three influenza polymerase proteins and a nuclear signal in polymerase PB2. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2371–2376. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptein J. S., Nayak D. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the polymerase 3 gene of human influenza virus A/WSN/33. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):55–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.55-63.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Ishihama A. RNA polymerase of influenza virus. III. Isolation of RNA polymerase-RNA complexes from influenza virus PR8. J Biochem. 1983 Apr;93(4):989–996. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemdirim S., Palefsky J., Briedis D. J. Influenza B virus PB1 protein; nucleotide sequence of the genome RNA segment predicts a high degree of structural homology with the corresponding influenza A virus polymerase protein. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90378-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Smith J. L. A mutant herpesvirus protein leads to a block in nuclear localization of other viral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2371–2381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauley J. W., Mahy B. W. Structure and function of the influenza virus genome. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):281–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2110281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen N., Nayak D. P., Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Polarized expression of a chimeric protein in which the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of the influenza virus hemagglutinin have been replaced by those of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9318–9322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. Translation of the leader region of the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1457–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1457-1466.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Nam H. G., Hereford L. M., Fried H. M. Identification of a nuclear localization signal of a yeast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Davis A. R., McQueen N. L., Bos T. J., Jabbar M. A., Sivasubramanian N., Lionelli G. Biological and immunological properties of haemagglutinin and neuraminidase expressed from cloned cDNAs in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Vaccine. 1985 Sep;3(3 Suppl):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Sivasubramanian N., Davis A. R., Cortini R., Sung J. Complete sequence analyses show that two defective interfering influenza viral RNAs contain a single internal deletion of a polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2216–2220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Tobita K., Janda J. M., Davis A. R., De B. K. Homologous interference mediated by defective interfering influenza virus derived from a temperature-sensitive mutant of influenza virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):375–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.375-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E., Miller H., Doyle M., Blatti S. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in influenza virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1369–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivasubramanian N., Nayak D. P. Sequence analysis of the polymerase 1 gene and the secondary structure prediction of polymerase 1 protein of human influenza virus A/WSN/33. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):321–329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.321-329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., Benichou D., Girard M. A domain of SV40 capsid polypeptide VP1 that specifies migration into the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]