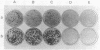
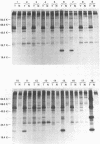
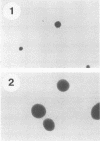
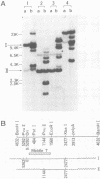
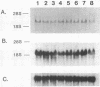
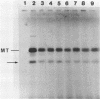
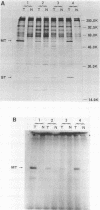
Abstract
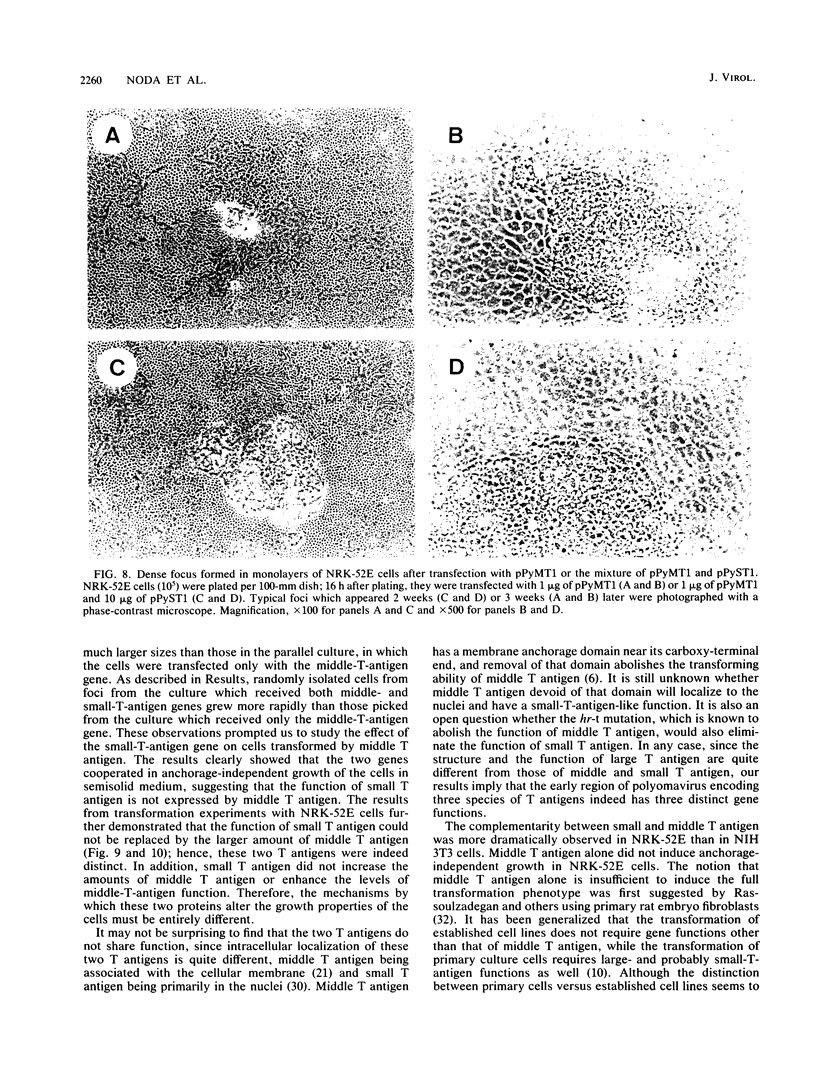
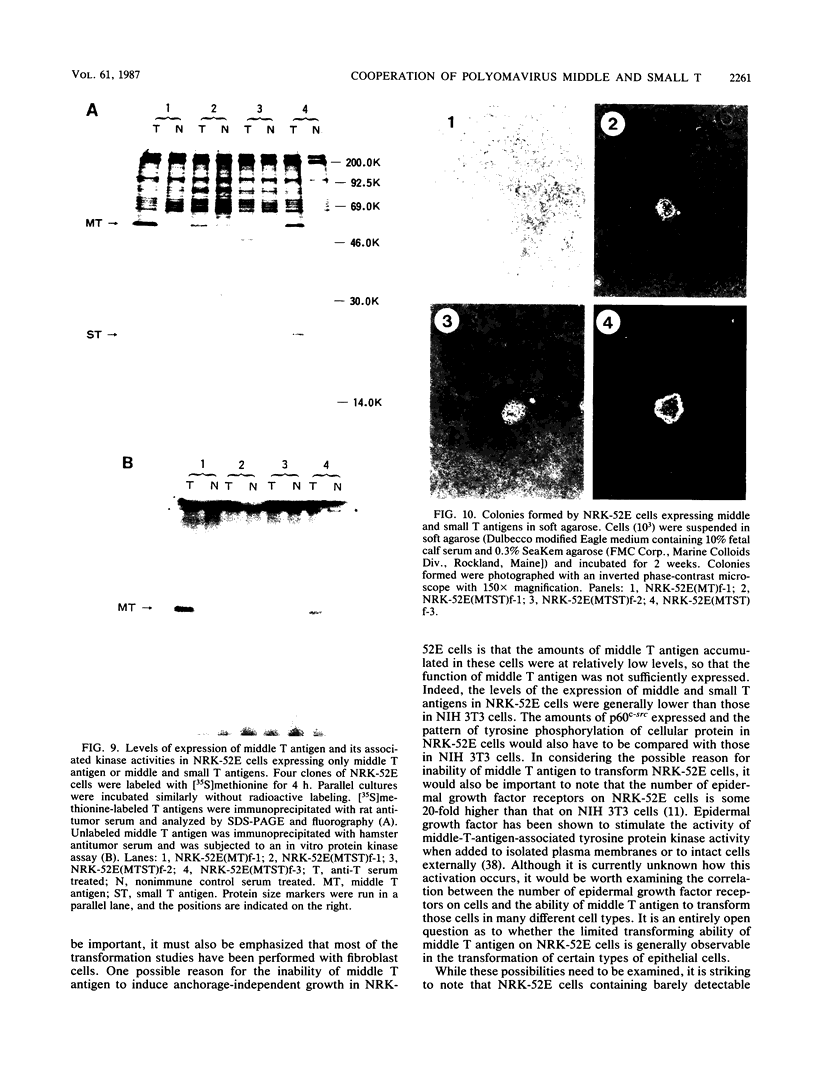
We have reported recently that small T antigen of polyomavirus stimulates the growth of NIH 3T3 cells beyond their saturation density and induces weak anchorage-independent growth (T. Noda, M. Satake, T. Robins, and Y. Ito, J. Virol. 60:105-113, 1986). We examined whether small T antigen would cooperate with middle T antigen in the in vitro transformation of NIH 3T3 (fibroblasts) and NRK-52E (epitheliallike) cells. The small-T-antigen gene, when cotransfected with the middle-T-antigen gene, had no additional effect on the efficiency or size of dense foci formation induced by the middle-T-antigen gene on a monolayer of NIH 3T3 cells. However, the small-T-antigen gene dramatically increased the rate of growth of NIH 3T3 cells transformed by middle T antigen in semisolid medium. Introduction of the small-T-antigen gene into middle-T-antigen-transformed cells did not disturb the integrated middle-T gene, alter expression of the middle-T gene, or enhance middle-T-antigen-associated tyrosine protein kinase activity. For NRK-52E cells, the expression of middle T antigen alone resulted in small, slow-growing foci on a monolayer. These cells did not show anchorage-independent growth, despite the fact that middle-T-antigen-associated tyrosine protein kinase activity was clearly detected in these cells. NRK-52E cells expressing both middle and small T antigens formed faster growing foci on a monolayer than middle-T-antigen-expressing cells did and grew in semisolid medium, even when the amounts of middle T antigen and its associated kinase activities were lower than those of middle-T-antigen-expressing cells. We conclude that small T antigen cooperates with middle T antigen in the in vitro transformation of established cell lines of fibroblast and epitheliallike cells, that it does not share the middle-T-antigen function even though they are structurally related, and that it has a significantly more important role in the transformation of NRK-52E cells than that of NIH 3T3 cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselin C., Bastin M. Sequences from polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T genes capable of immortalizing primary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):958–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.958-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Gelinas C., Bastin M. Role of the three polyoma virus early proteins in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Gélinas C., Branton P. E., Bastin M. Polyoma middle T antigen requires cooperation from another gene to express the malignant phenotype in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):755–760. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Schaffhausen B. S., Dorsky D. I., Oliver D. B., Benjamin T. L. Carboxy terminus of polyoma middle-sized tumor antigen is required for attachment to membranes, associated protein kinase activities, and cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3579–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington V., Morgan B., Spiegelman B. M., Roberts T. M. Recombinant retroviruses that transduce individual polyoma tumor antigens: effects on growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4307–4311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W., Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T. An activity phosphorylating tyrosine in polyoma T antigen immunoprecipitates. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIED M. CELL-TRANSFORMING ABILITY OF A TEMPERATURE-SENSITIVE MUTANT OF POLYOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:486–491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Viral gene expression in polyoma virus-transformed rat cells and their cured revertants. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):150–163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.150-163.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS L. A filterable agent, recovered from Ak leukemic extracts, causing salivary gland carcinomas in C3H mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jun;83(2):414–421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Maddock C. New classes of viable deletion mutants in the early region of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.645-656.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Brocklehurst J. R., Dulbecco R. Virus-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of cells lytically infected or transformed by pol-oma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4666–4670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Polyoma virus-specific 55K protein isolated from plasma membrane of productively infected cells is virus-coded and important for cell transformation. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Griffin B. E. Middle T antigen as primary inducer of full expression of the phenotype of transformation by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):219–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.219-232.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Large T antigens of simian virus 40 and polyomavirus efficiently establish primary fibroblasts. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.746-750.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J., Treisman R., Lania L., Fried M., Mellor A. Comparison of polyoma virus transcription in productively infected mouse cells and transformed rodent cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):63–75. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Cross F. R., Harbison M., Hanafusa H. Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts and tumor induction by the middle T antigen of polyomavirus carried in an avian retroviral vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1545–1551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):523–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.523-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda T., Satake M., Robins T., Ito Y. Isolation and characterization of NIH 3T3 cells expressing polyomavirus small T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.105-113.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis L., Lamfrom H., Benjamin T. L. Regulation of cellular phenotype and expression of polyomavirus middle T antigen in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2476–2486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Naghashfar Z., Cowie A., Carr A., Grisoni M., Kamen R., Cuzin F. Expression of the large T protein of polyoma virus promotes the establishment in culture of "normal" rodent fibroblast cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert N. D., Davies P. J., Jay G., Pastan I. H. Characterization of an immune complex kinase in immunoprecipitates of avian sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.696-706.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Benjamin T. L. Phosphorylation of polyoma T antigens. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):935–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Ito Y. Differential subcellular localization of in vivo-phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated middle-sized tumor antigen of polyoma virus and its relationship to middle-sized tumor antigen phosphorylating activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6812–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Ito Y. Enhancement of polyoma virus middle T antigen tyrosine phosphorylation by epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):742–744. doi: 10.1038/304742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Ito Y. Three species of polyoma virus tumor antigens share common peptides probably near the amino termini of the proteins. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1427–1437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Griffin B., Fried M. Protein kinase activity associated with polyoma virus middle T antigen in vitro. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z. Y., Veldman G. M., Cowie A., Carr A., Schaffhausen B., Kamen R. Construction and functional characterization of polyomavirus genomes that separately encode the three early proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):170–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.170-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Epithelioid and fibroblastic rat kidney cell clones: epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors and the effect of mouse sarcoma virus transformation. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Mar;94(3):335–342. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040940311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]