Abstract
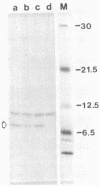
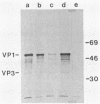
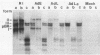
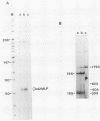
We described previously a simian virus 40 (SV40) mutant, pSVAdL, that was defective in synthesis of the late viral protein VP1. This mutant, which contains a 100-base-pair fragment of adenovirus DNA encompassing the major late promoter inserted in the SV40 late promoter region (SV40 nucleotide 294), efficiently synthesizes agnoprotein, a protein encoded by the leader region of the same mRNA that encodes VP1. When the agnoprotein AUG initiation codon in pSVAdL was mutated to UUG, agnoprotein synthesis was abolished, and VP1 synthesis was elevated to wild-type levels. Because levels of late mRNA synthesis were not affected by this mutation, these results support a scanning model of translation initiation and suggest that internal translational reinitiation does not occur efficiently in this situation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Evidence for simian virus 40 late transcriptional control: mixed infections of wild-type simian virus 40 and a late leader deletion mutant exhibit trans effects on late viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.798-803.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Resnick J., Alwine J. C. Construction and characterization of CV-1P cell lines which constitutively express the simian virus 40 agnoprotein: alteration of plaquing phenotype of viral agnogene mutants. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):415–422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.415-422.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Verderame M., Lo A., Pollack R. Nonlytic simian virus 40-specific 100K phosphoprotein is associated with anchorage-independent growth in simian virus 40-transformed and revertant mouse cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):994–1006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Structure of a large segment of the genome of simian virus 40 that does not encode known proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):827–831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Hohn T. Initiation of translation of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome from a polycistronic mRNA: evidence from deletion mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2731–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Choudary P. V., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. The 5'-terminal leader sequence of late 16 S mRNA from cells infected with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3643–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grass D. S., Manley J. L. Effects of the adenovirus 2 late promoter on simian virus 40 transcription and replication. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):129–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.129-137.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Mellstrom K., Kosik E., Tamanoi F., Brugge J. Mutation of a termination codon affects src initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1738–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M., Filipowicz W., Domdey H., Gross H. J. Binding of ribosomes to linear and circular forms of the 5'-terminal leader fragment of tobacco-mosaic-virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Inability of circular mRNA to attach to eukaryotic ribosomes. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):82–85. doi: 10.1038/280082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Gefter M. L. Transcription of mammalian genes in vitro. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Khoury G., Jay G. Subcellular localization of the simian virus 40 agnoprotein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):428–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.428-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Subramani S., Berg P. Effect of upstream reading frames on translation efficiency in simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2704–2711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick J., Shenk T. Simian virus 40 agnoprotein facilitates normal nuclear location of the major capsid polypeptide and cell-to-cell spread of virus. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1098–1106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1098-1106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]