Abstract
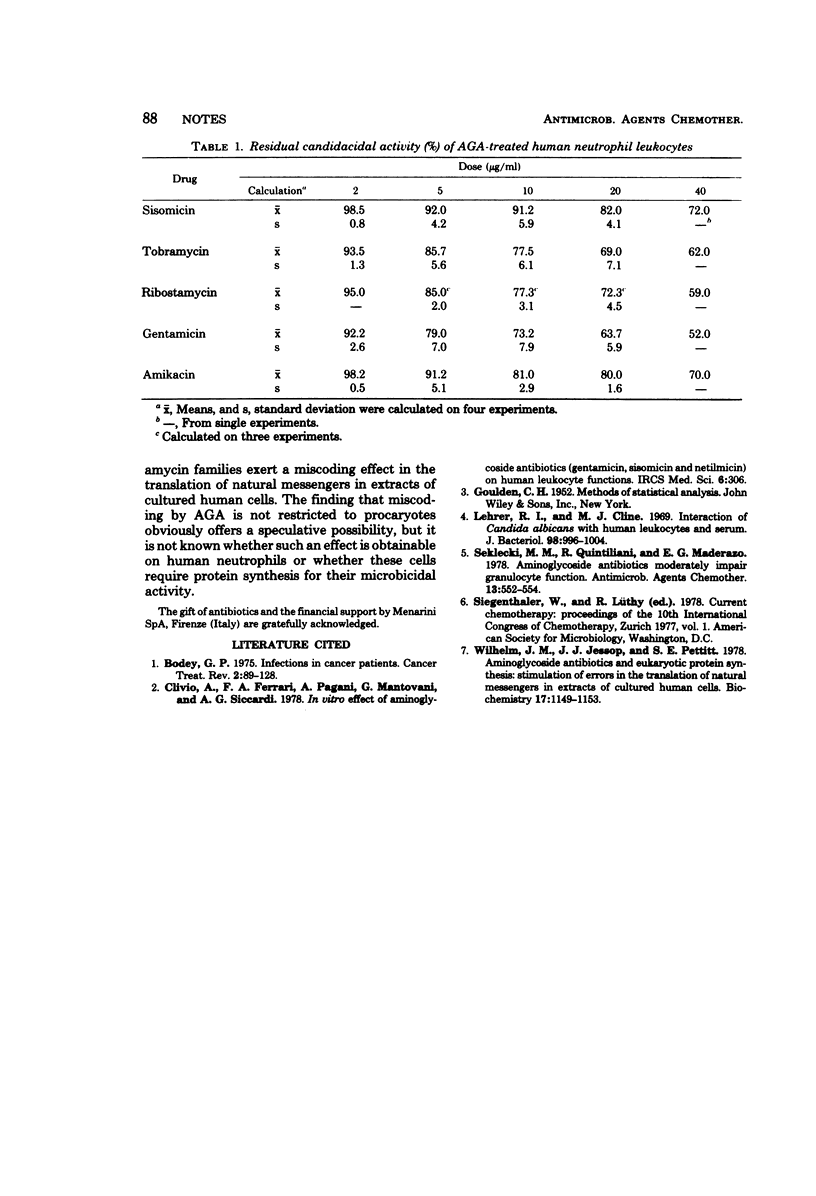
We have tested the effect of five aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin, sisomicin, tobramycin, ribostamycin, and amikacin) on the candidacidal activity of human neutrophils in vitro; all of them are inhibitory and can be grouped into three significantly different levels of toxicity. Gentamicin in the most toxic and sisomicin is the least toxic.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P. Infections in cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975 Jun;2(2):89–128. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seklecki M. M., Quintiliani R., Maderazo E. G. Aminoglycoside antibiotics moderately impair granulocyte function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):552–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Jessop J. J., Pettitt S. E. Aminoglycoside antibiotics and eukaryotic protein synthesis: stimulation of errors in the translation of natural messengers in extracts of cultured human cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1149–1153. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


