Abstract
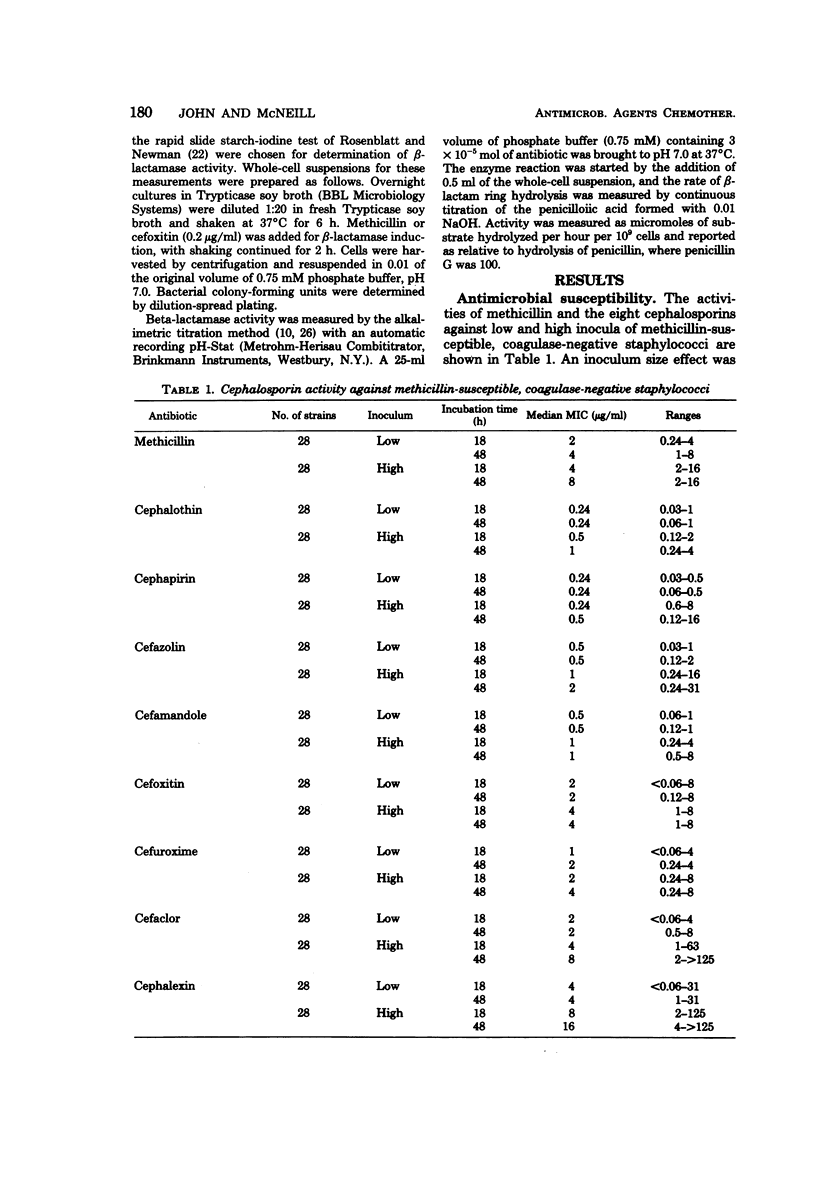
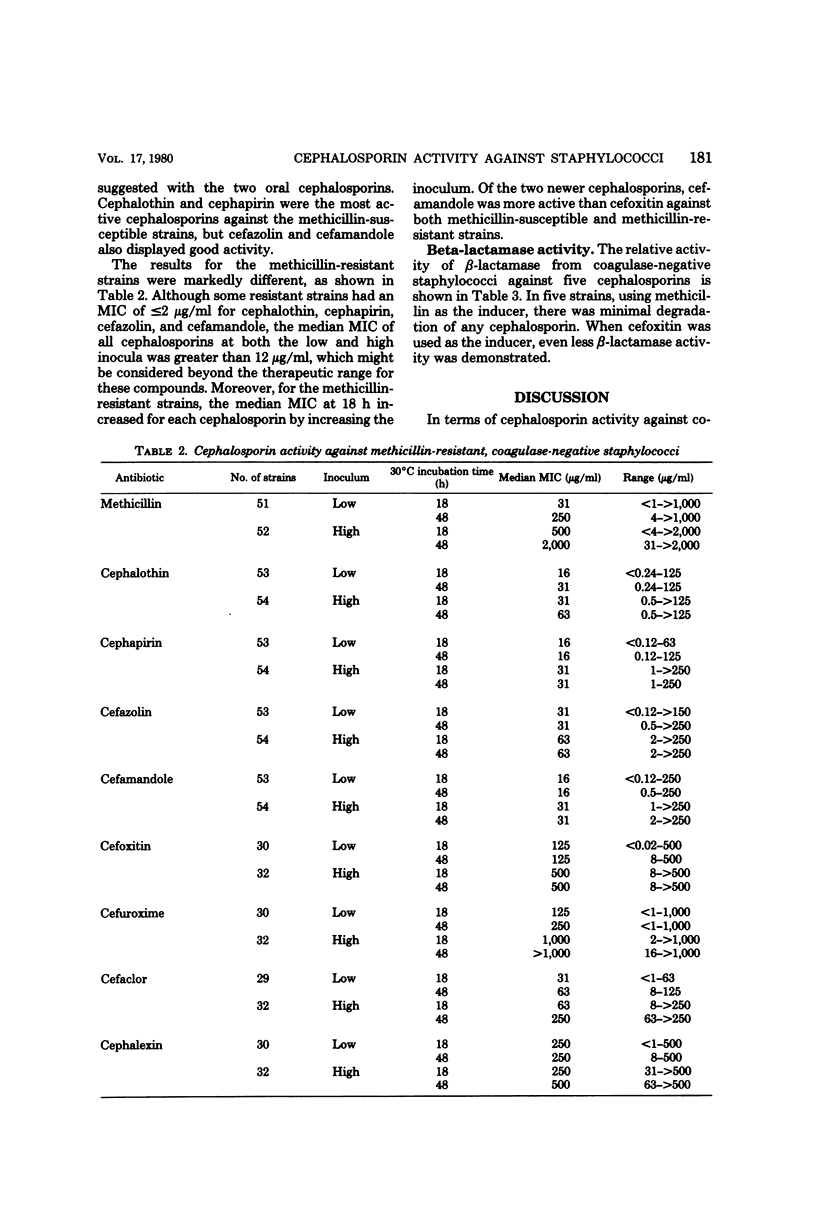
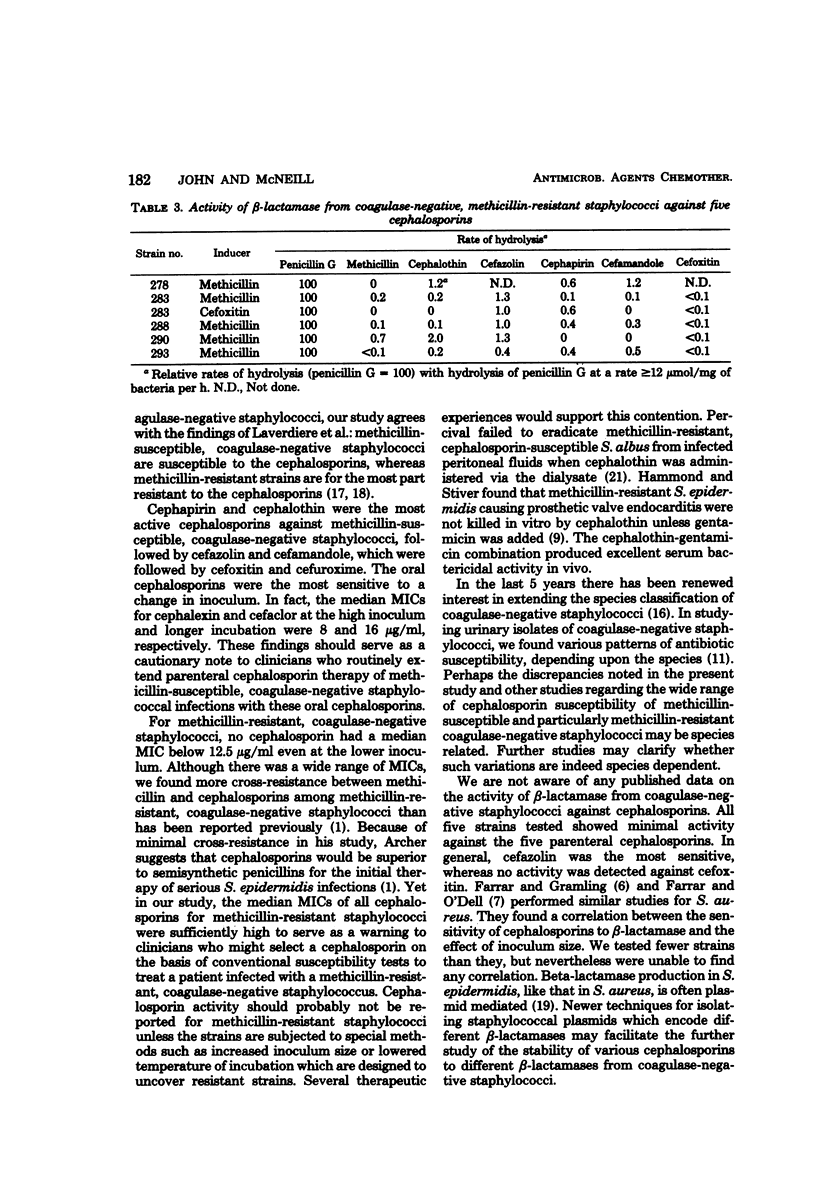
Eight cephalosporins were tested for their activity against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci and for their resistance to beta-lactamase from methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. Susceptibility testing by the agar plate method was evaluated for the effect of inoculum size and duration of incubation. Methicillin-susceptible, coagulase-negative staphylococci were highly susceptible to the cephalosporins, with cephapirin and cepahlothin showing the greatest activity, followed by cefazolin and cefamandole. Methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci displayed nearly total cross-resistance to the cephalosporins. Resistance increased with increasing inoculum size. Beta-Lactamases produced by methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci had a minimal hydrolytic effect on cepahlothin, cephapirin, cefazolin, and cefamandole and no measurable effect on cefoxitin. There was no correlation between the anti-staphylococcal activity and resistance to beta-lactamases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Steigbigel R. T. Infective endocarditis and access site infections in patients on hemodialysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Nov;55(6):453–466. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197611000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry J. C., Borovian G. E. Selective medium for distinguishing micrococci from staphylococci in the clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):455–457. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.455-457.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards L. D. The epidemiology of 2056 remote site infections and 1966 surgical wound infections occurring in 1865 patients: a four year study of 40,923 operations at Rush-Presbyterian-St. Luke's Hospital, Chicago. Ann Surg. 1976 Dec;184(6):758–766. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197612000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Smith P. B. The gram positive cocci. Hum Pathol. 1976 Mar;7(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr, Gramling P. K. Antistaphylococcal activity and beta-lactamase resistance of newer cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):691–695. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr, O'Dell N. M. Comparative beta-lactamase resistance and antistaphylococcal activities of parenterally and orally administered cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):490–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Stiver H. G. Combination antibiotic therapy in an outbreak of prosthetic endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Can Med Assoc J. 1978 Mar 4;118(5):524–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. P., Poole J. W. Measurement of beta-lactamase activity and rate of inactivation of penicillins by a pH-stat alkalimetric titration method. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Oct;61(10):1594–1598. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600611010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Gramling P. K., O'Dell N. M. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.435-437.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJELLANDER J. O., KLEIN J. O., FINLAND M. IN VITRO ACTIVITY OF PENICILLINS AGAINST STAPHYLOCOCCUS ALBUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:1023–1031. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys T. F., Hewitt W. L. Endocarditis due to Micrococci and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Aug;132(2):216–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek J. J., Marsik F. J., Bartlett R. C., Weir B., Shea P., Quintiliani R. Clinical, epidemiologic and bacteriologic observations of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a large community hospital. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Peterson P., Verhoef J., Williams D. N., Sabath L. D. In vitro activity of cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Welter D., Sabath L. D. Use of a heavy inoculum in the in vitro evaluation of the anti-staphylococcal activity of 19 cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):669–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson W. C., Jr, Parisi J. T., Totten P. A., Baldwin J. N. Transduction of penicillinase production in Staphylococcus epidermidis and nature of the genetic determinant. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):508–511. doi: 10.1139/m79-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. A., Tuazon C. U. Cervical osteomyelitis. Infection due to Staphylococcus epidermidis in hemodialysis patients. JAMA. 1978 Jul 7;240(1):50–51. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Cohen S. L. The treatment of peritoneal infections in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Aug;43(Suppl):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Neumann A. M. A rapid slide test for penicillinase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Mar;69(3):351–354. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert W. T., Moreland N., Williams T. W., Jr Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. South Med J. 1978 Nov;71(11):1353–1355. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197811000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



