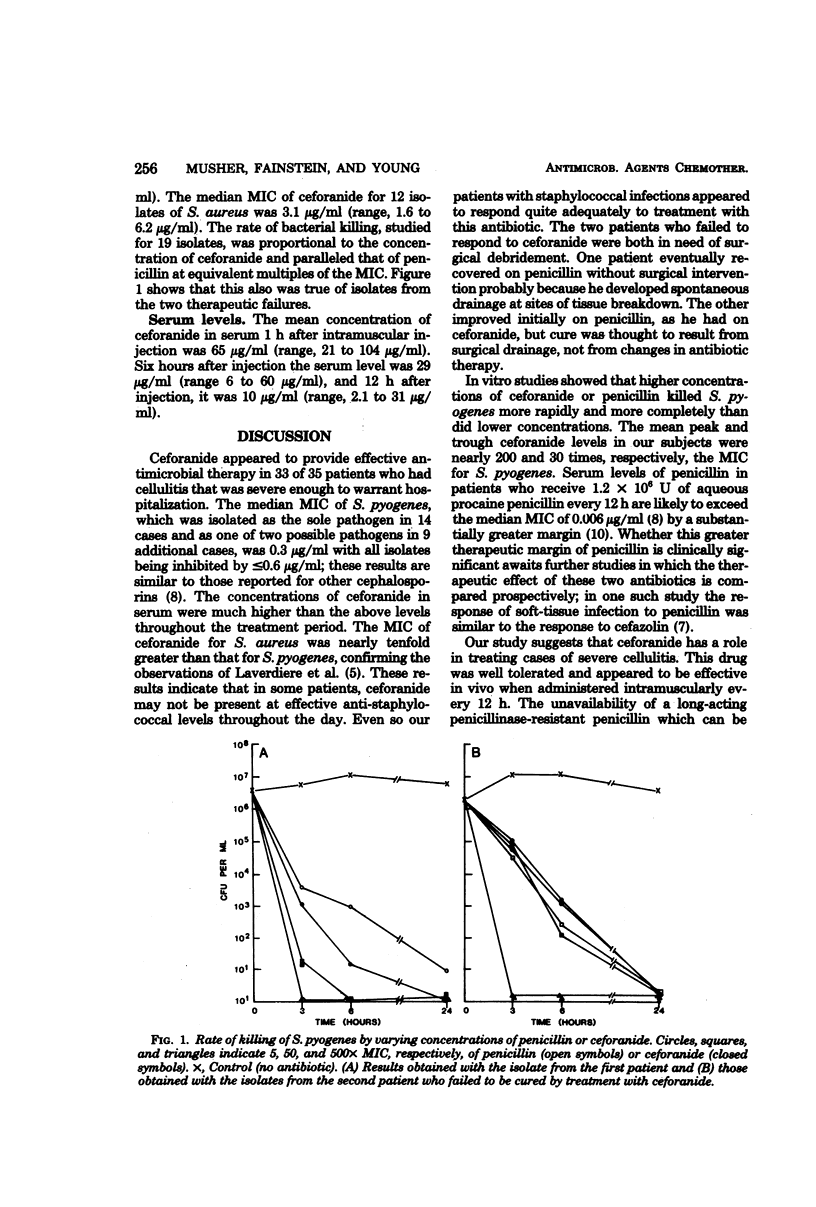
Abstract
Thirty-five patients with cellulitis were treated with ceforanide, 1 g every 12 h, intramuscularly. A good clinical response was observed in 33 cases. Drug failure in the remaining two patients was thought to be due to the lack of surgical debridement. Drug concentrations well in excess of inhibitory levels for Streptococcus pyogenes were generally present throughout the treatment period; although this was not true of ceforanide concentrations relative to inhibitory levels for Staphylococcus aureus, the clinical response in patients with staphylococcal infection still appeared to be entirely satisfactory. Killing of S. pyogenes by 5, 50, and 500X the minimum inhibitory concentration of ceforanide proceeded at the same rate in vitro as did killing by 5, 50, and 500X the minimum inhibitory concentration of penicillin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter C. R. Surgical management of soft tissue infections. Surg Clin North Am. 1972 Dec;52(6):1483–1499. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)39893-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch K. H., Pohlod D., Saravolatz L. D., Madhavan T., Kiani D., Quinn E. L., Del Busto R., Cardenas J., Fisher E. J. Ceforanide: in vitro and clinical evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):386–391. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Sanders C. C., Sanders W., Jr Comparison of BL-S786 with cephalothin, cefamandole and cefoxitin in vitro and in treatment of experimental infections in mice. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Apr;31(4):363–372. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammar H., Wanger L. Erysipelas and necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Dermatol. 1977 Apr;96(4):409–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb07137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Welter D., Sabath L. D. Use of a heavy inoculum in the in vitro evaluation of the anti-staphylococcal activity of 19 cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):669–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., O'Connor D. M., Anderson D., Bairan A. C., Feigin R. D., Cherry J. D. Clinical and pharmacologic evaluation of cefazolin in children. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S407–S401. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wilcox C., Garner C., Finland M. In vitro activity of cefazolin against recent clinical bacterial isolates. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S320–S326. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Wagner G., Carver M. In vitro and in vivo studies with BL-S786, cefoxitin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):412–415. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., McCravey J. W., Masi A. T. Low dose penicillin for gonococcal arthritis. A comparative therapy trial. JAMA. 1976 Nov 22;236(21):2410–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Martin R. R., Greenberg S. B. Ceforanide (BL-S786) in the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. Infection. 1979;7(4):176–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01640937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



