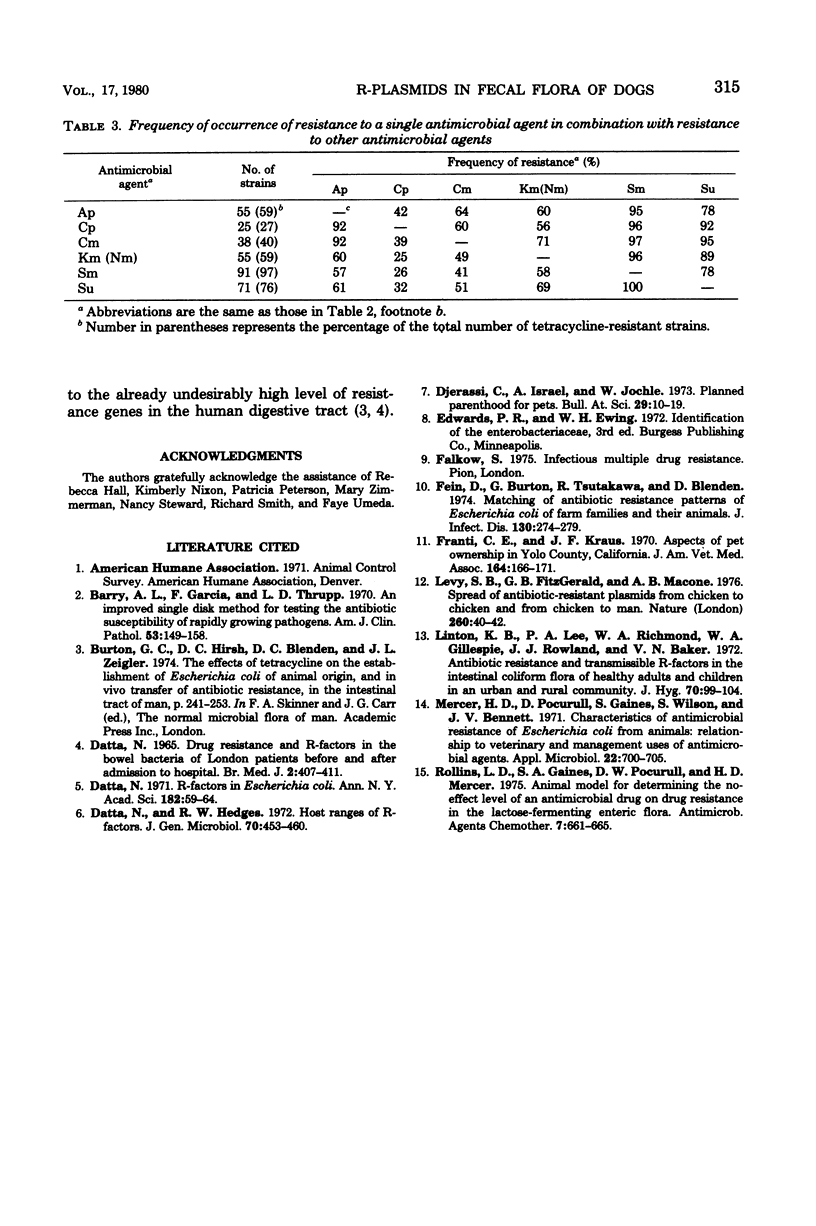
Abstract
Rectal swabs were taken from healthy household dogs that, insofar as could be determined, had not received antimicrobial drugs. Tetracycline-resistant coliforms comprised 80 to 100% of the total number of coliforms in 61 (65%) of the 94 dogs sampled. The median number of other resistance determinants possessed by these tetracycline-resistant coliforms was 5.1. Of the tetracycline-resistant strains studied, 97% were resistant to streptomycin; 76% were resistant to sulfonamides; 59% were resistant to ampicillin; 59% were resistant to kanamycin/neomycin; and 40% were resistant to chloramphenicol. A total of 64% of the strains was shown to transfer resistance by conjugation or by the aid of the sex factor F. Of the strains transferring resistance, 33% were found to transfer all of their resistance determinants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Garcia F., Thrupp L. D. An improved single-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of rapidly-growing pathogens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):149–158. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton G. C., Hirsh D. C., Blenden D. C., Zeigler J. L. The effects of tetracycline on the establishment of Escherichia coli of animal origin, and in vivo transfer of antibiotic resistance, in the intestinal tract of man. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1974;3(0):241–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N. Drug resistance and R factors in the bowel bacteria of London patients before and after admission to hospital. Br Med J. 1969 May 17;2(5654):407–411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5654.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Host ranges of R factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):453–460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein D., Burton G., Tsutakawa R., Blenden D. Matching of antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli of farm families and their animals. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):274–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franti C. E., Kraus J. F. Aspects of pet ownership in Yolo County, California. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974 Jan 15;164(2):166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton K. B., Lee P. A., Richmond M. H., Gillespie W. A., Rowland A. J., Baker V. N. Antibiotic resistance and transmissible R-factors in the intestinal coliform flora of healthy adults and children in an urban and a rural community. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Mar;70(1):99–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer H. D., Pocurull D., Gaines S., Wilson S., Bennett J. V. Characteristics of antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli from animals: relationship to veterinary and management uses of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):700–705. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.700-705.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins L. D., Gaines S. A., Pocurull D. W., Mercer H. D. Animal model for determining the no-effect level of an antimicrobial drug on drug resistance in the lactose-fermenting enteric flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):661–665. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


