Abstract
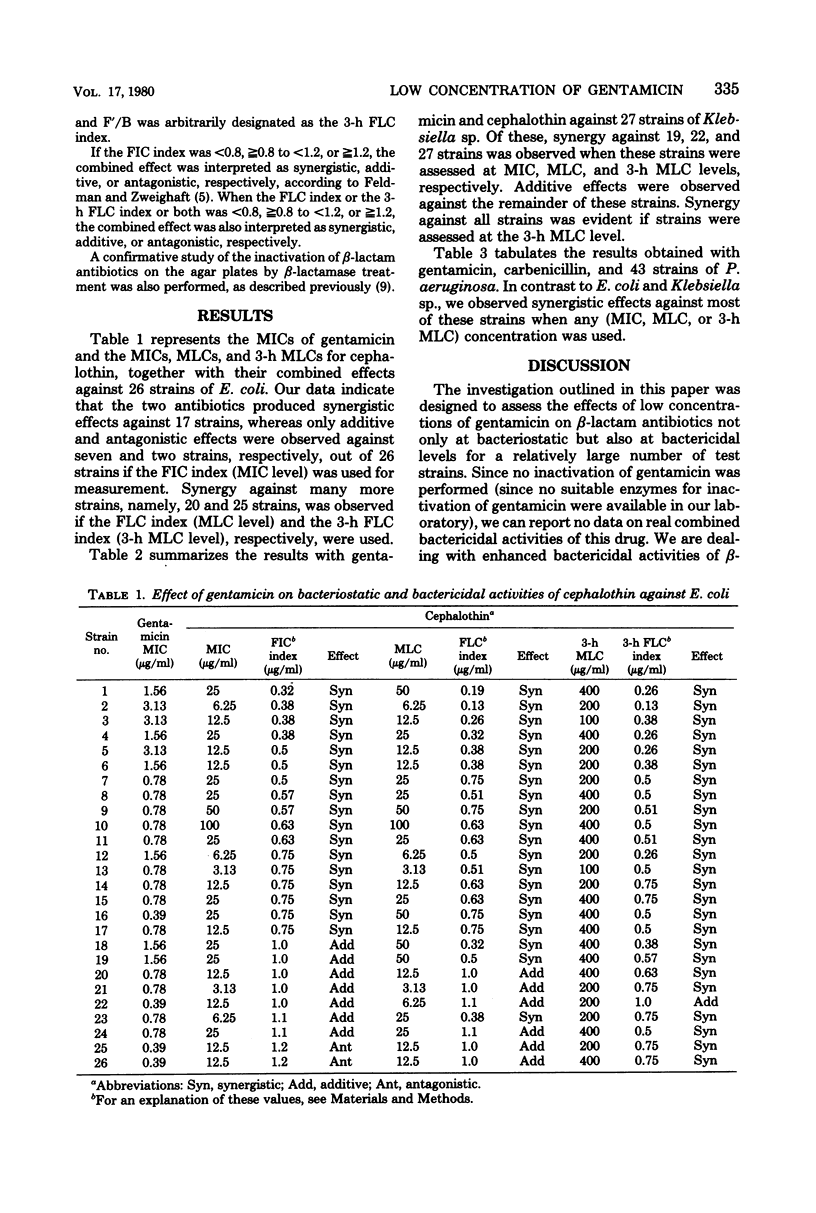
The combined effects of low concentrations of gentamicin on certain beta-lactam antibiotics were studied by the agar plate method. the combination of gentamicin with cephalothin produced synergism against 17 of 26 strains of Escherichia coli and 19 of 27 strains of Klebsiella sp. if assessed at the bacteriostatic (minimal inhibitory concentration) level. Synergy against many more strains was apparent when bactericidal concentrations were used. Synergy against most of these strains was observed if bactericidal concentrations with brief exposure times (3 h) to the antibiotics were used for measurement. Additive effects were observed in almost all of the remaining strains. The combination of gentamicin and carbenicillin were synergistic against most strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa when any bacteriostatic or bactericidal measurement was used as the criterion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. T., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Antimicrobial synergism in the therapy of gram-negative rod bacteremia. Chemotherapy. 1978;24(1):45–54. doi: 10.1159/000237759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. Y., Rodriguez V., Narboni G., Bodey G. P., Luna M. A., Freireich E. J. Causes of death in adults with acute leukemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 May;55(3):259–268. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197605000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Spink W. W. Infections due to gram-negative organisms: an analysis of 860 patients with bacteremia at the University of Minnesota Medical Center, 1958-1966. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):307–332. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E., Zweighaft T. Effect of ampicillin and chloramphenicol against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):240–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAWETZ E. Antibiotic synergism and antagonism; review of experimental evidence. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1952 Sep;90(3):301–309. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1952.00240090022003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Henri A., Vandenborre L. Antimicrobial activity of tobramycin and gentamicin used in combination with cephalothin and carbenicillin. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Jul;266(1):13–21. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197307000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda G., Tomioka S. Quantitative assessment of bactericidal activities of beta-lactam antibiotics by agar plate method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):587–595. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda G., Tomioka S., Uchida H., Hasegawa M. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of selected beta-lactam antibiotics studied on agar plates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):376–382. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda G., Yajima T., Nakamura K., Yanagishita T., Hayashi H. Comparative bactericidal activities of beta-lactam antibiotics determined in agar and broth media. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Nov;32(11):1168–1173. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Antibiotic susceptibility of gram-negative bacilli isolated from blood cultures. Results of tests with 35 agents and strains from 169 patients at Boston City Hospital during 1972. Am J Med. 1974 Aug;57(2):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. E., Reeves D. S. Clinical and laboratory evidence for inactivation of gentamicin by carbenicillin. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):261–264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall M. H., Spiers A. S., Darrell J. H. Initial therapy with combination of five antibiotics in febrile patients with leukaemia and neutropenia. Lancet. 1972 Jan 22;1(7743):162–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivieso M., Gil-extremera B., Zornoza J., Rodriquez V., Bodey G. P. Gram-negative bacillary pneumonia in the compromised host. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 May;56(3):241–254. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197705000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



