Abstract
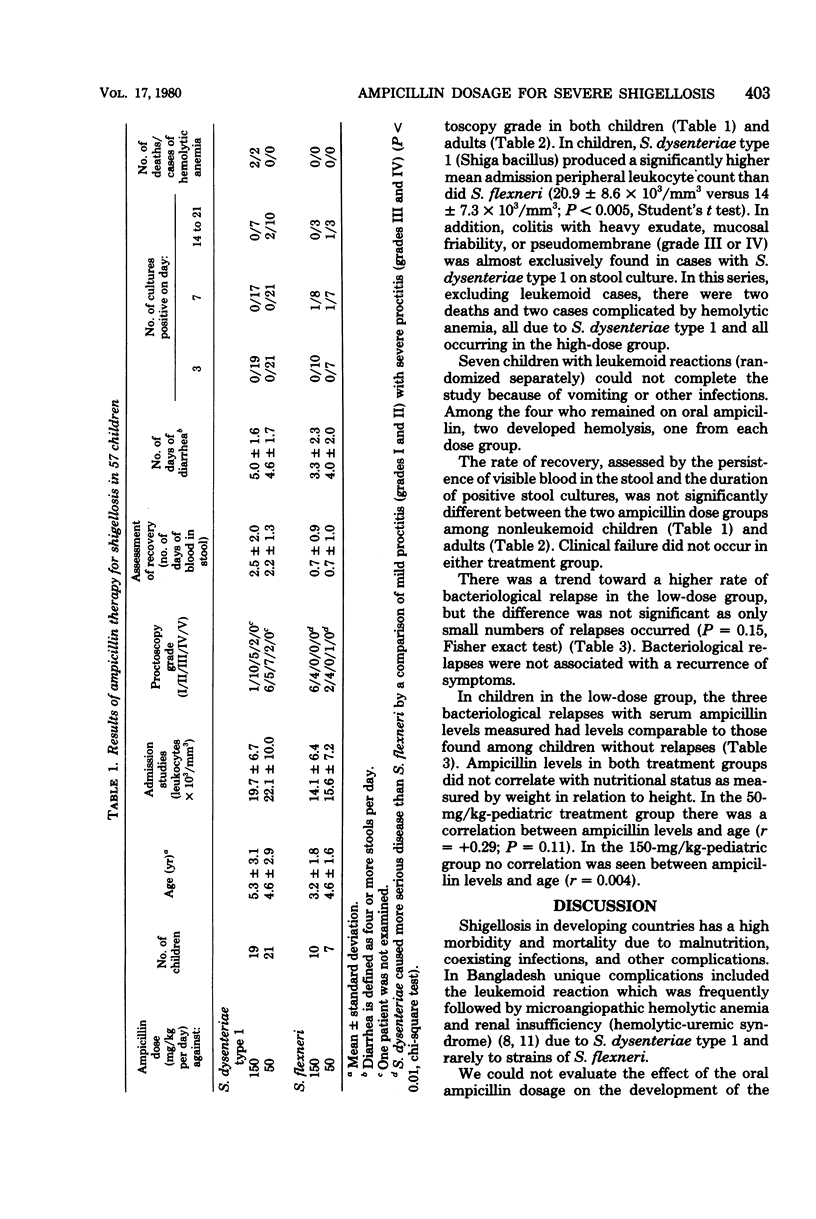
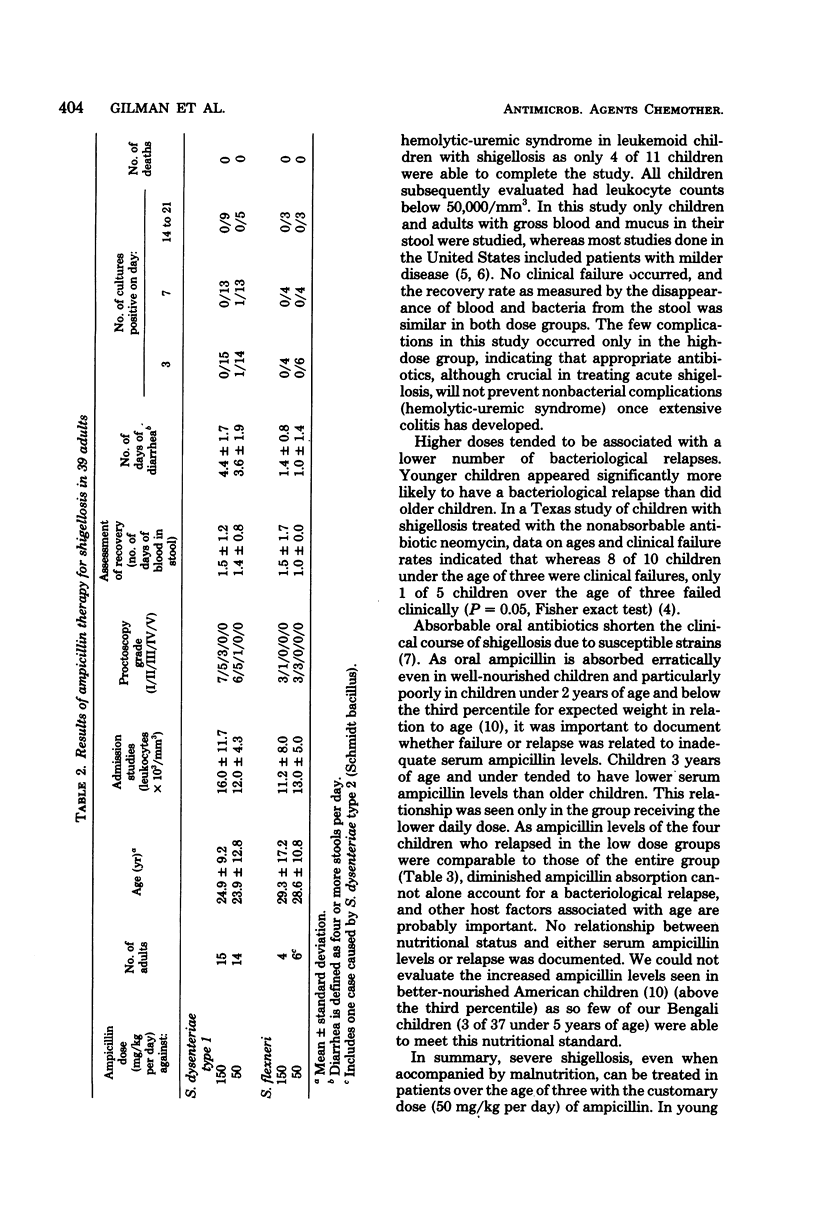
To establish optimal therapy for severe dysentery due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1 and Shigella flexneri, we compared in a prospective randomized trial two oral ampicillin doses (50 and 150 mg/kg per day) in 57 children and 39 adults in Dacca, Bangladesh. Clinical failure did not occur in either group, indicating that conventional doses need not be increased even in severe disease. Among children 3 years of age or under, bacteriological relapses tended to be more frequent in the low-dose group and were not related to serum levels of ampicillin, nutritional status, or the severity of colitis on admission. Therefore, we recommend that younger children be treated with 100 mg/kg per day of oral ampicillin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangarosa E. J., Perera D. R., Mata L. J., Mendizábal-Morris C., Guzmán G., Reller L. B. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. II. Epidemiologic studies in 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):181–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Hinton L. V., Kusmiesz H. T., Sladoje M. Comparison of orally absorbable and nonabsorbable antibiotics in shigellosis. A double-blind study with ampicillin and neomycin. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):708–720. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Kusmiesz H. T., Hinton L. V. Comparison of intramuscular and oral ampicillin therapy for shigellosis. J Pediatr. 1968 Oct;73(4):617–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Kusmiesz H. T., Hinton L. V. Optimal dosage of ampicillin for shigellosis. J Pediatr. 1969 Apr;74(4):626–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Ring R., 3rd, Sladoje M., Hinton L. V. Double-blind treatment study of shigellosis comparing ampicillin, sulfadiazine, and placebo. J Pediatr. 1967 Jun;70(6):970–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Gangarosa E. J., Cáceres A., Perera D. R., Mejicanos M. L. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. I. Etiologic investigations in Guatemala, 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):170–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D., Shelton S., Kusmiesz H. T., Haltalin K. C. Absorption of ampicillin and nalidixic acid by infants and children with acute shigellosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Nov-Dec;13(6):879–886. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972136879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman M. M., JamiulAlam A. K., Islam M. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd Shiga bacillus dysentery associated with marked leukocytosis and erythrocyte fragmentation. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1975 Feb;136(2):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman M. M., Khan M. M., Aziz K. M., Islam M. S., Kibriya A. K. An outbreak of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on a coral island in the Bay of Bengal. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):15–19. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



