Abstract
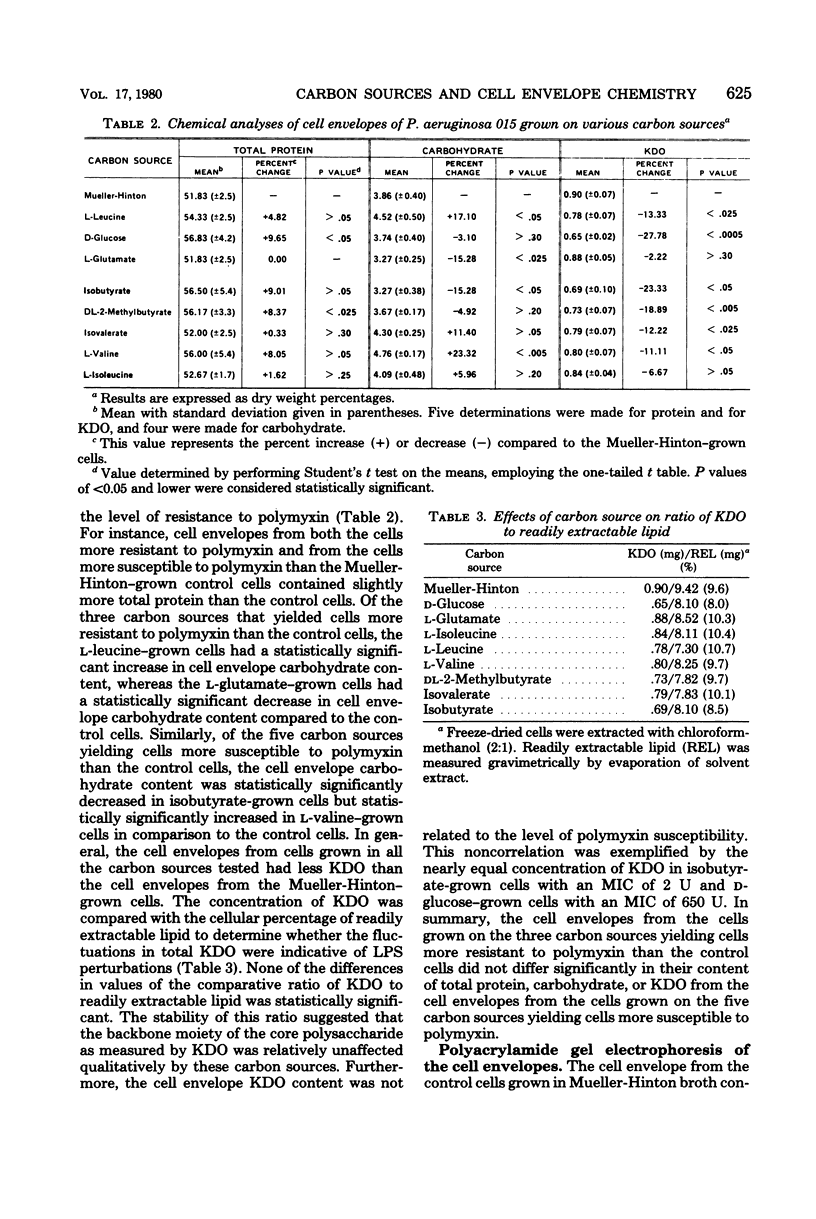
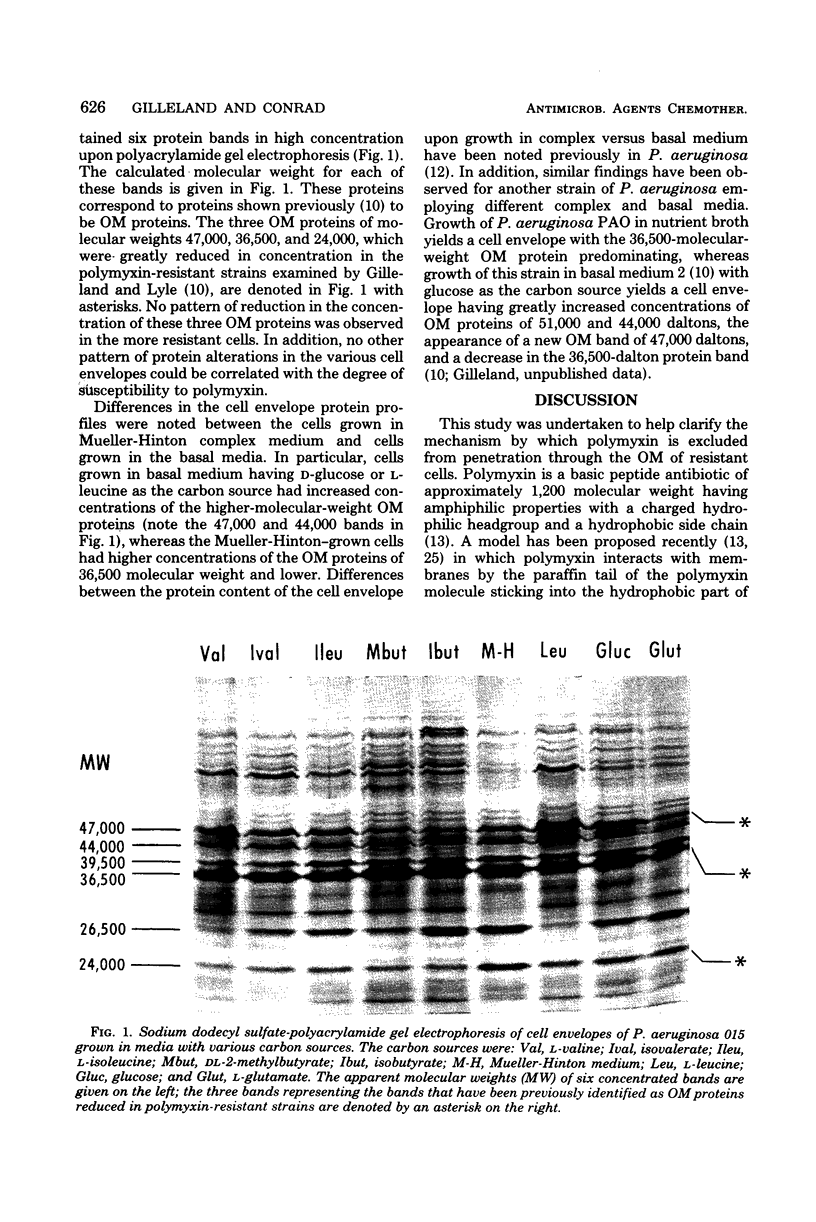
Cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 015 were grown in basal medium with isobutyrate, DL-2-methylbutyrate, isovalerate, L-valine, L-isoleucine, L-leucine, D-glucose, or L-glutamate as the carbon source. Their resultant susceptibility to polymyxin B varied from a minimal inhibitory concentration of 2 U of polymyxin per ml for isobutyrate-grown cells to 975 U/ml for L-glutamate-grown cells. Cell envelopes from cells grown with each carbon source were compared with cell envelopes from cells grown in Mueller-Hinton broth as to their content of total protein, carbohydrate, and 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate and as to their protein composition as determined by slab polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. No pattern of cell envelope content of total protein, carbohydrate, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate, or outer membrane protein concentrations could be correlated with the degree of resistance to polymyxin. In these cells increased resistance to polymyxin was not associated with the loss of outer membrane proteins and lipopolysaccharide by the cell envelope.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. R., Watkins W. M. Low magnesium and phospholipid content of cell wals of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to polymyxin. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1360–1361. doi: 10.1038/2271360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R. S., Wulf R. G., Clay D. L. Effects of carbon sources on antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Shapiro B. M. Lipid and lipopolysaccharide composition of Escherichia coli surface-altered mutants selected for resistance to levallorphan, tetracaine, and polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):1043–1047. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.1043-1047.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrer E., Teuber M. Induction of polymyxin resistance in Pseudomonas fluorescens by phosphate limitation. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):87–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00429636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Lyle R. D. Chemical alterations in cell envelopes of polymyxin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.839-845.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Murray R. G. Ultrastructural study of polymyxin-resistant isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):267–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.267-281.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Eagon R. G. Ultrastructural and chemical alteration of the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, associated with resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate resulting from growth in a Mg2+-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):302–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.302-311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann W., Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Polymyxin binding to charged lipid membranes. An example of cooperative lipid-protein interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 16;510(1):124–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson L. A., Bartholomaus R. C., Gunsalus I. C. Repression of malic enzyme by acetate in Pseudomonas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):955–960. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I. R., Bach D., Teuber M. Effect of polymyxin B on the structure and the stability of lipid layers. J Membr Biol. 1978 Feb 6;39(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01872754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixl F., Galla H. J. Cooperative lipid-protein interaction. Effect of pH and ionic strength on polymyxin binding to phosphatidic acid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnett J. D., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Proteins released from cell envelopes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on exposure to ethylenediaminetetraacetate: comparison with dimethylformamide-extractable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):399–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.399-407.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Mechanism of polymyxin B resistance in Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):289–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.289-294.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. Binding capacities for polymyxin B of inner and outer membranes isolated from Salmonella typhimurium G30. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00425112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang J. C., Weber D. A., Brown D. A. Evidences for complex formation between polymyxin B and lipopolysaccharides from Serratia marcescens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jul;29(7):735–742. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



