Abstract
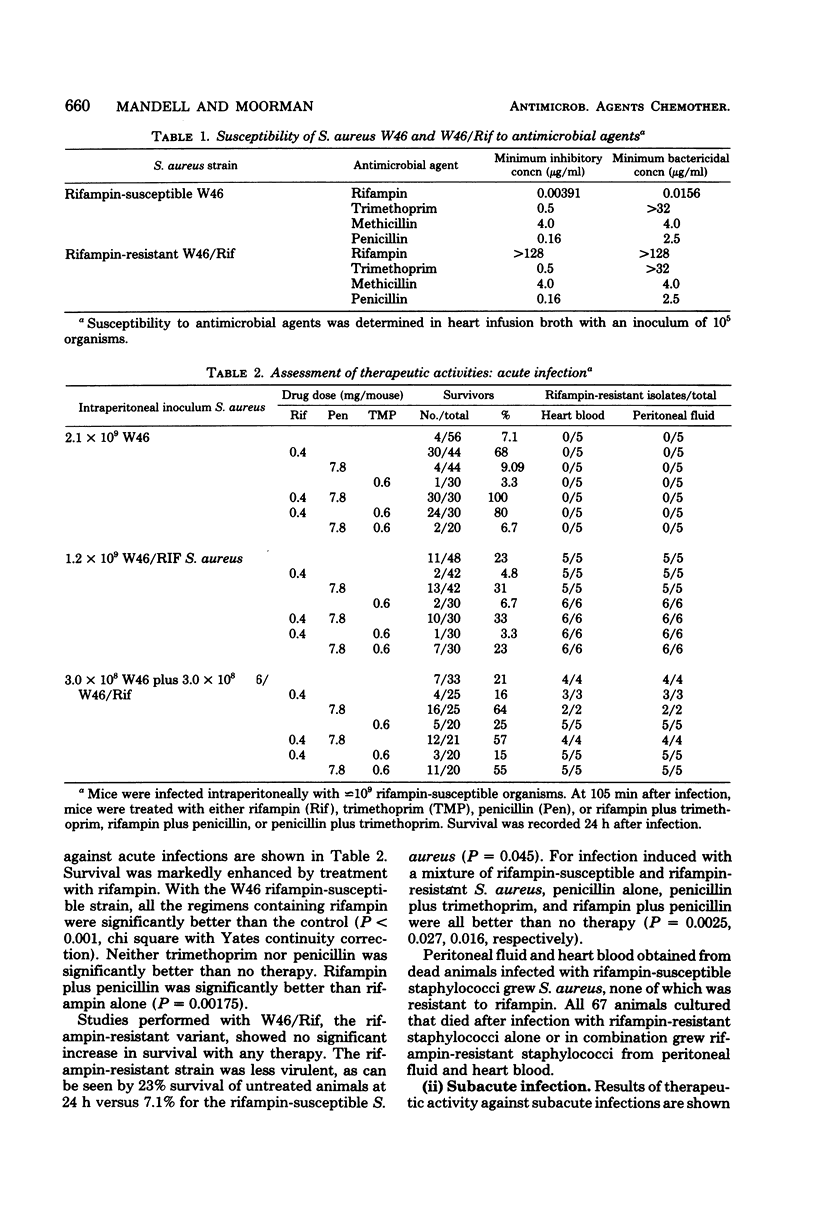
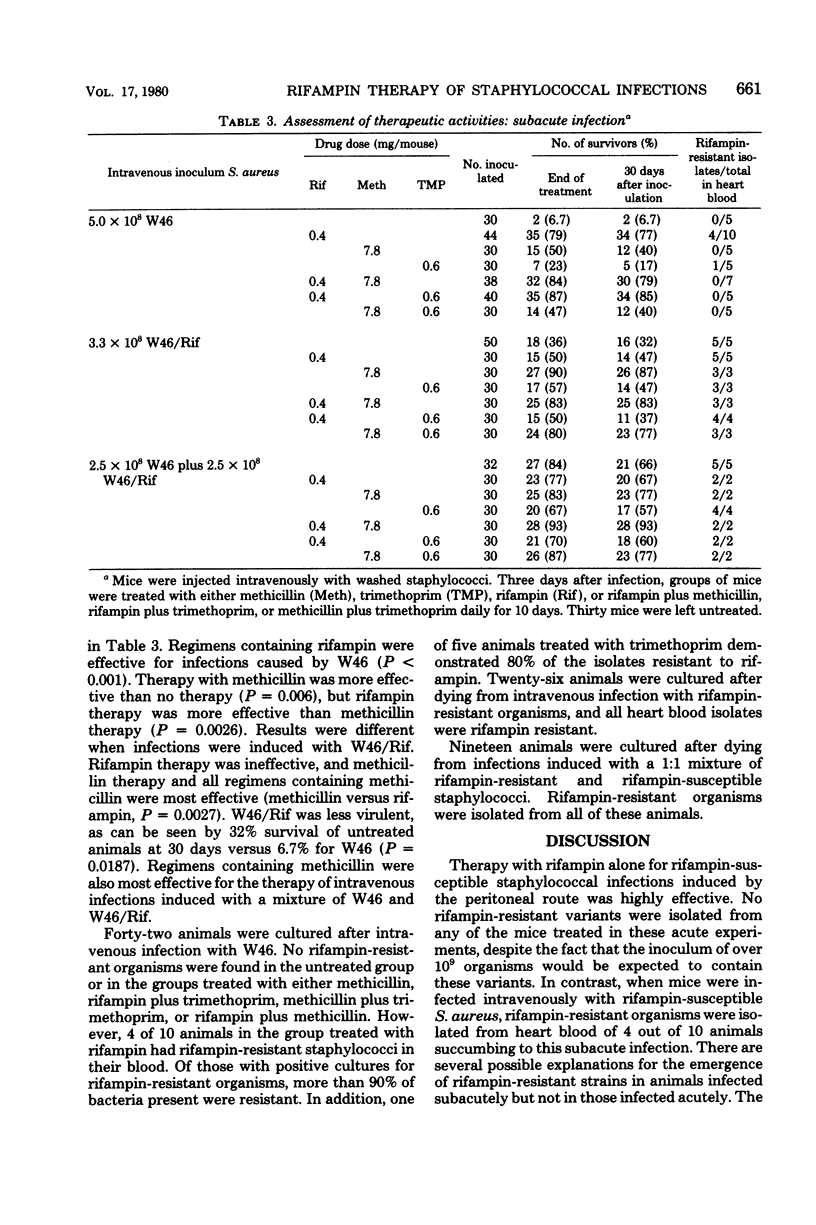
Rifampin is a potentially useful anti-staphylococcal agent, but resistance develops frequently when the drug is used alone. The efficacy of rifampin, trimethoprim, and a penicillin alone or in combination was examined in mice with acute or subacute infections. Mice were infected intraperitoneally with penicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Survival after penicillin therapy was only 9.1% in contrast to survival after rifampin therapy which was 68% (P less than 0.001). No rifampin-resistant S. aureus were isolated from peritoneal fluid or heart blood samples from dead animals in these short-term experiments. Rifampin was ineffective (survival, 4.8%) for infections instituted with rifampin-resistant strains. Long-term experiments were conducted after intravenous injection of 4 x 10(8) S. aureus. Forty percent of the animals survived after methicillin therapy; 77% survived after rifampin therapy (P less than 0.001). However, 40% of those animals that died after rifampin therapy died with rifampin-resistant organisms. No animal dying in groups treated with a combination of rifampin and trimethoprim (85% survival) or rifampin and methicillin (79% survival) died with rifampin-resistant organisms. Thus, rifampin combined with a penicillin or trimethoprim was effective in preventing the development of rifampin-resistant strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kunin C. M., Brandt D., Wood H. Bacteriologic studies of rifampin, a new semisynthetic antibiotic. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):132–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo M. C., Mandell G. L. Treatment of experimental staphylococcal infection with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Catalase, superoxide dismutase, and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro and in vivo studies with emphasis on staphylococcal--leukocyte interaction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):561–566. doi: 10.1172/JCI107963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1673–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI107348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Vest T. K. Killing of intraleukocytic Staphylococcus aureus by rifampin: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):486–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Lin M. Y., Sheagren J. N. In vitro activity of rifampin alone and in combination with nafcillin and Vancomycin against pathogenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):759–761. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


