Transcriptional targets of Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway signalling as effectors of haematopoietic tumour formation
In this paper, Zeidler and colleagues describe the use of transcript profiling approaches in the low complexity Drosophila system to identify genes regulated by STAT transcription factors that are necessary for the development of JAK/STAT-induced blood cell cancers. Not only do they use in vivo approaches to show that knock down of these genes reduces tumour formation in flies, but they also link these findings to the expression of human homologues, thereby using this animal model of disease to identify potentially important targets in the human system.
Keywords: HopTumL, Kc167, transcript profiling, V617F, cancer
Abstract
Although many signal transduction pathways have been implicated in the development of human disease, the identification of pathway targets and the biological processes that mediate disease progression remains challenging. One such disease-related pathway is the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) cascade whose constitutive misactivation by the JAK2 V617F mutation underlies most human myeloproliferative disorders. Here, we use transcript profiling of Drosophila haemocyte-like cells to identify JAK/STAT target genes, combined with an in vivo model for JAK-induced blood cell overproliferation, to identify the main effectors required for haematopoietic tumour development. The identified human homologues of the Drosophila effectors were tested for potential V617F-mediated transcriptional regulation in human HeLa cells and compared with small interfering RNA-derived data, quantify their role in regulating the proliferation of cancer-derived cell lines. Such an inter-species approach is an effective way to identify factors with conserved functions that might be central to human disease.
Introduction
The Janus kinase (JAK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling pathway has been conserved throughout evolution and consists of a large family of extracellular ligands that bind to transmembrane receptors, which are themselves associated with JAK kinases. Following stimulation, ligand/receptor/JAK complexes are activated by tyrosine phosphorylation to recruit STATs, which are then tyrosine-phosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus. In the canonical model of pathway signalling, activated STAT dimers then bind to palindromic DNA-binding sites in the promoters of pathway target genes to activate transcription. In Drosophila, the DNA-binding sites recognized by the STAT92E transcription factor are separated either by three nucleotides (3n sites), generating a high-affinity site, or by four nucleotides (4n sites), which are bound with lower affinity (Rivas et al, 2008). In addition, recent reports suggest a non-canonical association of STAT92E/HP1 complexes to heterochromatic DNA in the absence of JAK signalling, thus representing an alternative mechanism by which STAT92E might indirectly regulate transcription in vivo (Shi et al, 2008).
Although JAK/STAT pathway signalling is required during development, its inappropriate activation is also responsible for a range of human malignancies. In particular, the dominant gain-of-function mutation JAK2 V617F is central to most myeloproliferative diseases (Kota et al, 2008). Interestingly, V617F is located in the regulatory JH2 domain of JAK2, the same domain that is affected by gain-of-function mutations in the Drosophila JAK homologue Hopscotch (Hop). The principal phenotype associated with these Drosophila mutations is an overproliferation of prohaemocytes and their inappropriate differentiation into lamellocytes, ultimately producing large black melanotic tumours (Luo et al, 1995).
The low redundancy of the evolutionarily conserved JAK/STAT pathway components, combined with the conservation of developmental roles of the pathway (Arbouzova & Zeidler, 2006), makes Drosophila an effective animal model for human disease development. Although JAK/STAT pathway components and regulators have been studied in detail and the tumour phenotypes are well characterized, the biological processes triggered by JAK/STAT signalling that produce the terminal phenotype are less well understood. Here, we use the strengths of the Drosophila system to identify candidate effectors that have a part in this process.
Results And Discussion
Transcript profiling
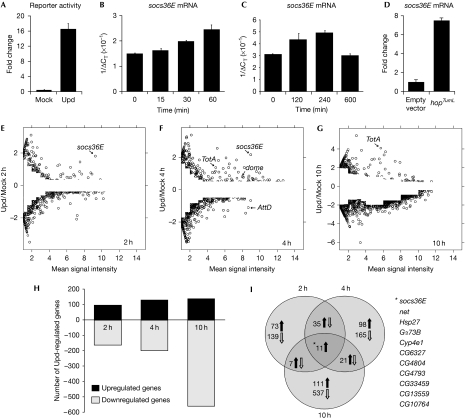
Drosophila haemocyte-like Kc167 cells endogenously express JAK/STAT pathway components, respond to the Unpaired (Upd) ligand (Harrison et al, 1998) and have been used to undertake genome-wide RNA interference (RNAi) screens for regulators of pathway signalling (Müller et al, 2005). We therefore used this ex vivo system as a starting point to identify pathway targets and mediators of JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila haematopoiesis. Treating Kc167 cells with Upd-conditioned media is sufficient to induce luciferase-based reporters (Fig 1A). To test the temporal expression profile mediated by Upd stimulation, the immediate-early pathway target gene socs36E was assessed by quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) and found to be expressed rapidly and strongly over several hours (Fig 1B,C), an upregulation recapitulated by HopTumL stimulation (Fig 1D). To reflect the socs36E profile and the time course of haematopoietic organ development in vivo, 2h, 4h and 10 h time points were selected for analysis. The aim was to capture the response of genes stimulated directly by the pathway (2 h), later genes representing both direct targets and early secondary effects (4 h), and longer term responses probably representing the secondary and possibly tertiary effects of JAK/STAT signalling (10 h).
Figure 1.
Transcript profile analysis of Upd-induced JAK/STAT activation. (A) Upd is able to stimulate a luciferase JAK/STAT pathway reporter construct (Müller et al, 2005). (B–D) Quantitative PCR showing socs36E mRNA levels in Kc167 cells after either Upd stimulation (B,C) or 72 h after HopTumL transfection (D). (E–G) Plots of genes expressed at the indicated time points showing the log2 ratio for each gene as a function of the mean signal intensity. Differentially expressed genes were identified by calculating intensity-dependent z-scores and filtered to remove those differing by less than two standard deviations from the mean. (H) The number of genes either upregulated or downregulated at the 2 h, 4 h and 10 h time points. (I) Venn diagram showing the distribution of upregulated and downregulated genes at the 2 h, 4 h and 10h time points. The 11 loci upregulated at all time points are listed. Hop, Hopscotch; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Upd, Unpaired.
The transcription profiles generated from microarrays were analysed by using the propagating uncertainty in microarray analysis (PUMA) algorithm to assign a confidence score to each gene (Pearson et al, 2009). A differential fold change cutoff was applied to define genes whose expression was significantly different (P<0.05) from that of the mock control at various expression levels (Fig 1E–G; Yang et al, 2002). This approach increases the stringency applied to genes expressed at lower levels where the effect of experimental noise and non-specific hybridization is greater (Fig 1E–G). In total, 1,168 genes were identified as being expressed differentially at one or more time point (Fig 1H–I; supplementary Fig S1 and Table S1 online).
JAK/STAT pathway stimulation has long been considered a positive regulator of transcription. However, treatment of Kc167 cells with Upd clearly induces both upregulation and downregulation of a wide range of transcripts, with the proportion of downregulated loci increasing at later time points (Fig 1E–I). Q-PCR analysis of selected loci validated the chip-derived data and confirmed the existence of downregulated genes (supplementary Fig S1A,B online). While many of the loci regulated negatively at 10 h might represent secondary or tertiary consequences of pathway activation, more than 150 loci are also regulated negatively at 2 h. Although mechanisms responsible for these early effects remain to be identified, this negative transcriptional regulation is not unprecedented, with examples of downregulation in Dictyostelium (Mohanty et al, 1999), the Drosophila eye (Mukherjee et al, 2006) and vertebrate cancers (Dauer et al, 2005; Qu et al, 2009).
Clustering of genes and functional enrichment
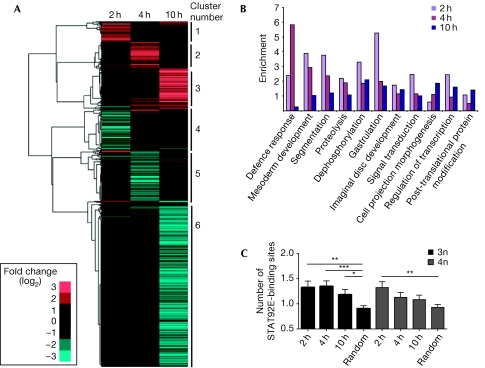
Hierarchical clustering of the data set (Eisen et al, 1998) identified six distinct clusters of co-regulated loci (Fig 2A), with subsequent analysis of associated gene ontology (GO) terms showing enrichment of functionalities such as endopeptidase activity (cluster 3), cell differentiation and morphogenesis (cluster 6), and humoral immune responses (cluster 5). Interestingly, when similar GO analysis is undertaken within each time point (Fig 2B), processes such as mesoderm development, segmentation and gastrulation are represented strongly at 2 h, defence responses are enriched at 4 h and cell morphogenesis and post-translational modifications are more prevalent at 10 h. These roles are consistent with the known developmental roles of JAK/STAT pathway signalling, including haematopoiesis and immune responses (Arbouzova & Zeidler, 2006). As such, GO-based analysis suggests that the genes identified reflect a bona fide response to pathway stimulation.
Figure 2.
Clustering, gene ontology and binding-site analysis of putative JAK/STAT target genes. (A) Hierarchical cluster analysis of 1,168 Upd-regulated genes using log2 ratios. The blue tiles represent downregulated genes and red tiles indicate upregulated genes. Six main clusters were identified. (B) The functional enrichment of the 1,168 Upd-regulated genes according to gene ontology terms. (C) The average number of potential 3n and 4n STAT92E-binding sites present in the upstream region of positively regulated genes at each time point, compared with the number of sites in a randomly selected ‘control' group of genes. *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005. JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Upd, Unpaired.
STAT92E-binding sites
The single Drosophila STAT92E protein has recently been shown to bind to both 3n and 4n DNA-binding sites, with higher affinity for 3n sites (Rivas et al, 2008). Given that co-expression (or repression) of genes is probably a consequence of common cis-regulatory elements within promoters, we assessed the frequency with which either 3n or 4n sites are found in the genomic interval 3 kb upstream of the transcriptional start site of the 1,168 genes identified and a randomly selected group of unrelated Drosophila genes. The negatively regulated genes did not show enrichment of STAT92E-binding sites and are therefore unlikely to be regulated by the canonical STAT92E-binding sites (data not shown). Interestingly, for upregulated loci, 3n sites are present at significantly higher frequencies at each time point (Fig 2C), whereas 4n sites are only enriched at 2 h. Given that Upd-induced STAT92E activity is probably strongest at 2 h (Fig 1B,C), it seems plausible that transcription driven by lower affinity 4n STAT92E-binding sites reflects a requirement for higher levels of STAT92E activity.
Roles in Drosophila haematopoietic tumour development
Given the number of loci differentially regulated by Upd, other criteria were used to select potential JAK/STAT pathway effectors for testing in vivo. The 1,168 genes were therefore compared with genes identified in published microarray experiments and RNAi screens focused on Drosophila immunity. Comparison of these data sets identified 22 differentially regulated genes (including socs36E) that may represent potential mediators of JAK/STAT pathway signalling in vivo (Table 1). These include components of other signalling pathways such as the Wnt4 ligand, the Gα73B subunit and the negative regulator of Hedgehog signalling pxb, as well as l(2)gl and the negatively regulated bazooka (baz), two loci previously implicated in tumorigenesis and cell polarity.
Table 1. Upd-responsive genes selected for in vivo RNAi assays.
| Gene name Drosophila melanogaster | Fold change log(2) | STAT92E-binding sites | Gene ontology | Gene name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 4 h | 10 h | 3n | 4n | Homo sapiens | ||
| baz | −0.2 | −0.6 | −1.9 | 0 | 1 | Asymmetric protein localization | PARD3, PARD3B, MPDZ |
| CG10764 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.5 | 6 | 4 | Serine endopeptidase | — |
| CG13559 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 2 | 1 | — | LITAF |
| CG15211 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 1 | 0 | — | — |
| CG15678 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1 | 0 | Negative regulation of innate immune response | — |
| CG1572 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 2 | 1 | — | — |
| CG31158 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 1 | 0 | Regulation of ARF protein signal transduction | PSD3, PSD, PSD2 |
| CG3829 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 2 | 0 | Defence response | SCARB1, SCARB2, CD36 |
| CG4080 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 | Protein binding | MARCH8, MARCH2, MARCH1 |
| CG4793 | 0.7 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 6 | 2 | Serine endopeptidase | TMPRSS13, KLKB1, CTRB2 |
| CG4804 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 4 | 2 | Serine endopeptidase | PAI-2, SERPINI1, SERPINB8 |
| CG6014 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0 | — | REG1A |
| Gα73B | 1.2 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2 | 0 | GTPase activity | GNAS, GNAL, GSA |
| idgf1 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | Imaginal-disc development | CHIT1, CHI3L2, CHIA |
| l(2)gl | 0.0 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 1 | 0 | Protein localization | LLGL1, LLGL2, STXBP5 |
| mfas | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 2 | 0 | Axonegenesis | TGFBI, POSTN |
| mthl3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6 | 4 | G-protein-coupled receptor activity | GPR112 |
| net | 2.3 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2 | 2 | Imaginal-disc-derived wing vein morphogenesis | ATOH8 |
| pxb | −0.7 | −0.8 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | Smoothened signalling pathway | — |
| socs36E | 1.8 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 5 | 3 | Negative regulation of JAK/STAT cascade | SOCS5, SOCS4, SOCS6 |
| TotA | 0.0 | 1.1 | 4.1 | 2 | 2 | Response to stress | — |
| Wnt4 | 2.2 | −1.5 | 0.0 | 0 | 2 | Signal transducer activity | WNT9A, WNT9B, WNT16 |
| Bold gene names indicate homologues tested by quantitative PCR. | |||||||
| baz, bazooka; RNAi, RNA interference; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Upd, Unpaired. | |||||||
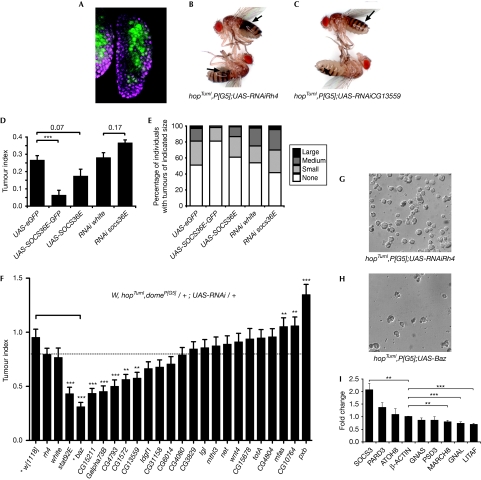
JAK/STAT pathway signalling has an important role in the larval haematopoietic organ (Krzemien et al, 2007), where haematopoietic stem cells are maintained in the medullary zone (MZ) of the lymph gland by pathway activity. The MZ is marked by expression of the pathway receptor dome (Fig 3A, green). However, in the hopTumL gain-of-function mutant, increased levels of JAK/STAT pathway signalling result in additional cellular proliferation in the lymph gland, a massive increase in circulating haemocytes, engulfment of ‘self' tissue and ultimately formation of black melanotic tumours (Fig 3B,C; Luo et al, 1995). Altered expression of JAK/STAT pathway targets and effectors in the lymph gland, elicited by the activating HopTumL mutation (Fig 1D), might therefore be central to melanotic tumour formation.
Figure 3.
In vivo characterization of JAK/STAT targets. (A) The third-instar lymph gland showing the domain of p[G5] expression (green) in the central MZ. DNA is shown in magenta. (B,C) Adult flies of the specified genotypes carrying the gain-of-function hopTumL allele contain multiple, large black tumours (indicated by arrows) when a control shRNA targeting rhodopsin 4 (rh4) is expressed in the MZ by the p[G5] driver (B). Flies in which the pathway effector CG13559 is knocked down contain fewer, smaller tumours (C). The TI (D) and percentage of adults with tumours of the indicated size (E) are shown for the specified genotypes, which either overexpress or knock down socs36E. Overexpression using UAS-SOCS36E-GFP flies showed significant reduction in TI as compared with that in the control (D). (F) The TI of flies of the indicated genotype expressing shRNAs targeting 21 potential effectors as well as rh4 and white as controls. The bar indicates the link between baz misexpression and w[1118] used as the control for this cross. (G,H) Representative differential interference contrast image of haemocytes from hopTumL larvae of the indicated genotypes showing reduction in circulating cells present after UAS-baz overexpression. (I) Fold change in the expression of selected homologues of Drosophila genes in HeLa cells after stimulation by the gain-of-function JAK2 V617F mutation. For all graphs, error bars represent standard error. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. baz, bazooka; GFP, green fluorescent protein; hop, Hopscotch; JAK, Janus kinase; MZ, medullary zone; shRNA, short-hairpin RNA; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TI, tumour index.
To test this hypothesis, we first overexpressed the pathway target gene and negative regulator socs36E in the MZ of HopTumL individuals. Counts of the size and frequency of melanotic masses present in adult flies were used to generate a quantitative ‘tumour index' (TI; Shi et al, 2006). Notably, overexpression of SOCS36E by two independently generated transgenes reduced the TI of HopTumL individuals (Fig 3D), with a corresponding decrease in the distribution of tumour sizes (Fig 3E). Conversely, in vivo RNAi constructs targeting socs36E mRNA marginally increased the TI and the proportion of larger tumours (Fig 3D,E). These results indicate that modulation of JAK/STAT pathway activity by overexpression, or knockdown of a JAK/STAT pathway regulator in the MZ, is sufficient to alter the HopTumL-induced tumour phenotype.
To test the functional roles of the potential JAK/STAT effectors in vivo, RNAi was used to knock down the expression of the remaining 21 loci in the MZ of hopTumL mutants with the TI of the resulting adults compared to a range of controls (Fig 3F). In addition to stat92E itself, five novel effector loci—CG15221, Gα73B, CG4793, CG1572 and CG13559—were identified whose knockdown significantly reduces the development of tumours in the adult fly, three of which (Gα73B, CG4793 and CG13559) are also upregulated at each of the three time points assayed originally (Fig 1I). This suggests that these five loci represent true in vivo effectors of JAK/STAT-mediated tumorigenesis. In addition, knockdown of three loci—mfas, CG10764 and pxb—results in significant increases in TI (Fig 3F), suggesting that they function as ‘anti-oncogenes' in vivo. This result is consistent with the Upd-mediated decrease in pxb expression observed at both 2h and 4 h time points (Table 1).
In addition to RNAi-mediated knockdown, overexpression of Baz was also tested, given the decrease in observed baz expression after pathway stimulation. Strikingly, ectopic baz expression is one of the strongest suppressors of tumour development, significantly reducing both the size and frequency of tumours (Fig 3F; supplementary Fig S2 online), as well as the number of circulating haemocytes present in late third-instar larvae (Fig 3G,H). However, knockdown of baz mRNA also seems to produce a reduction in TI and size (supplementary Fig S2 online), suggesting that any alteration of Baz is sufficient to reduce HopTumL-induced tumorigenesis. Interestingly, Baz has recently been shown to drive the apical localization of STAT92E in ectodermally derived tissues in vivo (Sotillos et al, 2008), suggesting a model in which increased Baz binds to and sequesters STAT92E, thereby attenuating its tumorigenic function. However, the validity of this model in mesodermally derived haematopoietic precursors, and the relative expression of endogenous Baz in wild-type and hopTumL lymph glands, remains to be determined.
In addition to Baz, other JAK/STAT effectors identified have close human homologues, including the Gα73B putative homologues GNAL and GNAS, which are key elements of G-protein pathways. In a striking parallel to our findings from the Drosophila system, mutations in the GNAS locus, which is heavily maternally imprinted and associated with a range of human diseases, have been reported to be a marker of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia disease progression (Frey et al, 2006).
JAK/STAT effectors in humans
To extend our studies and begin to test the relevance of our findings to humans, we used one-way and reciprocal BLAST searches to identify the putative human homologues of the 1,168 differentially regulated Drosophila genes. These searches identified 1,818 human genes (292 from reciprocal alignments) representing putative homologues of 717 (61%) of the Drosophila genes identified (supplementary Table S1 online). Direct comparison of these human loci to published lists of genes differentially regulated by STAT3 seems to identify relatively few common targets, with an overlap of eight out of 100 genes identified in human lung-carcinoma cells (Dauer et al, 2005), and 12 out of 159 genes (7.5%) in murine lung tumours (Li et al, 2007; supplementary Table S4 online). However, both overlaps represent significant scores when compared to a randomly selected set of control genes (z-scores of 2.34 and 3.25, respectively), suggesting that downstream targets of STAT signalling have been partly conserved through evolution.
To obtain data relating directly to the Drosophila effectors tested in vivo, we examined the expression of human homologues in cancer-derived HeLa cells stimulated by transfection with the dominant gain-of-function JAK2 V617F mutation (Kota et al, 2008). Of 15 homologues tested (Table 1, bold), eight are expressed in HeLa cells. Of these, GNAL, LITAF, MARCH8 and SOCS3, used as a positive control, were all significantly differentially regulated (Fig 3I; supplementary Table S3 online). This suggests that, although direction is not necessarily maintained, changes in the expression of these loci after JAK/STAT signalling are common to both Drosophila and human systems.
Finally, we cross-referenced the human loci homologous to 16 of the 22 selected Drosophila genes with a database of three genome-wide, small interfering RNA-mediated cell viability screens undertaken with Hela, HEK293T and HepG2 cells (T. Horn & M. Boutros, www.genomeRNAi.org). Although these viability data remain to be validated, the human homologues MARCH2, GPR112 and LLGL1 represent strong suppressors of proliferation in one or more human cancer cell lines (supplementary Table S2 online). These results indicate a potential role for these loci in the development or progression of cancer, and represent a potentially important insight into the role of these putative effectors.
The GNAL/Gα73B locus is a particularly intriguing example of a gene identified repeatedly in this study. We have shown that Drosophila Gα73B is upregulated at all three time points in response to Upd (Fig 1I and Table 1) and its knockdown in hopTumL flies significantly reduces tumorigenesis (Fig 3F). By contrast, its human homologue GNAL is downregulated significantly by V617F in HeLa cells (Fig 3I), while its knockdown in the HepG2 cancer cell line significantly increases cellular proliferation. Therefore, in both systems, disease-related JAK mutations result in differential regulation of this Gα subunit to promote cellular proliferation and tumorigenesis, respectively. Encouragingly, previous reports have identified downregulation of GNAL in leukaemic cells (Koldehoff et al, 2008), supporting the possibility that this locus has an important effector function downstream from JAK/STAT signalling.
Although encouraging, cell culture-based proliferation data must be interpreted with caution and ultimate proof that the genes identified represent the bona fide effectors of tumorigenesis in vivo remains to be determined. However, we have identified JAK/STAT pathway effectors in Drosophila and have identified conserved homologues of these in humans. In addition, we have shown examples of common transcriptional regulation as well as potential links with haematopoietic malignancies and proliferation of cancer-derived cell lines. Although detailed mechanistic analysis of individual effectors and their roles in disease progression remains the ultimate goal, our genetic approach has effectively identified pathway effectors likely to mediate human disease.
Methods
Upd-conditioned media and transcript profiling. Conditioned media was prepared as described by Harrison et al (1998) and assayed for activity by using the 6x2xDrafluc reporter (Müller et al, 2005). Kc167 cells were treated with Upd or mock-conditioned media for 30 min, washed and total RNA was extracted after 2h, 4h or 10 h according to the Affymetrix protocols. Twelve samples were hybridized to the GeneChip® Drosophila Genome 2.0 arrays. The raw probeset data were analysed by using the PUMA package (Pearson et al, 2009) to generate intensity-dependent z-scores for each log2 ratio (Yang et al, 2002). Genes ⩾2 standard deviations from the mean were flagged as differentially expressed. Raw data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus database under accession number GSE15584.
Q-PCR of Kc167 cells. Q-PCR used the total RNA and primers shown in supplementary Table S4 online, the SYBR® Green JumpStart™ TaqReadyMix™ (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and followed a standard Verso™ reverse transcription-PCR (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) protocol. PCR was performed in triplicate in a Bio-Rad MyIQ™, analysed by ΔΔCT and normalized to Rpl32.
Cell culture. HeLa cells grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with 10% fetal calf serum were transfected with pMX-IRES-JAK2 V617F or empty vector using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK). The cells were harvested after 24 h and total RNA was extracted. Q-PCR was performed in triplicate as described above and normalized to β-actin.
In vivo tumour assays. In vivo tumour assays used a hopTuml, domeP[G5] recombinant crossed to the individual inducible UAS-RNAi and misexpression stocks as described by Dietzl et al (2007; supplementary Table S5 online). The TI scores of the resulting adults were calculated as described by Shi et al (2006). For blood-cell pictures, wandering third-instar larvae were bled by tearing the larva in a 15 μl drop of serum-free Schneider's medium placed on a haemocytometer.
Further details, including bioinformatic techniques, are available in the supplementary information online or from the authors on request.
Supplementary information is available at EMBO reports online (http://www.emboreports.org).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Jäckle, S. Häder, D. Pugazhendhi, E. Ziviani, A.S. Georgiou and K. Johnstone for valuable support during this project. A. Vincent, A. Wodarz, S. Constantinescu, P. Karsten, F. Serras, M. Boutros and T. Horn provided reagents and unpublished data. H. Strutt gave comments on the paper. Confocal imaging was undertaken at the Wellcome Trust-supported Sheffield Light Microscopy Facility. S.B. is a fellow of the Göttingen International MSc/PhD Program and was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. M.M. is supported by the National Institute for Health Research through its Sheffield Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit. K.H.F. is funded by the European Union ‘Cancer Pathways' FP7 project. M.P.Z. is a Cancer Research UK Senior Cancer Research Fellow.
Footnotes
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Arbouzova NI, Zeidler MP (2006) JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila: insights into conserved regulatory and cellular functions. Development 133: 2605–2616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauer DJ, Ferraro B, Song L, Yu B, Mora L, Buettner R, Enkemann S, Jove R, Haura EB (2005) Stat3 regulates genes common to both wound healing and cancer. Oncogene 24: 3397–3408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzl G et al. (2007) A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila. Nature 448: 151–156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 14863–14868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey UH, Nuckel H, Sellmann L, Siemer D, Kuppers R, Durig J, Duhrsen U, Siffert W (2006) The GNAS1 T393C polymorphism is associated with disease progression and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 12: 5686–5692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison DA, McCoon PE, Binari R, Gilman M, Perrimon N (1998) Drosophila unpaired encodes a secreted protein that activates the JAK signaling pathway. Genes Dev 12: 3252–3263 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koldehoff M, Zakrzewski JL, Klein-Hitpass L, Beelen DW, Elmaagacli AH (2008) Gene profiling of growth factor independence 1B gene (Gfi-1B) in leukemic cells. Int J Hematol 87: 39–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kota J, Caceres N, Constantinescu SN (2008) Aberrant signal transduction pathways in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 22: 1828–1840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzemien J, Dubois L, Makki R, Meister M, Vincent A, Crozatier M (2007) Control of blood cell homeostasis in Drosophila larvae by the posterior signalling centre. Nature 446: 325–328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Du H, Qin Y, Roberts J, Cummings OW, Yan C (2007) Activation of the signal transducers and activators of the transcription 3 pathway in alveolar epithelial cells induces inflammation and adenocarcinomas in mouse lung. Cancer Res 67: 8494–8503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H, Hanratty WP, Dearolf CR (1995) An amino acid substitution in the Drosophila hopTum-l Jak kinase causes leukemia-like hematopoietic defects. EMBO J 14: 1412–1420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty S, Jermyn KA, Early A, Kawata T, Aubry L, Ceccarelli A, Schaap P, Williams JG, Firtel RA (1999) Evidence that the Dictyostelium Dd-STATa protein is a repressor that regulates commitment to stalk cell differentiation and is also required for efficient chemotaxis. Development 126: 3391–3405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee T, Schäfer U, Zeidler MP (2006) Identification of Drosophila genes modulating janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signal transduction. Genetics 172: 1683–1697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P, Kuttenkeuler D, Gesellchen V, Zeidler MP, Boutros M (2005) Identification of JAK/STAT signalling components by genome-wide RNA interference. Nature 436: 871–875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson RD, Liu X, Sanguinetti G, Milo M, Lawrence ND, Rattray M (2009) puma: a Bioconductor package for propagating uncertainty in microarray analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 10: 211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu P, Roberts J, Li Y, Albrecht M, Cummings OW, Eble JN, Du H, Yan C (2009) Stat3 downstream genes serve as biomarkers in human lung carcinomas and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung Cancer 63: 341–347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas ML, Cobreros L, Zeidler MP, Hombria JC (2008) Plasticity of Drosophila Stat DNA binding shows an evolutionary basis for Stat transcription factor preferences. EMBO Rep 9: 1114–1120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi S, Calhoun HC, Xia F, Li J, Le L, Li WX (2006) JAK signaling globally counteracts heterochromatic gene silencing. Nat Genet 38: 1071–1076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi S, Larson K, Guo D, Lim SJ, Dutta P, Yan SJ, Li WX (2008) Drosophila STAT is required for directly maintaining HP1 localization and heterochromatin stability. Nat Cell Biol 10: 489–496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotillos S, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Castelli-Gair Hombria J (2008) Polarized subcellular localization of Jak/STAT components is required for efficient signaling. Curr Biol 18: 624–629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang IV et al. (2002) Within the fold: assessing differential expression measures and reproducibility in microarray assays. Genome Biol 3: research0062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.