Abstract
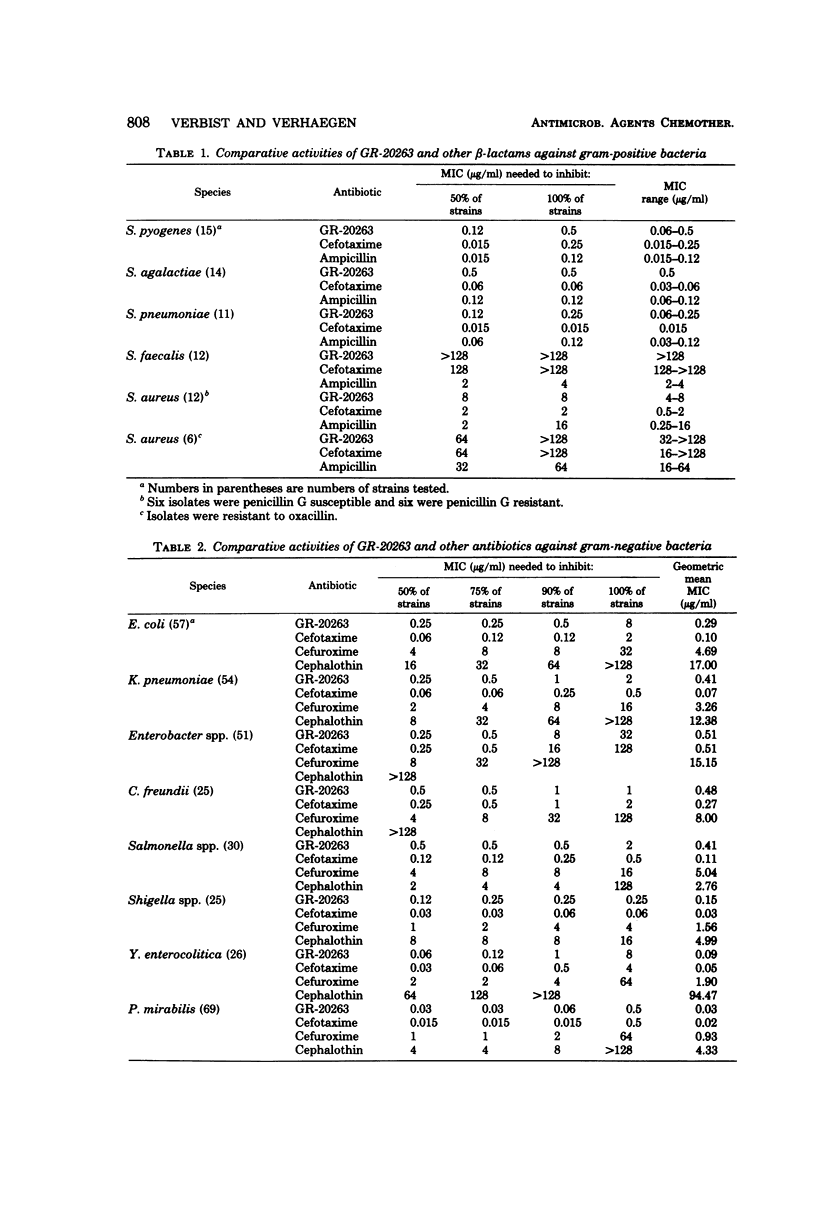
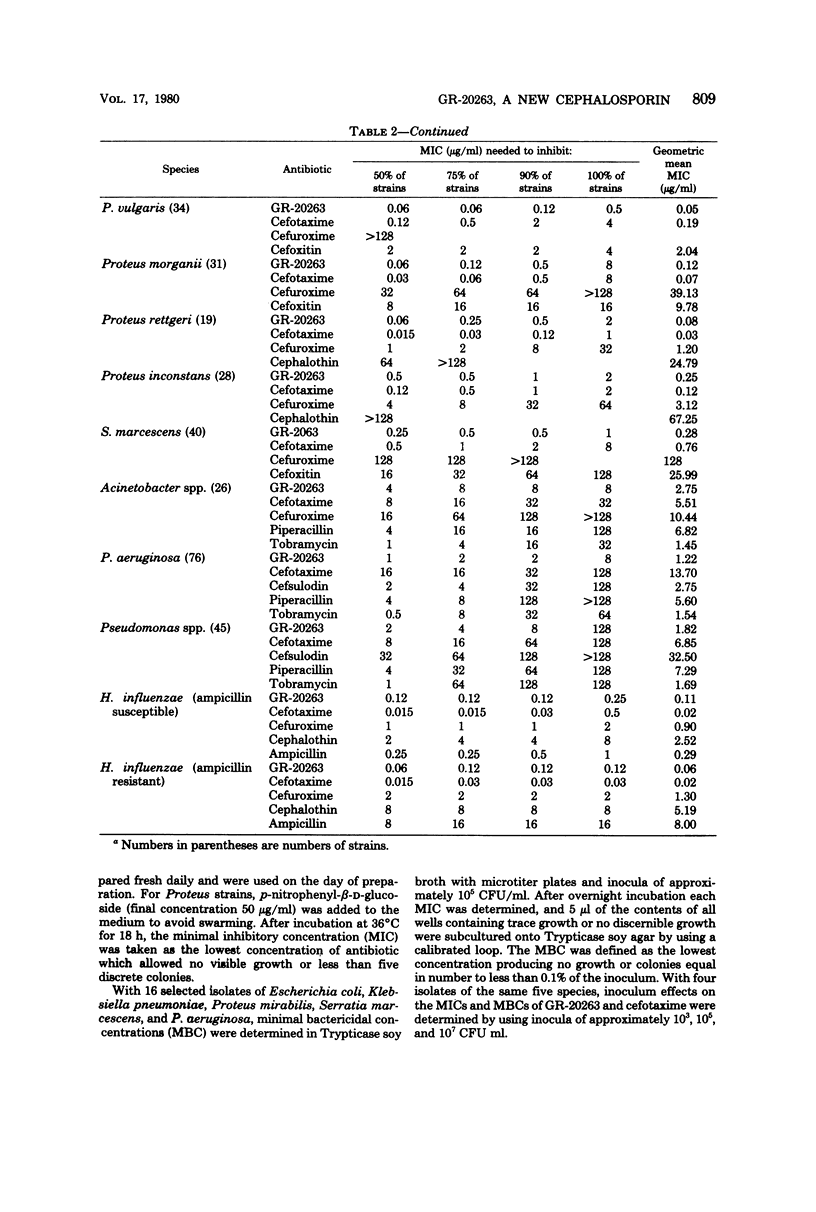
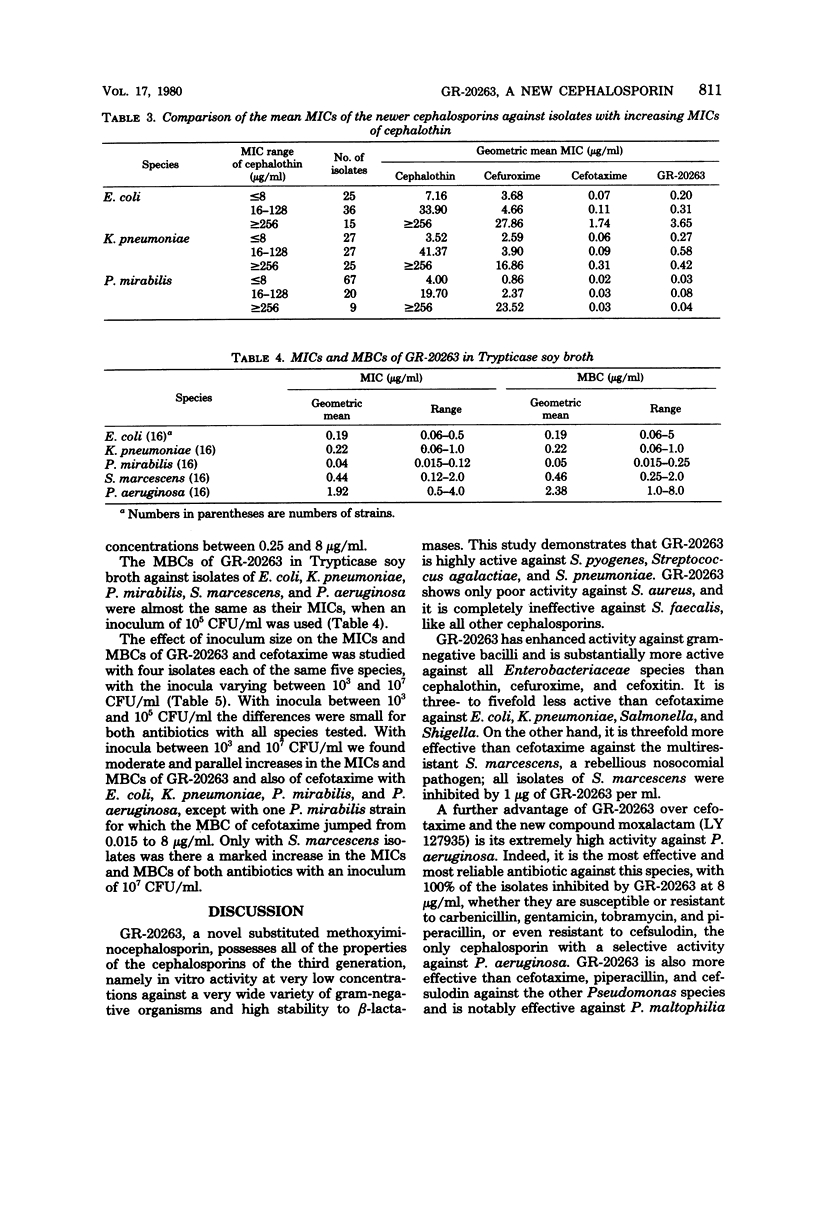
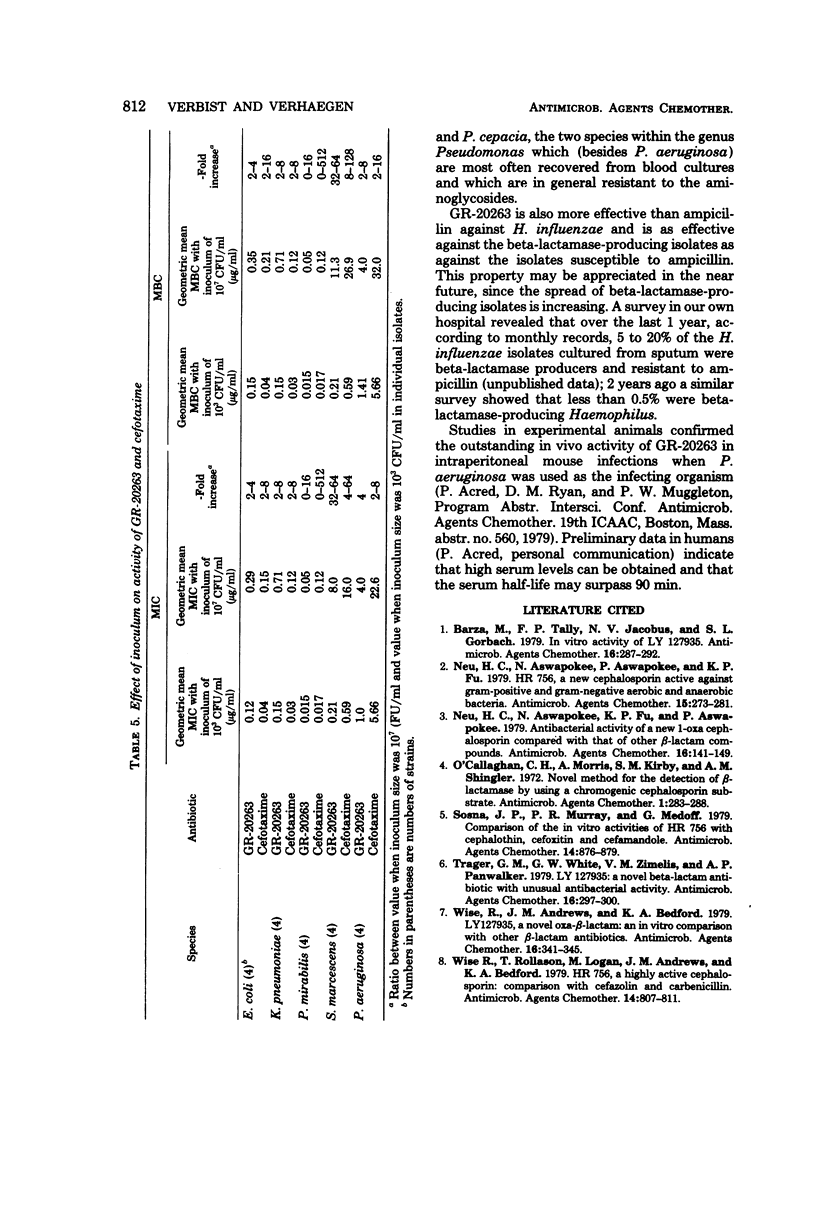
The in vitro activity of GR-20263, a new aminothiazolyl cephalosporin, was compared with the activities of other beta-lactam antibiotics by using 800 clinical bacterial isolates. GR-20263 was highly active (inhibition of 90% of the isolates between 0.03 and 1 microgram/ml) against the common Enterobacteriaceae and 5 to 20 times more active than cefuroxime, cefoxitin, and cephalothin. GR-20263 was three to six times less active than cefotaxime against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella, and Shigella, but three to four times more active than cefotaxime against Proteus vulgaris and Serratia marcescens. The activity of GR-20263 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (with minimal inhibitory concentrations of 2 and 8 micrograms/ml for 90 and 100% of the isolates, respectively) was similar to that of tobramycin, 2 times that of cefsulodin, 5 times that of piperacillin, and 10 times that of cefotaxime. Against Haemophilus influenzae GR-20263 was three time more active than ampicillin. The beta-lactamase-producing strains were as susceptible to GR-20263 as the beta-lactamase-negative strains. GR-20263 was less active than cefotaxime and ampicillin against Staphylococcus aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Aitken C. L., Dennis P. G., Forsythe P. S., Patrick K. E., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C. Relationship of early readings of minimal inhibitory concentrations to the results of overnight tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Ayres C., Sabath L. D. Rapid semiquantitative testing of antibiotic susceptibility: use of a multicell disk elution system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):543–548. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Fu K. P. HR 756, a new cephalosporin active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):273–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Fu K. P., Aswapokee P. Antibacterial activity of a new 1-oxa cephalosporin compared with that of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Schoenknecht F. D., Kenny M. A., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: selection of a control strain and criteria for magnesium and calcium content in media. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):454–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenknecht F. D., Washington J. A., 2nd, Gavan T. L., Thornsberry C. Rapid determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial agents by the Autobac method: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):824–833. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosna J. P., Murray P. R., Medoff G. Comparison of the in vitro activities of HR756 with cephalothin, cefoxitin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):876–879. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Gavan T. L., Sherris J. C., Balows A., Matsen J. M., Sabath L. D., Schoenknecht F., Thrupp L. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Laboratory evaluation of a rapid, automatic susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):466–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager G. M., White G. W., Zimelis V. M., Panwalker A. P. LY-127935: a novel beta-lactam antibiotic with unusual antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):297–300. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. LY127935, a novel oxa-beta-lactam: an in vitro comparison with other beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):341–345. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Rollason T., Logan M., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. HR 756, a highly active cephalosporin: comparison with cefazolin and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):807–811. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witebsky F. G., Maclowry J. D., French S. S. Broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentrations: rationale for use of selected antimicrobial concentrations. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):589–595. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.589-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



