Abstract
Robust activity of some networks, such as central pattern generators, suggests the existence of physiological mechanisms which maintain the most important characteristics, for example, the period and spike frequency of the pattern. Whatever these mechanisms are, they change the appropriate model parameters to or along the isomanifolds on which the characteristics of the pattern are constant, while their sensitivities to parameters may be different. Setting synaptic connections to zero at the points of isomanifolds allows for dissecting the maintenance mechanisms into components involving synaptic transmission and components involving intrinsic currents. The physiological meaning of the intrinsic current changes might be revealed by analysis of their impact on endogenous neuronal dynamics. Here, we sought answers to the following two questions: 1) Do parameter variations in insensitive directions, i.e. along isomanifolds, change endogenous dynamics of the network neurons? 2) Do sensitive and insensitive directions for network pattern characteristics depend on endogenous dynamics of the network neurons?
We considered a leech heartbeat half-center oscillator model network, and analyzed isomanifolds on which the burst period and/or spike frequency of the model are constant. Based on our analysis, we hypothesize that the dependence on endogenous dynamics of the isolated neurons is the stronger the more characteristics of the pattern have to be maintained. We also found that in general, the network was more flexible when it consisted of endogenously tonically spiking rather than bursting or silent neurons. Finally, we discuss physiological implications of our findings.
1 Introduction
Neuronal networks must function reliably yet be flexible enough to change their activity smoothly or even switch from one functional regime to another when necessary. These contrasting properties can be produced by a variety of intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, such as homeostatic regulation and neuromodulation (Calabrese, 1998; Marder & Thirumalai, 2002; Turrigiano & Nelson, 2004; Marder & Goaillard, 2006). In particular, as suggested by Goldman et al. (2001), there might be mechanisms that prepare a neuron for the subsequent action of neuromodulators by changing sensitivities of the activity characteristics to parameter changes.
The aim of the present study was to use the concepts of sensitive and insensitive directions for the analysis of the mechanisms regulating network activity. Network connections modify the dynamical repertoire of a neuron considerably. For example, in central pattern generators such as leech heart timing network and the Pre-Bötzinger complex, essential to the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals, neurons in the network burst in a much wider range of parameters than when isolated (Butera et al, 1999; Cymbalyuk et al., 2002). In our study, we explored the relations between the sensitivities of the network activity characteristics and dynamics of isolated neurons. We considered two specific questions. 1) Do parameter variations in insensitive directions change the dynamics of isolated network neurons? 2) Do sensitive and insensitive directions for network pattern characteristics depend on endogenous dynamics of the network neurons?
We based our analysis on the notion of an isomanifold, a manifold in the parameter space on which functional characteristics of the neuronal system are constant (Olypher & Calabrese, 2007). Insensitive directions at a point are tangent to the isomanifold at the point. In these directions none of the characteristics, constant on the isomanifold, change. The most sensitive direction for a functional characteristic at a point is, by definition, the direction of the characteristic’s gradient at that point.
We considered a network, consisting of two reciprocally inhibitory neurons that paces the leech heartbeat (Kristan, Calabrese, & Friesen, 2005). The network produces a characteristic pattern of activity, half-center oscillations, with the two neurons bursting alternately (Fig. 1). We considered a well-developed model of this half-center oscillator, HCO, described in Hill et al. (2001). Our focus was on the isomanifolds on which the burst period and spike frequency - the most important functional characteristics of the network – were constant while parameters critically affecting these characteristics, varied. As was shown in our earlier experiments and simulations (Hill et al., 2001; Cymbalyuk et al., 2002; Sorensen et al., 2004; Olypher, Cymbalyuk, & Calabrese, 2006) those parameters are the maximal conductances of the hyperpolarization-activated, spike-mediated synaptic, and leak currents, and the rate of inactivation of a low-threshold slowly inactivating calcium current. To explore the interplay between dynamics of the isolated network neurons and the mechanisms, maintaining the burst period and spike frequency, we analyzed the isomanifolds for the networks composed of endogenously bursting, silent, or tonically spiking neurons. We found that insensitive directions and sensitivities in the HCO model do depend on endogenous dynamics of the network neurons. On the basis of our analysis, we hypothesize that this dependence is the stronger the more characteristics of the pattern are maintained. We also found that in general, a network of endogenously tonically spiking neurons is more flexible than a network of endogenously bursting or silent neurons. Finally, we discuss physiological implications of our analysis.
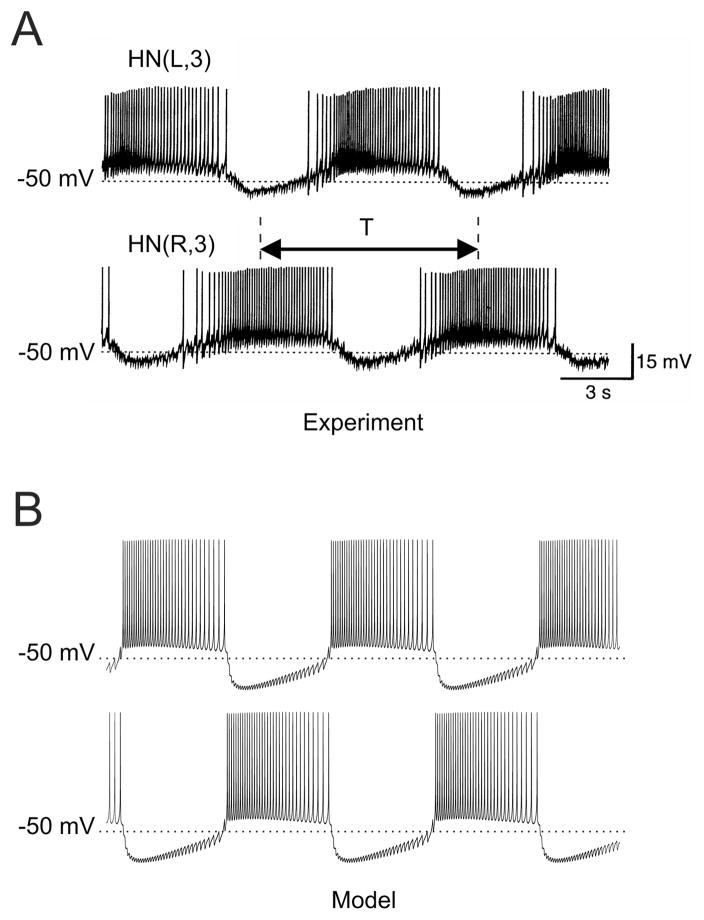
FIG. 1.
Electrical activity of a leech heartbeat half-center oscillator. (A) Simultaneous intracellular recordings from two participating leech heart interneurons, HNs, in the third ganglion. (B) Simulations of the half-center oscillator model, used in the study, for “canonical” values of parameters. Burst period, T, defined here as the time interval between the middle spike of one burst and the middle spike of the next burst, is a physiologically important characteristic of the network; it is equal to the period of the leech heartbeat.
2 Methods and Theory
2.1 The model
We used the Hill et al. (2001) model of the HCO based on the Hodgkin-Huxley formalism, with five inward and three outward voltage-dependent currents. Among the model parameters, as in Olypher, Cymbalyuk, & Calabrese (2006) and Olypher & Calabrese (2007), we considered a scaling factor, η, for the inactivation time constant of a slowly inactivating low-threshold calcium current, ICaS. By definition, η greater (less) than one slows down (speeds up) the inactivation of ICaS. When a parameter in the model was varied, it was varied in both neurons simultaneously. As in Olypher & Calabrese (2007), the Hill et al. (2001) model was slightly modified to make it smooth with respect to the variables and parameters. Namely, in the expression for the total calcium current max(0, x) was substituted by f(x) · x with a smooth sigmoid function f(x). The effect of the neuropeptide FMRFamide was modeled by an additional K+ current described in (Nadim & Calabrese, 1997; Hill et al., 2001).
2.2 Details of the simulations
To quantify the system’s activity for a particular set of parameters, the model was simulated for 150 seconds. The first 50 seconds of the simulation were considered as an interval sufficient for stabilizing the pattern and were discarded from analysis. To determine stable regimes of isolated neurons, the model was simulated for 700 seconds. The initial conditions for all simulations were the same. Simulations were performed with the Matlab (MathWorks, Natick, MA) solver ode15s with the absolute and relative tolerances 10−9 and 10−8 respectively. The Matlab code is available at http://calabreselx.biology.emory.edu/pub/HC.zip.
In our analysis, we focused on the burst period and spike frequency as the most important functional characteristics of the network activity. In the living system, the burst period sets the heartbeat period and the spike frequency determines the level of inhibition both within the HCO and between the oscillator interneurons and their motor neuron targets (Hill et al., 2001).
The following definitions were used. The period is the time between the middle spikes of consecutive bursts. The spike frequency is a number of spikes in a burst divided by the burst duration. Burst duration is a time interval between the first and the last spike of a burst. A sensitivity of a characteristic with respect to a parameter is a change, in percent, of a characteristic caused by a one percent change of the parameter. Sensitivities were considered to be proportional to partial derivatives; see details in Olypher & Calabrese (2007).
To find the isocurve, on which the period T of the model is equal to T*, and the spike frequency F is equal to F*, we used the Matlab (MathWorks, Natick, MA) function fminsearch to minimize (T − T*)2 + (F − F*)2. We stopped the minimization when both T and F were less than 0.5% different from their target values. Initial approximations for new points were based on previously found points of the isocurves. New points were calculated with the step of ḡSynS equal to 30 nS. In some cases, the continuation of an isocurve to certain values of ḡSynS was impossible. We checked this by calculating the period and the spike frequency at a fine grid in a large domain around the last point found on the isocurve. To build the isoperiod and isofrequency curves in the plane (ḡL, EL ) we used the Matlab function contour.
2.3 Theory
Our main idea is that whatever the biological mechanisms maintaining the activity pattern of a network are, their effect can be modeled as moving parameters of the network back to the isomanifold on which the characteristics of the pattern have target values. The sensitivities of the characteristics to parameter changes from their values on the isomanifolds can vary along the isomanifolds. With decreased/increased sensitivities the network is more robust/flexible to subsequent modulations. By studying what co-variations of parameters form these isomanifolds and how sensitivities of the activity pattern characteristics change at the points of the isomanifold, one can therefore better understand mechanisms regulating network activity.
The subspace of parameters in which the isomanifolds were considered in this study, included the maximal conductances of the spike-mediated, ḡSynS, and graded, ḡSynG, synaptic currents. Setting ḡSynS and ḡSynG to zero allowed us to dissect the maintenance mechanisms into components involving synaptic transmission and components involving intrinsic currents.
3 Results
3.1 Maintenance of burst period and of spike frequency in the face of variation of leak current parameters
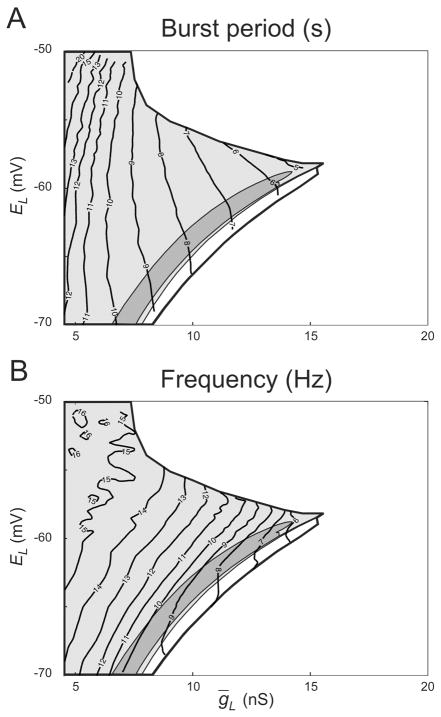
First, we found isoperiod and isofrequency curves in the plane of the maximal conductance, ḡL, and the reversal potential, EL, of the leak current. Cymbalyuk et al. (2002) determined the domain in the plane (ḡL, EL ) where the HCO model exhibits half-center oscillations, and subdomains where the neurons burst, tonically spike, or are silent, when isolated. In the plane (ḡL, EL), insensitive directions for the burst period and spike frequency are directions, tangent to the isoperiod and isofrequency curves respectively. Sensitive directions are the directions orthogonal to the isocurves.
For the period, insensitive and sensitive directions were similar in the whole bursting area. The isofrequency curves bend visibly at the border between tonic spiking and silence. In other words, maintaining the burst period or its efficient change require similar co-variation of ḡL and EL for all three types of endogenous neuronal dynamics. The maintenance of spike frequency or its efficient change require similar co-variation of ḡL and EL in the HCOs consisting of bursting and tonically spiking neurons, but different co-variation in the case of silent neurons.
The isoperiod and isofrequency curves had different tangent slopes almost everywhere. Consequently, it is impossible to vary ḡL and EL, and preserve both the period and frequency. Indeed, to get a one-dimensional isomanifold on which two characteristics are maintained, at least three parameters have to be co-regulated; two of them, like ḡL and EL, are not sufficient (Olypher & Calabrese, 2007). In the next simulations, we chose these three parameters to be ḡSynS, ḡh, and η because we showed previously that these parameters effectively control the period of the network (Nadim & Calabrese, 1997; Hill et al., 2001; Sorensen et al., 2004; Olypher, Cymbalyuk, & Calabrese, 2006).
3.2 Isocurves of constant burst period and spike frequency in the space of ḡh, η, and ḡSynS
In (Olypher & Calabrese, 2007), we found the isocurve in the space of ḡh, η, and ḡSynS for the HCO model composed of bursting neurons with ḡL = 9.9 nS and EL = −63.5 mV. On that isocurve, the burst period was equal to 7.91 s and the frequency was equal to 8.82 Hz. Here we compared this isocurve with the isocurves for the HCO models with tonically spiking or silent neurons. Using the results of Cymbalyuk et al. (2002) we set ḡL = 8.0 nS and EL = −60 mV, and ḡL = 9.9 nS and EL = −65.8 mV (cf. Fig. 2) for these models respectively. The other parameters of the models at the initial point with ḡSynS = 150 nS had canonical values, in particular ḡh = 4 nS and η = 1. In what follows, we refer to these models as consisting of originally tonically spiking or silent neurons. It was not a priory clear if the variations of parameters along the isocurves would conserve original types of endogenous neuronal dynamics.
FIG. 2.
Isoperiod and isofrequency curves of burst activity in the leech heartbeat HCO model in the plane of the leak current parameters. (A) Isoperiod curves for the period. (B) Isofrequency curves for the intraburst spike frequency. The thick black curve circumscribes the domain where the model exhibits half-center oscillations. Within the bursting area, there are subdomains where isolated model interneurons spike tonically (light gray), burst (dark gray), or are silent (white). A thin stripe between intrinsic bursting and quiescence is a subdomain of multistability (cf. Cymbalyuk et al., 2001).
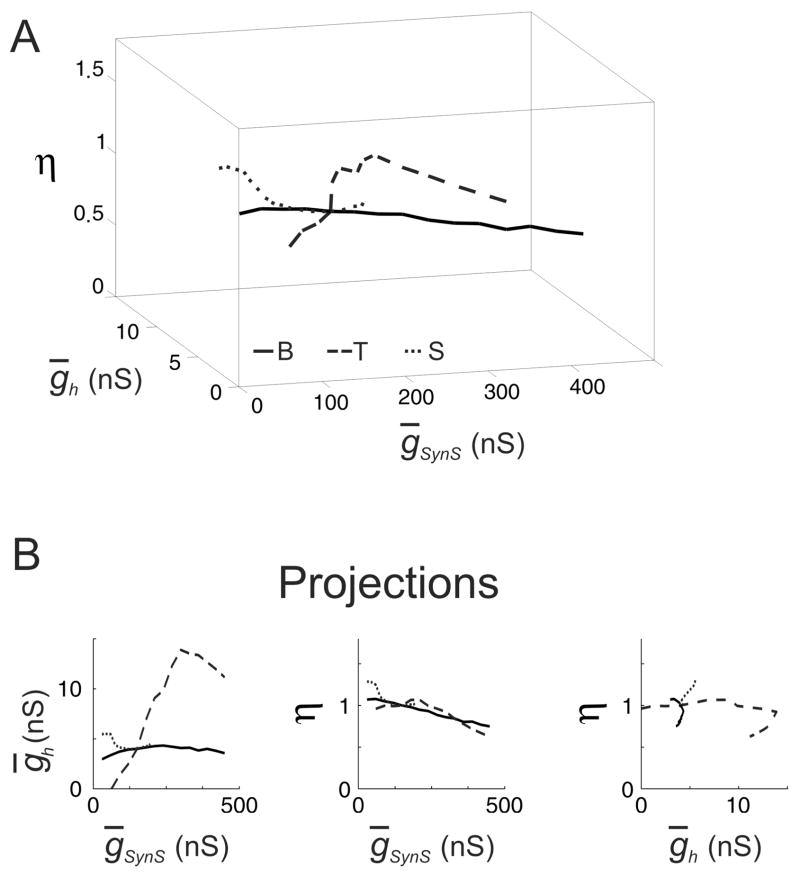
The target values of the burst period, T, and spike frequency, F, were taken from the HCO simulations for ḡSynS = 150 nS: T = 8.58 s and F = 13.37 Hz for tonically spiking neurons, and T = 7.99 s and F = 8.33 Hz for silent neurons. The chosen values of the burst period and spike frequency, though arbitrary, lie within the ranges 6.4–12.7 s and 10.2–20.0 Hz observed in the experiment by Cymbalyuk et al. (2002). The isocurves for these models are shown in Fig. 3. In what follows these isocurves are referred to as N-isocurves with “N” standing for the choice of the “natural” values of T and F maintained at these isocurves.
FIG. 3.
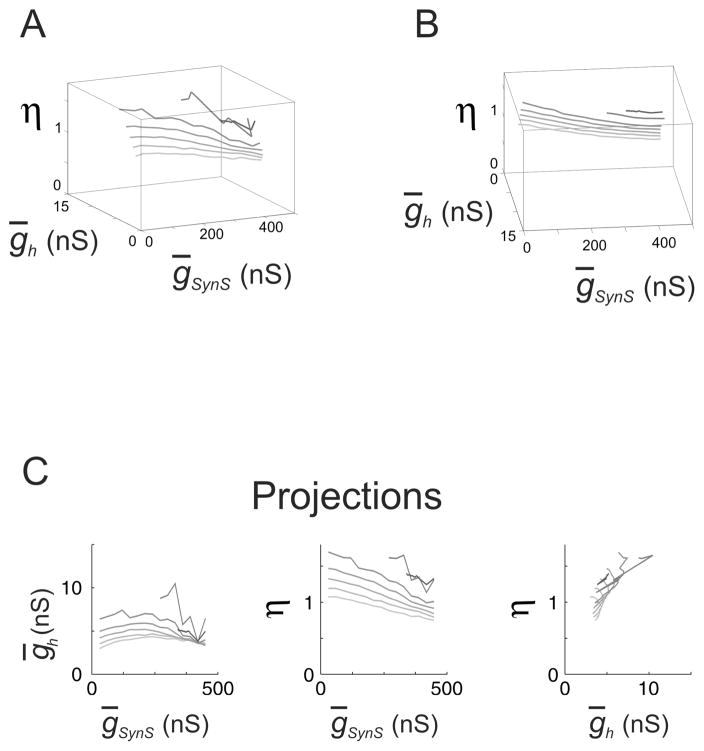
The isocurves of the constant period and spike frequency of the HCO model for three networks with the different target values of the period and spike frequency, and for ḡSynS = 150 nS, consisting of neurons with three different types of endogenous dynamics, N-isocurves. For ḡSynS = 150 nS, the HCO models were different only in the parameters of the leak current, (ḡL, EL ), which were (9.9 nS, −63.5 mV) for bursting neurons, solid curve, (8 nS, −60 mV) for tonically spiking neurons, dashed curve, and (9.9 nS, −65.8 mV) for silent neurons, dotted curve. All the other parameters had canonical values. The target values of the period and frequency were 7.91 sec and 8.82 Hz (bursting neurons, “B”), 7.99 sec and 8.33 Hz (tonically spiking neurons, “T”), 8.58 sec 13.37 Hz (silent neurons, “S”). (A) The N-isocurves in the space of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η Note, that all three isocurves cross at the same point, corresponding to the canonical values ḡSynS = 150 nS, ḡh = 4nS, and η= 1. (B) Planar projections of the isocurves. Note, that the dependence between ḡSynS and η was qualitatively the same for all the three types of networks: η decreased proportionally to the increase of ḡSynS. Note also a wide range of ḡh values which could be tolerated by the network of tonically spiking neurons. This range was much wider than for the networks of bursting and silent neurons.
N-isocurves demonstrated that the three HCO models sustained different variations of parameters. Especially distinctive were the ranges of ḡSynS and ḡh. With originally bursting and tonically spiking neurons the networks sustained large variations of ḡSynS, while with originally silent neurons, ḡh and η could compensate variations of ḡSynS in the range 30–180 nS only (Fig. 3B, left). On the other hand, the networks of originally bursting and originally silent neurons sustained only small variations of ḡh (Fig. 3B, right). N-isocurves also revealed that in the three network models the co-regulation implied a similar dependence of η on ḡSynS: greater values of ḡSynS required almost proportionally smaller values of η (Fig. 3B, middle).
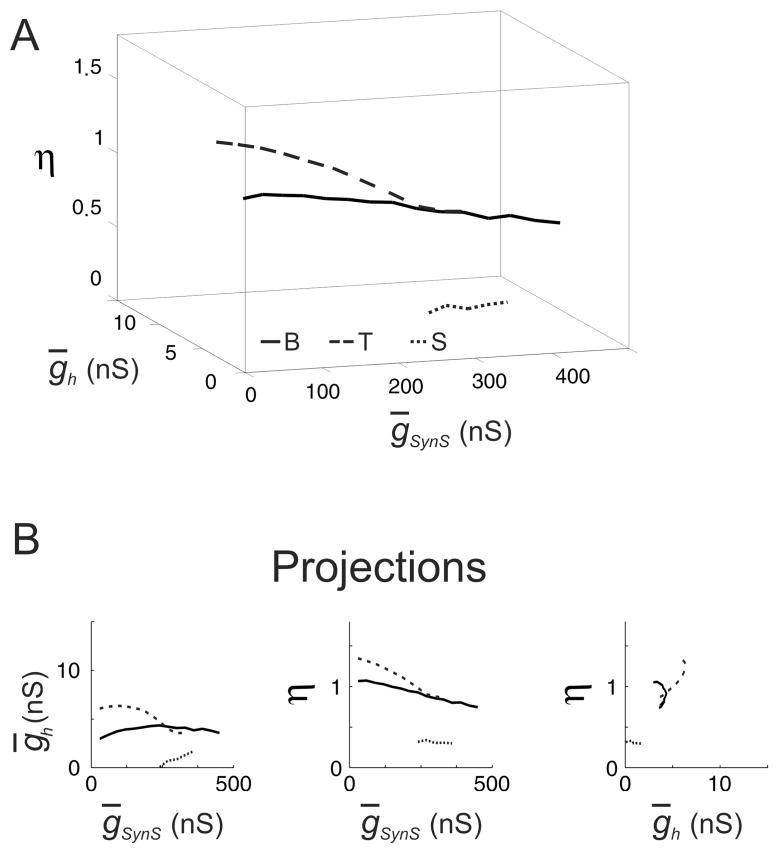
Could the target values for period and spike frequency influence the range of inhibition for which the network models with originally tonic spikers and silent neurons can maintain these values? To answer this question we chose the target values for these networks to be the same as for the network of originally bursting neurons, i.e., T=7.91 s and F = 8.82 Hz. In what follows the resulting isocurves (Fig. 4) are referred to as C-isocurves with “C” standing for the “canonical” target values of T and F.
FIG. 4.
The isocurves of the constant period and spike frequency of the HCO model for three networks with the same target values of the period and spike frequency, C-isocurves. The network models were different in the parameters of the leak current, (ḡL, EL), which were (9.9 nS, −63.5 mV), solid curve, (8 nS, −60 mV), dashed curve, and (9.9 nS, −65.8 mV), dotted curve. As in Fig. 3, these three pairs of parameters corresponded to three types of endogenous neuronal dynamics, bursting, tonic spiking, and silence, provided all the other parameters of the model had canonical values. The target values of the period and frequency were 7.91 sec and 8.82 Hz for the all three networks. (A) The C-isocurves in the space of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η Note, that the three isocurves do not cross at the point, corresponding to the canonical values ḡSynS = 150 nS, ḡh = 4nS, and η = 1. The HCOs of tonically spiking neurons and silent neurons could have the same values of period and frequency for the canonical values of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η as the HCO composed of bursters. In fact, in the case of tonically spiking neurons, there were no values of ḡh, and η for which the HCO model could have target values of the period and burst frequency for ḡSynS = 150 nS. (B) Planar projections of the isocurves. Note, that the dependence between ḡSynS and η was qualitatively the same for all the three types of networks: η decreased proportionally to the increase of ḡSynS. However, the dependence between ḡSynS and η for the tonically spiking neurons shifted to smaller values of η. Note that a range of ḡh which could be tolerated by the network of tonically spiking neurons, was smaller in this case compared to Fig. 3.
The period and spike frequency of the network models with originally silent and tonically spiking neurons, as expected, did not have the target values of T and F for the canonical values of parameters. For ḡSynS = 150 nS, the network of originally silent neurons had the target values of T and F when ḡh and η were equal to 6.13 nS and 1.18 respectively. In the case of the originally tonically spiking neurons and ḡSynS = 150 nS, there were no values of ḡh and η for which the HCO model had the target values of T and F.
The ranges of inhibition for which the network could maintain the canonical period and spike frequency by co-variation of ḡh and η changed differently depending on the original type of neuronal dynamics. In the network model with originally silent neurons, the range of ḡSynS grew to 30–330 nS. In the network model with originally tonically spiking neurons, it shrank to 240–360 nS. The proportionality between ḡSynS and η remained.
3.3 Endogenous neuronal dynamics on the isocurves of constant burst period and spike frequency
To further characterize the mechanisms of activity pattern maintenance, we explored whether maintenance of period and spike frequency on the isocurves was achieved by changing the original neuronal dynamics. The simulations of the isolated model neurons (ḡSynS = 0 nS) with ḡh, and η at the points along the isocurves gave the following results. Originally tonically spiking neurons exhibited tonic spiking at all the points along the N- and C-isocurves. Despite considerable changes of ḡh and η along the isocurves, the frequency of tonic spiking varied only a little: 7.14 – 7.19 Hz for the N-isocurve and 7.09 – 7.14 Hz for the C-isocurve.
Originally silent neurons remained silent at most of the points of the isocurves. On the N-isocurve, the isolated neurons were silent at points with ḡSynS in the range of 90–180 nS, including ḡh = 4 nS, η = 1, and ḡSynS = 150 nS where they were silent by definition. At two other points of the isocurve with ḡSynS equal 30 nS or 60 nS, the isolated neurons turned into bursters, and had a period of 7.41 s and 7.19 s and a frequency of 8.43 Hz and 8.42 Hz respectively.
In the case of the C-isocurve, originally silent neurons turned into bursters for ḡSynS in the range 30–210 nS. For other points, with ḡSynS in the range 240–330 nS, the neurons remained to be silent. When ḡSynS was in the range 30–210 nS, the burst period of the isolated neurons monotonically decreased from 7.91 s to 6.28 s; the spike frequency almost monotonically decreased from 9.11 Hz to 7.47 Hz.
Finally, we studied the dynamics in HCOs with originally bursting neurons. As we showed in (Olypher & Calabrese, 2007), the endogenous bursting of the isolated neurons was observed at the points of the isocurve. In the present study, we found that the period and spike frequency in the isolated bursting neurons decreased with increasing compensating inhibition. The period almost linearly decreased from 8.07 s to 5.90 s with increasing ḡSynS. For all the points with ḡSynS ≥ 90 nS, the period was less than 7.91 s. The spike frequency at those points monotonically decreased from 6.90 to 6.26 Hz.
3.4 Isocurves of constant burst period and spike frequency in the space of ḡh, η, and ḡSynS for different values of ḡKF
The previous set of simulations showed what changes in individual neurons allow the HCO to maintain the period and spike frequency despite the changes of reciprocal inhibition. Are these changes different in the presence of a neuromodulator? We modeled the effect of the endogenous neuropeptide FMRFamide by adding a slowly activating and deactivating outward current IKF (Nadim & Calabrese, 1997; Hill et al., 2001) with the maximum conductance ḡKF = 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, and 20 nS. The isocurves for the HCO model consisting of originally bursting neurons and different values of ḡKF are shown in Figure 5. As in previous simulations of originally bursting neurons ḡL = 9.9 nS and EL = −63.5 mV. The target values were 7.91 s for the burst period, and 8.82 Hz for the spike frequency. In the absence of compensating co-variation of ḡh and η, i.e., in the network with the canonical values of ḡh = 4 nS and η = 1, when ḡKF = 20nS and ḡSynS = 360 nS the period was equal to 6.45 s and the spike frequency was equal to 8.87 Hz.
FIG. 5.
The isocurves of the constant burst period and frequency of the HCO model consisting of endogenous bursters for different values of ḡKF. The maintained period and frequency on each isocurve were the same, and were calculated for the canonical set of parameters with the parameters of the leak current, (ḡL, EL) corresponding to endogenous bursting: (9.9 nS, −63.5 mV). ḡKF was varied from 0 nS (the lightest curve) to 20 nS (the darkest curve) including the following values: 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, 20 nS. (A) The isocurves in the space of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η. Note that with the increase of ḡKF above 10 nS the network model could assume the target values of the period and frequency only for high values of ḡSynS. (B) The same as (A) but from a different viewpoint. Note the inverse order of the ḡh axis. All the isocurves are restricted to almost parallel planes. (C) Planar projections of the isocurves. Note, that the dependence between ḡSynS and η was qualitatively the same for all the values of ḡKF: η decreased proportionally to the increase of ḡSynS. However, the dependence between ḡSynS and η shifted to greater values of η with the increase of ḡKF.
With the increase of ḡKF the target values of the period and spike frequency could be maintained only with the increasingly strong inhibition: ḡSynS ≥ 270nS for ḡKF = 15 nS, and ḡSynS ≥360 nS for ḡKF = 20nS. The increase of ḡKF decreased the range of ḡSynS and simultaneously increased the ranges of ḡh and η that could co-vary with ḡSynS. In particular, for ḡKF = 0 nS, the ranges of ḡh and ηproducing the maintenance of the burst period and spike frequency were 1.37 nS and 0.33 respectively, while for ḡKF = 10 nS the ranges were 5.98 nS and 1.54.
All the isocurves lie within almost parallel planes (Fig. 5B, Table 1). This means that there is a strong and similar linear relationship between the three parameters for all the values of ḡKF considered. For example, for ḡKF =10 nS the relationship has the form η + 0.0015 · ḡSynS − 0.0339 ḡh 1.5161 = 0. Importantly, these relationships held even for ḡKF greater than or equal to 15 nS where there was no apparent linear dependence between ḡSynS and η.
TABLE 1.
Planar fitting of the isocurves for HCOs composed of bursters. Fitting plane equation: η = A · ḡSynS + B · ḡSynh + C.
| ḡKF (nS) | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −8.47E-04 | 0.0135 | 1.07 |
| 2.5 | −9.78E-04 | 0.0104 | 1.12 |
| 5 | −0.0012 | 0.0207 | 1.28 |
| 7.5 | −0.0013 | 0.0293 | 1.37 |
| 10 | −0.0015 | 0.0339 | 1.52 |
| 15 | −8.48E-04 | 0.0676 | 1.23 |
| 20 | −3.90E-04 | 0.0878 | 1.07 |
When isolated, the neurons fired in bursts at all the points of the isocurves for ḡKF equal to 0 and 5 nS. When ḡKF was equal to 10 nS, the neurons fired in bursts everywhere but at the point with ḡSynS = 420 nS where the isolated model neuron exhibited bistability: one of the isolated neurons fired in bursts while the other was silent. When ḡKF = 15 nS and ḡSynS = 420 nS both isolated neurons were silent. Finally, when ḡKF = 20 nS both isolated neurons were silent at all four points of the isocurve. For all isocurves, the period of the isolated neurons mostly decreased with the increase of the inhibition and was smaller than the target value, T = 7.91 s for the HCO everywhere with the exception of two points with ḡKF = 0 nS and ḡSynS equal to 30 or 60 nS. At these points the period was equal to 7.97 s and 8.07 s respectively. In the living system, pharmacologically isolated interneurons indeed have a shorter period than the period of an intact HCO (Cymbalyuk et al., 2002).
3.5 Period sensitivities to ḡh, η, ḡSynS, and ḡKF on the isocurves of constant burst period and spike frequency
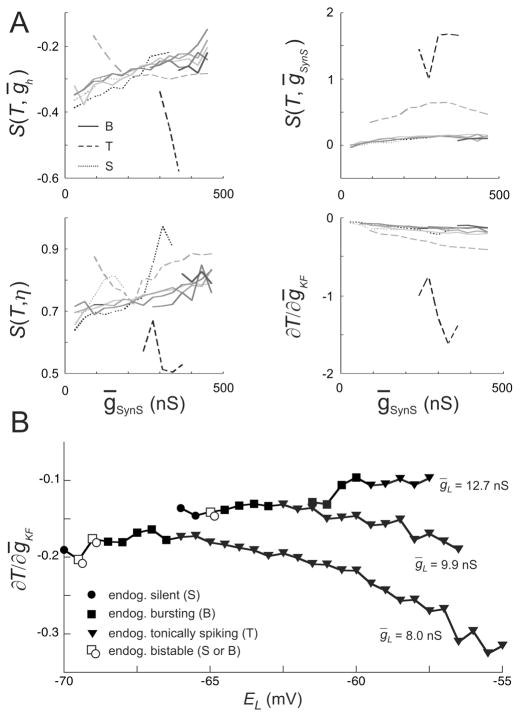
Sensitivity along isocurves characterizes the period’s flexibility to parameter changes from their values on the isocurves. For the isocurves with, ḡKF = 0 by sensitivity we mean partial derivatives of the period with respect to ḡKF. Our observations show (Fig. 6) that the sensitivities of the period with respect to each of the parameters ḡSynS, ḡh, η, and ḡKF were qualitatively the same when the network consisted of originally bursting or originally silent neurons. The behavior of sensitivities did not change qualitatively when the FMRFamide activated current, IKF, was added to the model with endogenously bursting neurons. The period sensitivity to ḡKF decreased with increasing ḡKF, indicating saturation to ḡKF’s impact on the network.
FIG. 6.
The sensitivities of the HCO period to ḡh, ḡSynS, η, and ḡKF. (A) The sensitivities of the HCO period to ḡh, ḡSynS, η, and ḡKF at the calculated points of the isocurves. The types of the curves are the same as in Figs. 3–5. Namely, the sensitivities for the model with ḡKF = 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 nS are in solid gray with darker colors for greater values of ḡKF. The networks with the originally tonically spiking neurons are dashed curves while the networks with the originally silent neurons are dotted curves, with gray standing for the N-isocurves (cf. Fig. 3), and black standing for the C-isocurves (cf. Fig. 4); see the definitions of the N- and C-isocurves in the text. (B) The sensitivity of the HCO period to ḡKF (∂T/∂ḡKF) for gL = 8, 9.9, and 12.7 nS with all the other parameters having canonical values, including ḡKF = 0. Isolated model neurons are endogenously silent (circles), burst (squares), spike tonically (triangles), or bistable (hollow square and circle) (cf. Fig. 2).
The period sensitivities for the HCO models with originally tonically spiking neurons were quite different. They were considerably larger and not monotonous. This observation implies that a HCOs consisting of tonic spikers are more flexible than HCOs consisting of busters or silent neurons: small changes of the parameters cause larger changes in the period.
We developed this result further by studying how the HCO’s period sensitivity to ḡKF depends on EL. To this end, ∂T/∂ḡKF was calculated, as a function of EL, for three values of gL to explore domains with low (gL = 8 nS, EL ∈[−70mV, −55mV]), moderate (gL = 9.9 nS, EL ∈ [−66mV, −55.5mV]), and strong (gL = 12.7 nS, EL ∈ [−61.5mV, −57.5mV]) dependence of T on EL (cf. Fig. 2); all the other parameters had canonical values, including ḡKF = 0. The results show that in the first two domains there is an increase of |∂T/∂ḡKF| with the increase of EL in endogenously tonically spiking neurons (Fig. 6B).
4 Discussion
Robust activity of some networks, such as central pattern generators, in the face of varying parameters (Marder & Goaillard, 2006) suggests the existence of physiological mechanisms which maintain the most important characteristics, for example the period and spike frequency of the pattern. Whatever the biological mechanisms maintaining network activity are, they change the appropriate model parameters to or along the isomanifolds on which the characteristics of the pattern are constant, while their sensitivities to parameters may be different. By studying the properties of these isomanifolds, one can therefore understand the mechanisms maintaining the pattern of the network activity in terms of co-variations of the model parameters. The physiological meaning of these co-variations can at least partially be interpreted by the analysis of their impact on endogenous neuronal dynamics.
In this study, we sought answers to the following two questions: 1) Do parameter variations in insensitive directions, i.e. along isomanifolds, change endogenous dynamics of the network neurons? 2) Do sensitive and insensitive directions for network pattern characteristics depend on endogenous dynamics of the network neurons?
For a leech heartbeat half-center oscillator model network we show that the answers to these questions can be positive or negative depending, in particular, on whether both the burst period and spike frequency, or only one of these characteristics is maintained. In accord with intuition the dependence on endogenous dynamics of the isolated neurons was the stronger the more characteristics of the pattern have to be maintained. We also found that in general, with endogenously tonically spiking neurons HCOs are more flexible than with endogenously bursting or silent neurons. We came to this conclusion by considering variations of the several parameters which according to our earlier experimental and modeling studies predominantly control the burst period and spike frequency in leech heart interneurons (Hill et al., 2001; Cymbalyuk et al., 2002; Sorensen et al., 2004; Olypher, Cymbalyuk, & Calabrese, 2006).
It is difficult to state definitively what activity synaptically isolated leech heart interneurons manifest and thus whether they exploit such flexibility. With intracellular recording (sharp electrodes) sufficient leak is introduced so that these neurons always spike tonically in the high concentrations of bicuculline needed to block inhibitory synaptic transmission between them (0.5 – 1.0 mM), but such neurons burst normally in HCOs after removal of the bicuculline (Cymbalyuk et al., 2002). With extracellular recording (suction electrodes), synaptic isolation by 1.0 mM bicuculline results in regular bursting that sometimes is interrupted by short bouts of tonic spiking (Cymbalyuk et al., 2002). Synaptic isolation by 0.5 mM bicuculline results in irregular bursting often interrupted by tonic spiking for many seconds and bursting is sped and greatly regularized by myomodulin (Tobin & Calabrese, 2005). Thus at the high concentrations needed in the leech, bicuculline itself appears to promote burst capabilities. With extracellular recording and synaptic isolation by eliminating inhibitory inputs with hyperpolarizing voltage clamp of the presynaptic neuron, heart interneuron exhibit very slow irregular bursting and bursting is greatly sped and regularized by myomodulin (Tobin & Calabrese, 2005).
4.1 Maintenance of the burst period or spike frequency in the face of leak current variations is not specific for the type of endogenous neuronal dynamics
The observation that for a wide range of the period and spike frequency values, the isoperiod and isofrequency curves crossed the borders between the subdomains of the plane (ḡL, EL) with different neuronal dynamics suggests that mechanisms maintaining either the period or the spike frequency of HCOs are not associated with dynamics of isolated neurons and can easily change the latter.
Can the leak current of the living neurons of a heartbeat HCO be selectively altered to check the predictions of the model? There are modulators that regulate the leak current parameters together with other currents. For example, Tobin & Calabrese (2005) showed recently that an endogenous leech peptide myomodulin (Wang, Price, & Sahley, 1998) decreases Na/K pump current and increases ḡh. A change of Na/K pump current is equivalent to the change of EL (Tobin & Calabrese, 2006). Hence, it is possible that in the experiment, a selective altering of the leak current might be achieved by a specific combination of myomodulin with Cs+ (Masino & Calabrese, 2002) to partially block ḡh to compensate its increase caused by myomodulin.
4.2 Maintenance of the burst period and spike frequency in the face of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η in the network of endogenously bursting neurons in presence of a neuropeptide FMRFamide
We modeled the effect of a neuropeptide FMRFamide by adding an FMRFamide-activated K+ current, IKF, to the model. We found an almost linear relationship between ḡSynS, ḡh, and η for all the isocurves corresponding to the different values of ḡKF. The relationship held even for g greater than or equal to 15 nS where there was no linear dependence between ḡSynS and η. The isolated neurons were bursters at all points of the isocurves.
4.3 Maintenance of the burst period and spike frequency in the face of ḡSynS, ḡh, and η variations depends on the type of endogenous neuronal dynamics
The relations between the period sensitivity to parameters and the types of endogenous neuronal dynamics, shown in Fig. 6, suggest a number of testable predictions expanding our understanding of possible interactions between myomodulin and FMRFamide. In particular, high period sensitivity to ḡKF for HCOs with originally tonically spiking neurons compared to the networks with originally bursting or originally silent neurons (Fig. 6A, bottom right) allows us to make the following prediction. Because an application of myomodulin increases regularity of bursting in isolated neurons (in particular by eliminating the intervals of tonic spiking (Tobin and Calabrese, 2005), then myomodulin application should decrease the sensitivity of the HCO period to FMRFamide. Further analysis is required for understanding the detailed mechanism of the FMRFamide and myomodulin interaction. This interaction can be quiet complex given that the effect of myomodulin on leech heart interneurons may not be restricted to the decrease of Na/K pump current and increase of ḡh found by Tobin and Calabrese (2005).
The approach, which we developed in the present study, is based on a general idea of dissecting the mechanisms maintaining network activity into the components involving synaptic transmission and components involving intrinsic neuronal ionic currents. This approach should be useful for understanding homeostatic regulation in various networks, especially central pattern generators, for which the characteristics of the pattern to be maintained are often quite obvious. In particular, the analysis of the synaptic (Soto-Trevino et al., 2001) and intrinsic current (Golowasch et al., 1999) plasticity in the somatogastric ganglion of decapod crustaceans might benefit from our approach.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge helpful comments of the anonymous reviewers. Supported by NIH grant NS-24072.
References
- Butera RJ, Jr, Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Botzinger complex. II Populations Of coupled pacemaker neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82(1):398–415. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.1.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese RL. Cellular, synaptic, network, and modulatory mechanisms involved in rhythm generation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1998;8(6):710–717. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(98)80112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cymbalyuk GS, Gaudry Q, Masino MA, Calabrese RL. Bursting in leech heart interneurons: cell-autonomous and network-based mechanisms. J Neurosci. 2002;22(24):10580–10592. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10580.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman MS, Golowasch J, Marder E, Abbott LF. Global structure, robustness, and modulation of neuronal models. J Neurosci. 2001;21(14):5229–5238. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-05229.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golowasch J, Casey M, Abbott LF, Marder E. Network Stability from Activity-Dependent Regulation of Neuronal Conductances. Neural Comp. 1999;11(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1162/089976699300016359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill AA, Lu J, Masino MA, Olsen OH, Calabrese RL. A model of a segmental oscillator in the leech heartbeat neuronal network. J Comput Neurosci. 2001;10(3):281–302. doi: 10.1023/a:1011216131638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristan WB, Jr, Calabrese RL, Friesen WO. Neuronal control of leech behavior. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76(5):279–327. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder E, Goaillard JM. Variability, compensation and homeostasis in neuron and network function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(7):563–574. doi: 10.1038/nrn1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder E, Thirumalai V. Cellular, synaptic and network effects of neuromodulation. Neural Netw. 2002;15(4–6):479–493. doi: 10.1016/s0893-6080(02)00043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masino MA, Calabrese RL. Period differences between segmental oscillators produce intersegmental phase differences in the leech heartbeat timing network. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87(3):1603–1615. doi: 10.1152/jn.00338.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadim F, Calabrese RL. A slow outward current activated by FMRFamide in heart interneurons of the medicinal leech. J Neurosci. 1997;17(11):4461–4472. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-11-04461.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olypher AV, Calabrese RL. Using constraints on neuronal activity to reveal compensatory changes in neuronal parameters. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98(6):3749–3758. doi: 10.1152/jn.00842.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olypher AV, Cymbalyuk GS, Calabrese RL. Hybrid Systems Analysis of the Control of Burst Duration by Low-Voltage-Activated Calcium Current in Leech Heart Interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96(6):2857–2867. doi: 10.1152/jn.00582.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen M, DeWeerth S, Cymbalyuk G, Calabrese RL. Using a hybrid neural system to reveal regulation of neuronal network activity by an intrinsic current. J Neurosci. 2004;24(23):5427–5438. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4449-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Trevino C, Thoroughman KA, Marder E, Abbott LF. Activity-dependent modification of inhibitory synapses in models of rhythmic neural networks. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4(3):297–303. doi: 10.1038/85147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin AE, Calabrese RL. Myomodulin increases Ih and inhibits the NA/K pump to modulate bursting in leech heart interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94(6):3938–3950. doi: 10.1152/jn.00340.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin AE, Van Hooser SD, Calabrese RL. Creation and reduction of a morphologically detailed model of a leech heart interneuron. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96(4):2107–2120. doi: 10.1152/jn.00026.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrigiano GG, Nelson SB. Homeostatic plasticity in the developing nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(2):97–107. doi: 10.1038/nrn1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Price DA, Sahley CL. Identification and characterization of a myomodulin-like peptide in the leech. Peptides. 1998;19(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(97)00419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]