Abstract
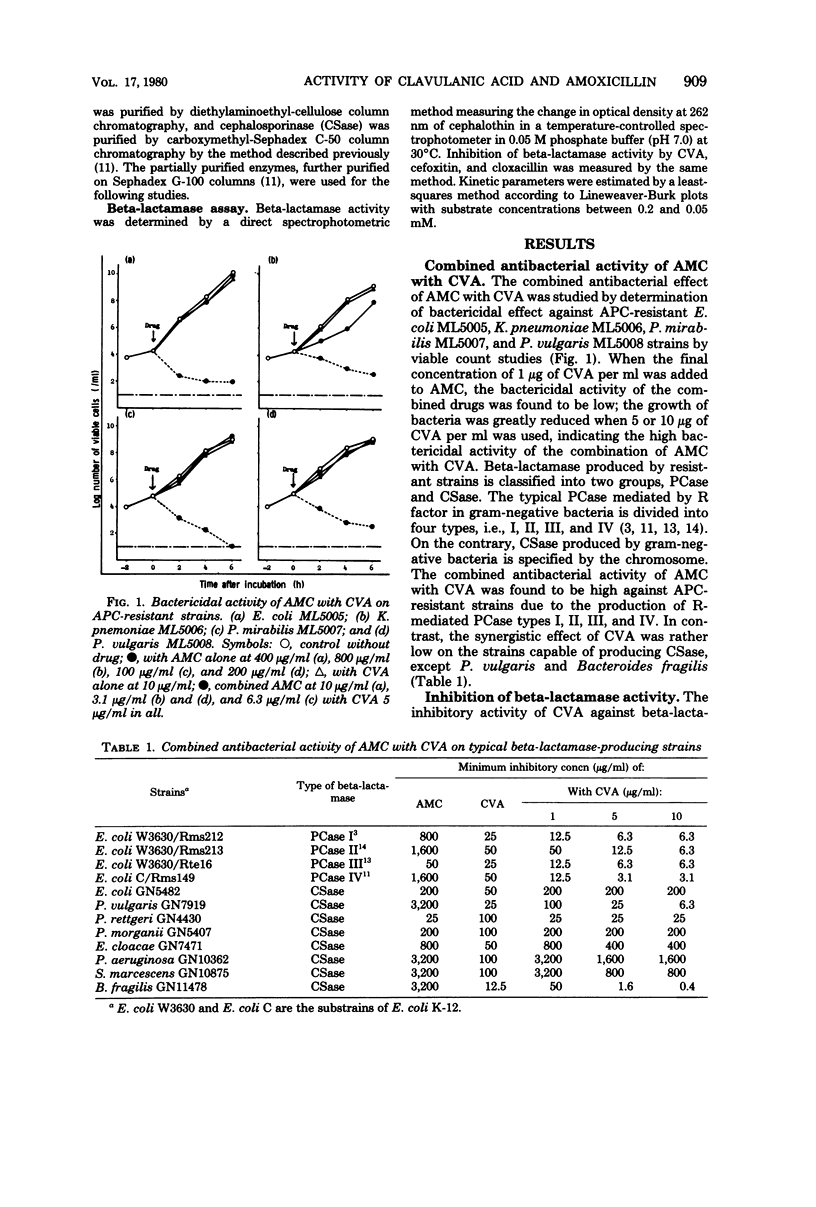
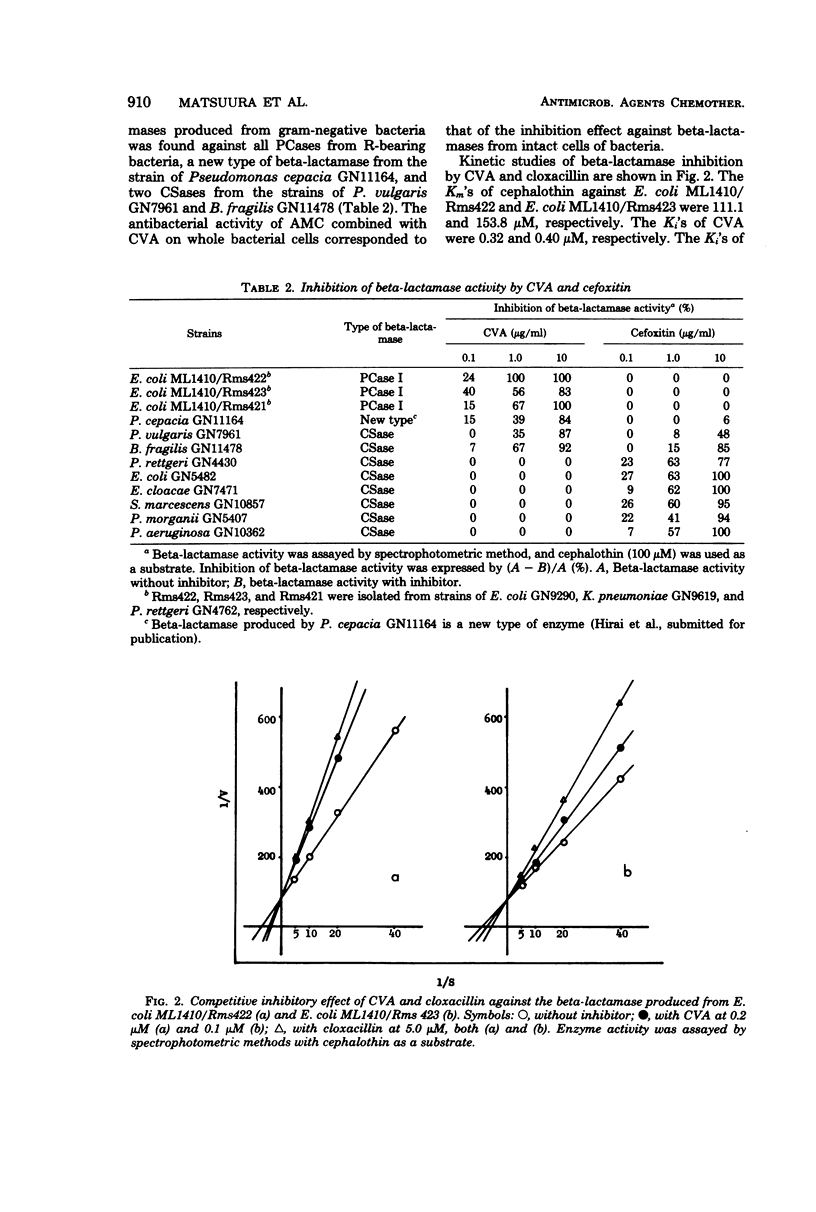
Strains of bacteria resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics have been increasing in number and are becoming troublesome in clinical medicine. The in vitro antibacterial activity of amoxicillin combined with clavulanic acid was determined on selected ampicillin-resistant clinical isolates. Synergistic effects were produced by amoxicillin with clavulanic acid against ampicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Bacteroides fragilis. Inhibition of the beta-lactamases produced by the ampicillin-resistant strains was confirmed, especially against the penicillinases mediated by the R factor and the cephalosporinases produced by P.vulgaris and B. fragilis. The inhibitory effect of clavulanic acid against beta-lactamases was irreversible because of the high affinity of clavulanic acid to the enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. G., Butterworth D., Cole M., Hanscomb G., Hood J. D., Reading C., Rolinson G. N. Naturally-occurring beta-lactamase inhibitors with antibacterial activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jun;29(6):668–669. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyobe S., Hasuda K., Fuse A., Mitsuhashi S. Demonstration of R factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):547–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. T., Harris L. F., Alford R. H. Sodium clavulanate potentiation of cephalosporin activity against clinical isolates of cephalothin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):118–125. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paisley J. W., Washington J. A., 2nd Combined activitiy of clavulanic acid and ticarcillin against ticarcillin-resistant, gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):224–227. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Mitsuhashi S. Antimicrobial evaluation of cefoxitin: a new semisynthetic cephamycin. Comparative studies with cefazolin and cefalotin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1977;27(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Terakado N., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of a penicillin beta-lactamase mediated by R factor from Bordetella bronchiseptica. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):238–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi S., O'Hara K., Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S. The purification and properties of penicillin beta-lactamases mediated by transmissible R factors in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Jul;66(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



