Abstract
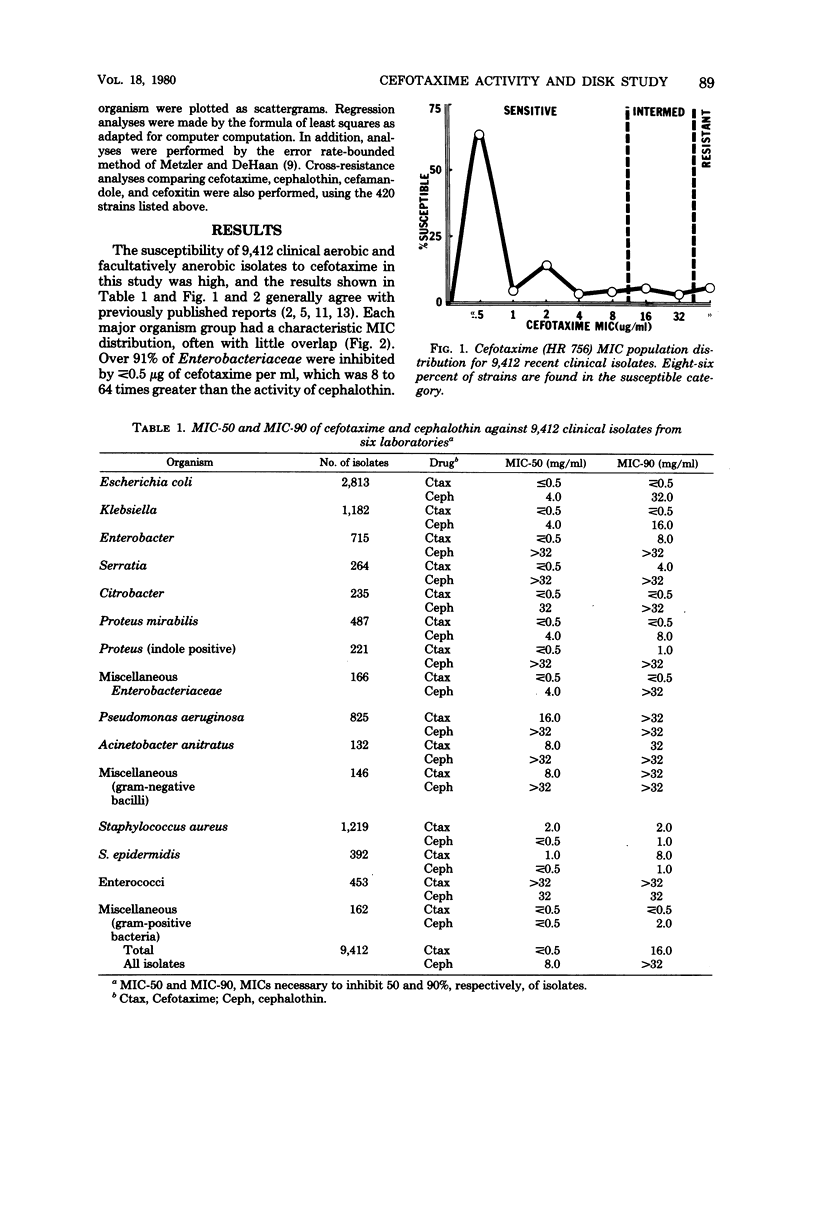
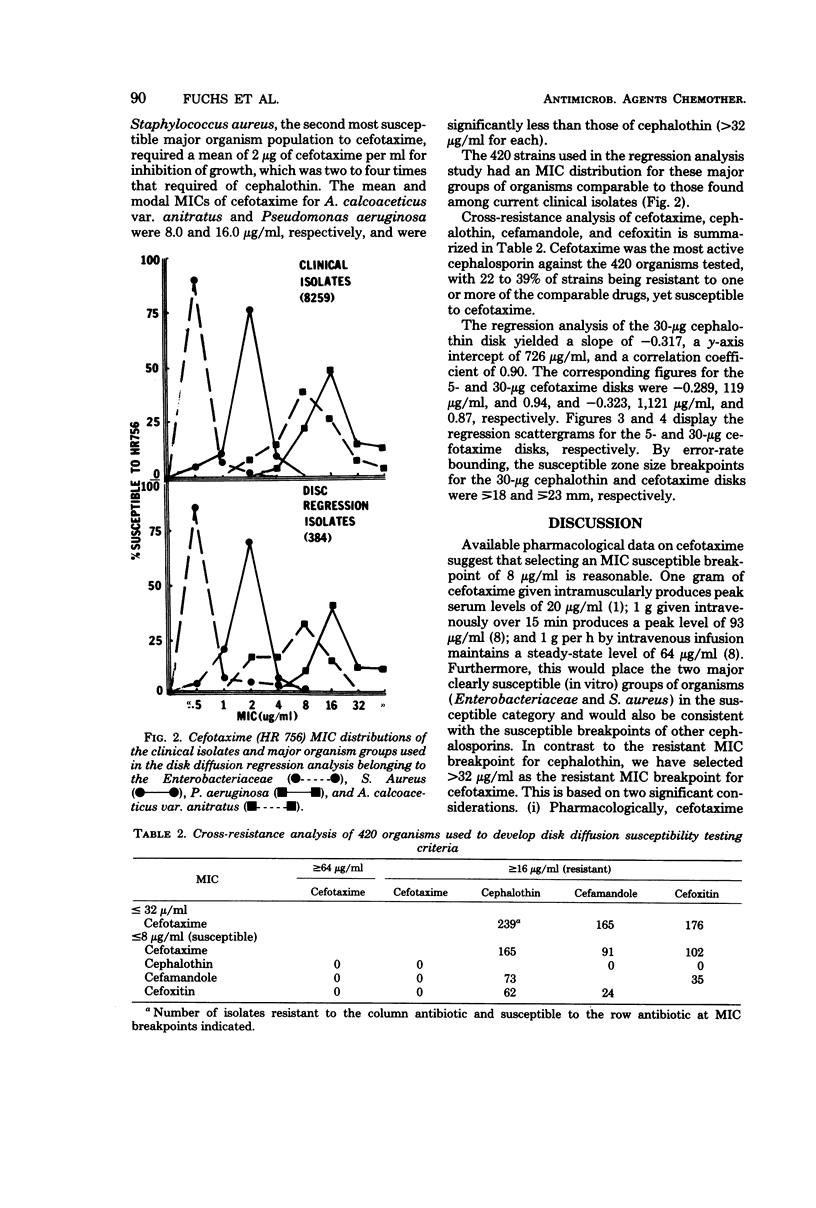
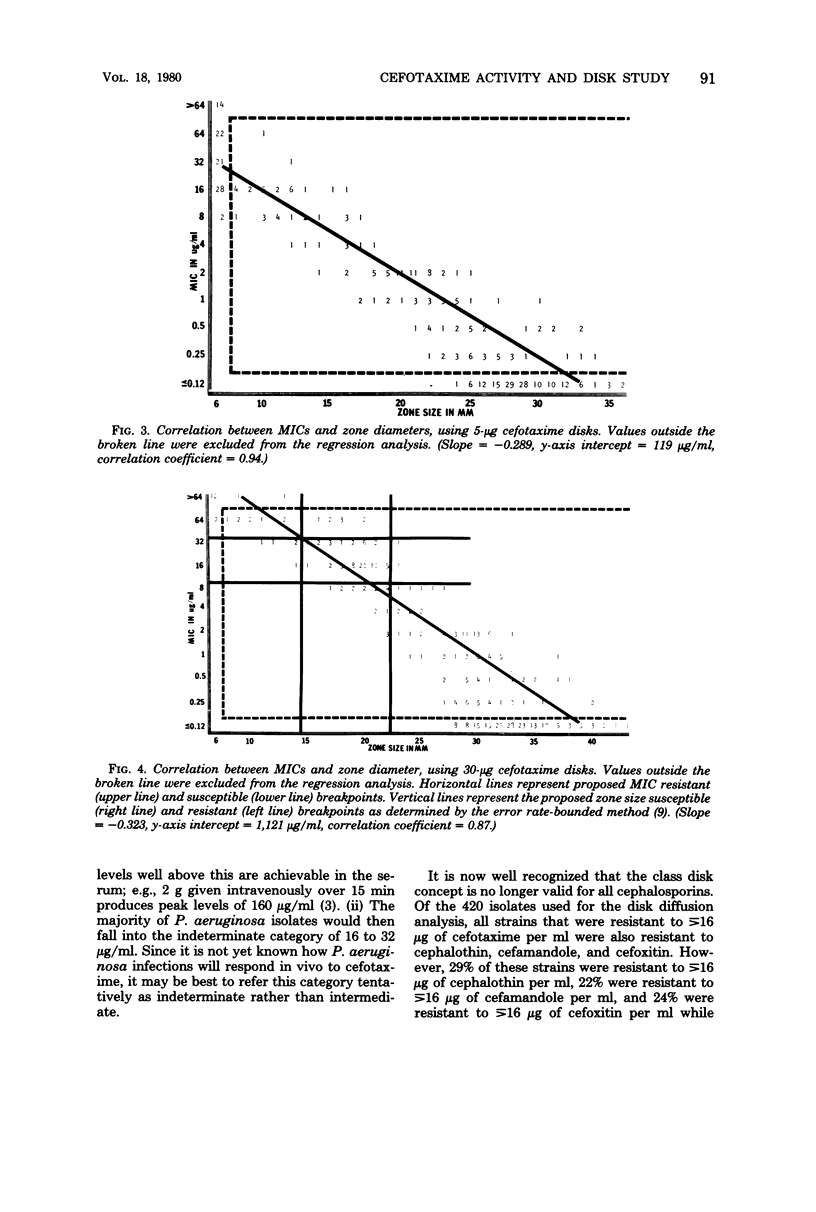
Tested against 9,412 recent clinical isolates, cefotaxime exhibited 8 to 64 times greater activity against the Enterobacteriaceae than did cephalothin and two to four times greater activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, but only one-half to one-eighth the activity of cephalothin against staphylococci. Using 420 different clinical isolates, but with comparable minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) distributions, disk diffusion-MIC regression analyses were performed, using 5- and 30-micrograms cefotaxime disks. Cefotaxime MIC susceptible and resistant breakpoints of less than or equal to 8 and greater than 32 micrograms/ml are tentatively proposed. Based on the MIC breakpoints, the data showed the best discrimination among the three susceptibility categories (susceptible, indeterminate, and resistant) when the 30-micrograms cefotaxime disk was used. The zone diameter breakpoints as determined by the error rate-bounded method and regression analysis were greater than or equal to 23 mm for susceptible, 15 to 22 mm for indeterminate, and less than or equal to 14 mm for resistant.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Diffusion disk susceptibility testing with cefotaxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):164–166. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Lutz A. J. HR 756, the syn isomer of a new methoxyimino cephalosporin with unusual antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):749–754. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar F. A., Farrell W., Howard A. J., Hince C., Leung T., Williams J. D. Activity of HR 756 against Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis and Gram-negative rods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):445–450. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):322–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W., Reynolds A. V. Cefotoxime (HR 756) a new cephalosporin with exceptional broad-spectrum activity in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):437–444. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gavin T. L., Gerlach E. H. BL-S786, a new parenteral cephalosporin. II. In vitro antimicrobial activity comparison with six related cephalosporins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):583–592. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Münch R., Blaser J., Bhend H., Siegenthaler W. Human pharmacology of cefotaxime (HR 756), a new cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):127–133. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. M., DeHaan R. M. Susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria: statistical and clinical considerations. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):588–594. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. M., Troche G., Stille W. In vitro activity of HR 756, a new cephalosporin compound. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Nov;31(11):1170–1174. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Landuyt H. W., Pyckavet M. In vitro of cefotaxime against cephalothin-resistant clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):109–111. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Rollason T., Logan M., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. HR 756, a highly active cephalosporin: comparison with cefazolin and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):807–811. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



