Abstract
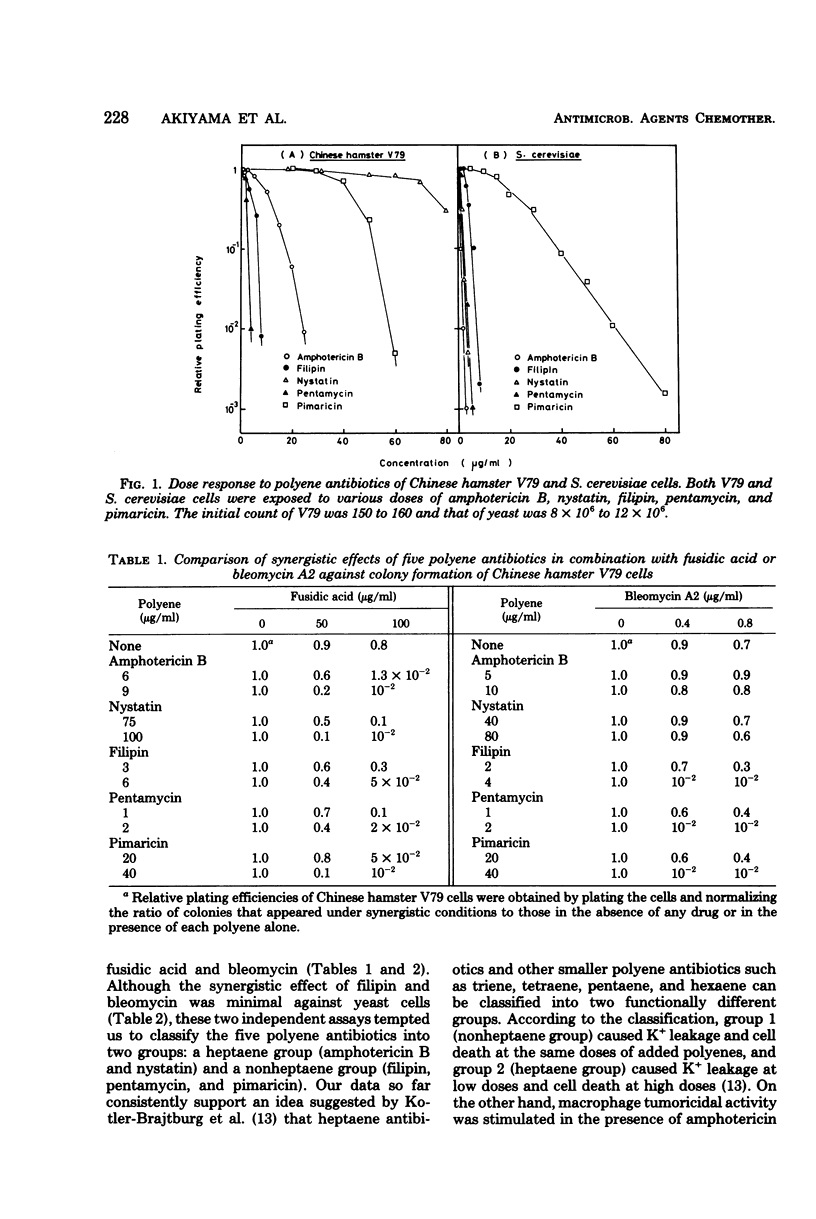
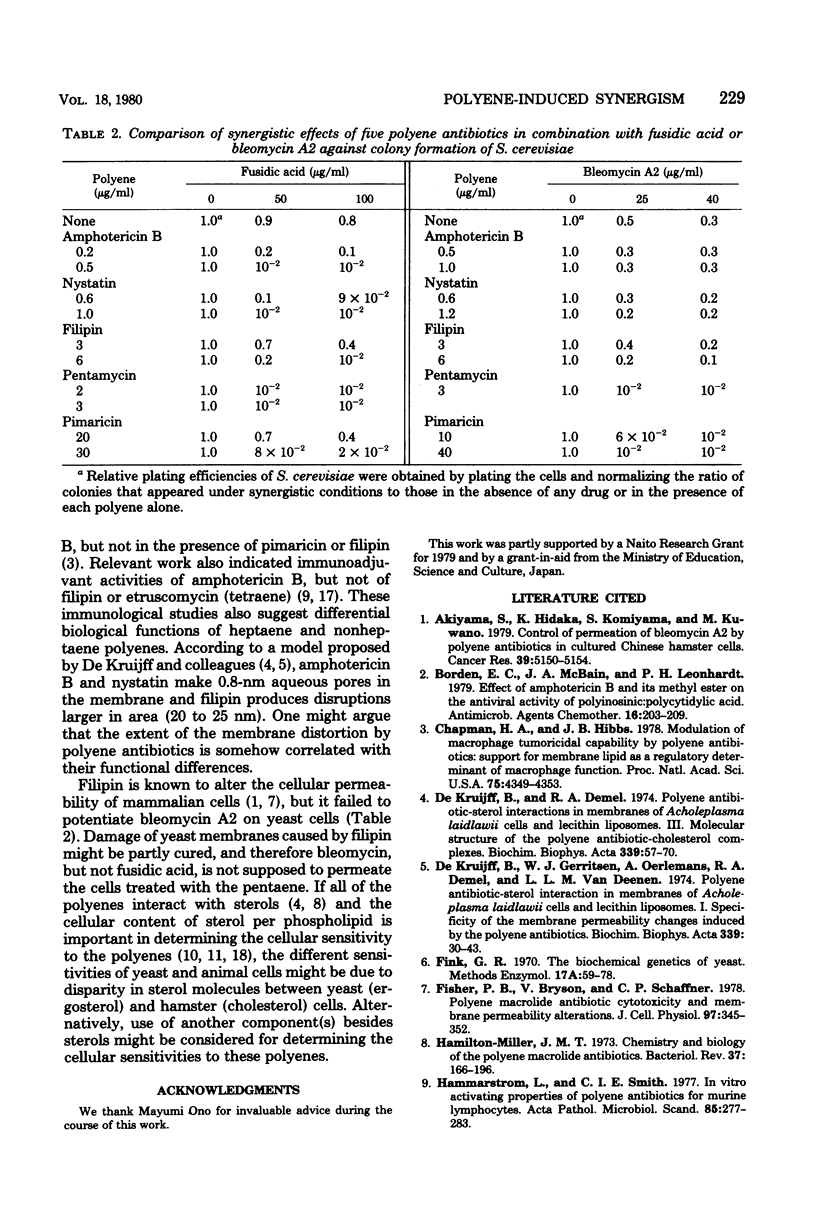
Five polyene antibiotics were compared for their effects on colony formation of either Chinese hamster V79 or Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. A 10 to 40 times higher concentration of amphotericin B (heptaene) or nystatin (degenerated heptaene) was necessary to inhibit colony formation of hamster cells than that needed to inhibit colony formation of yeast cells. In contrast, colony formation of both hamster and yeast cells was inhibited to the same extent by similar concentrations of filipin (pentaene), pentamycin (pentaene), or pimaricin (tetraene). The five polyene antibiotics were also compared for their effects on colony formation of either V79 or S. cerevisiae cells when combined with a nonpolyene antibiotic, fusidic acid or bleomycin A2. Amphotericin B or nystatin could augment the cytocidal effect of fusidic acid but not that of bleomycin A2, whereas pentamycin or pimaricin could augment the cytocidal effect of both fusidic acid and bleomycin A2 against hamster and yeast cells. Filipin was found to enhance the action of fusidic acid and bleomycin upon growth of mammalian cells, whereas the pentaene polyene significantly potentiated the action of fusidic acid, but not that of bleomycin A2, against S. cerevisiae. It was therefore suggested that these polyene antibiotics be classified into two groups: group 1 (pimaricin, pentamycin, and filipin) and group 2 (amphotericin B and nystatin).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. I., Hidaka K., Komiyama S., Kuwano M. Control of permeation of bleomycin A2 by polyene antibiotics in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):5150–5154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C., McBain J. A., Leonhardt P. H. Effects of amphotericin B and its methyl ester on the antiviral activity of polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):203–209. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Modulation of macrophage tumoricidal capability by polyene antibiotics: support for membrane lipid as a regulatory determinant of macrophage function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Bryson V., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide antibiotic cytotoxicity and membrane permeability alterations. I. Comparative effects of four classes of polyene macrolides on mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 1):345–351. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Chemistry and biology of the polyene macrolide antibiotics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):166–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka K., Endo H., Akiyama S., Kuwano M. Isolation and characterization of amphotericin B-resistant cell lines in Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka K., Matsui K., Endo H., Akiyama S. I., Kuwano M. Differential control of synergistic effect with polyene macrolide antibiotics upon Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4650–4653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Antifungal agents: recent developments. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:291–308. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler-Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Boggs S., Schlessinger D., Pandey R. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Classification of polyene antibiotics according to chemical structure and biological effects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):716–722. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Akiyama S., Endo H., Kohga M. Potentiation of fusidic acid and lentinan effects upon normal and transformed fibroblastic cells by amphotericin B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 4;49(5):1241–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Kamiya T., Endo H., Komiyama S. Potentiation of 5-fluorouracil, chromomycin A3, and bleomycin by amphotericin B or polymyxin B in transformed fibroblastic cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):580–584. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. N., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Schlessinger D., Raskas H. J. Potentiation of the antifungal effects of antibiotics by amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Aug;2(2):61–65. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.2.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Plut E. J., Kotler-Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Relationship between the antibiotic and immunoadjuvant effects of amphotericin B methyl ester. Immunochemistry. 1978 Apr;15(4):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Chou S. M., Silbert D. F. Animal cell mutants defective in sterol metabolism: a specific selection procedure and partial characterization of defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3730–3734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Demel R. A. Polyene antibiotic-sterol interactions in membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii cells and lecithin liposomes. 3. Molecular structure of the polyene antibiotic-cholesterol complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90332-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Gerritsen W. J., Oerlemans A., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Polyene antibiotic-sterol interactions in membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii cells and lecithin liposomes. I. Specificity of the membrane permeability changes induced by the polyene antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):30–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


